- Napier Lion
-
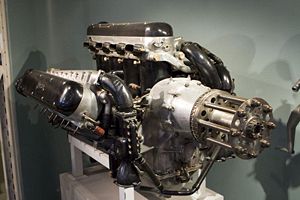
Lion Napier Lion II at Canada Aviation Museum Type Piston aero-engine Manufacturer Napier & Son First run 1917 Major applications Handley Page Hyderabad
Vickers VernonThe Napier Lion was a 12-cylinder broad arrow configuration aircraft engine built by Napier & Son starting in 1917, and ending in the 1930s. A number of advanced features made it the most powerful engine of its day, and kept it in production long after contemporary designs had stopped production. It is particularly well known for its use on a number of racing designs, in aircraft, boats, and cars.
Contents
Design and development
Early in in the First World War Napier were contracted to build aero engines to designs from other companies: initially a Royal Aircraft Factory model and then Sunbeams. Both proved to be rather unreliable, and in 1916 Napier decided to design their own instead. Reasoning that the key design criteria were high power, light weight, and low frontal area, the engine was laid out with its 12 cylinders in what they called a "broad arrow"—three banks of four cylinders sharing a common crankcase. This suggested the design's first name, the Triple-Four. Today these designs, of which there were only a few, are sometimes referred to as a W-block, although that designation applies more correctly to an engine in which a common crankcase is shared by not merely three but in fact four rows of cylinders (since a "W" is made of four lines or bars). The engine was also advanced in form, the heads using four valves per cylinder with twin overhead camshafts on each bank of cylinders and a single block being milled from aluminium instead of the more common separate-cylinder steel construction used on almost all other designs.
.
Under A. J. Rowledge, the design of the newly-renamed Lion was completed in 1917, and the first hand-built prototypes ran later that year. It was fitted to a de Havilland built DH.9 in early 1918, proving to have many cooling problems. In addition the milled block turned out to be difficult to build with any accuracy and they reverted to separate cylinders, although they remained aluminium. Both of these problems were worked out by the middle of the year and the engine entered production in June 1918. The first Lion I versions delivered 450 hp (335 kW) from their 24 litres. It then took the crown of the most powerful engine from the Liberty L-12, the excellent US wartime design of 400 hp (300 kW).
As the most powerful engine available (particularly after a turbocharger became an option in 1922), the Lion went on to be a huge commercial success. Through the years between the wars the Lion was ubiquitous, and Napier manufactured little else. They stopped making cars in 1925, and little thought was given to replacing their world-famous product. Between the wars it powered over 160 different types of aircraft.
In highly-tuned racing versions the engine could reach 1,300 hp (970 kW), and it was used to break a host of world records: height, air speed, and long distance in aircraft, water speed (delivering 1,375 hp (1,025 kW) in a highly tuned Lion for 100 miles per hour (160 km/h) in 1933) and even land speed: Lions powered many of Sir Malcolm Campbell's record breakers (including over 250 mph (400 km/h) in 1932) and John Cobb's 394 mph Railton Mobil Special in 1947—a record that came well after the Lion had passed its prime and stood until the 1960s. The record had been held by British drivers for 32 years. Lions powered successful entrants in the most prestigious event in air racing, the Schneider Cup, in 1922 and 1927, but were then dropped by Supermarine in favour of a new engine from Rolls-Royce, the Rolls-Royce R which had been especially designed for racing.
During the 1930s a new generation of much larger and more powerful engines started to appear, and the Lion was clearly past its prime. Gradually, they fell further and further behind. By the time the Bristol Hercules and the Rolls-Royce Merlin arrived in the late 1930s, the Lion was too small and old-fashioned.
A marine version of the Lion, unsurprisingly called the Sea Lion, was used to power high speed air-sea rescue launches operated by the RAF.
Another adaptation for the Lion aero engine was propeller-driven motor sleighs, which were used for high-speed transport and SAR duties on sea ice by the Finnish Air Force and Navy.
Turning away from the broad arrow layout, Napier started on the design of two new engines using the even more compact H engine layout. The 16-cylinder Rapier produced 400 hp (300 kW), the 24-cylinder Dagger delivered just under 1,000 hp (750 kW). However these were both smaller than contemporary designs from other companies, and Napier had to start afresh with a new sleeve valve design, which eventually matured into the superb Sabre.
Variants
Lion models[1] [2] Model Date Works No. Power Notes Notable uses I 1918 450 bhp at 1,950 rpm geared, also related IA and 1AY II 1919 E64 450 bhp at 2,000 rpm IIII experimental geared Gloster Gorcock V 470 hp at 2,000 rpm
500 hp at 2,250 rpmVA had increased CR to 5.8 Mainstay engine of the RAF in the late 1920s, replaced by Lion XI VS E79 Turbocharged, intercooled VIS 1927 Turbocharged Gloster Guan VII 1925 700 bhp (racing) Gloster III (Schneider Trophy entrant)
Supermarine S.4VIIA 1927 E86 900 bhp (racing) Golden Arrow
Blue Bird (1927)
Miss England I
Supermarine S.5
Gloster IVVIIB 1927 875 bhp (racing) geared Supermarine S.5
Gloster IVVIID 1929 E91 1,350 bhp at 3,600 rpm (racing) Supercharged, about 6-8 built Blue Bird (1931)
Fred H Stewarts Enterprise
Betty Carstairss Estelle V powerboat
Miss Britain III
Gloster VI (Schneider Trophy entrant)
Railton Special (John Cobb's land speed record car)VIII 1927 direct drive Gloster Gorcock XIA 1928 580 bhp at 2,585 rpm, 6:1 CR RAF production model Napier-Railton Lioness E71 Inverted layout, for better visibility. At least some were built turbocharged, for racing. Sea Lion 1933 500/600 bhp Marine version of Lion XI British Power Boat Company Type Two 63 ft HSL Applications
Aircraft
- Alliance P.2 Seabird
- Avro Bison
- Blackburn Blackburn
- Blackburn Dart
- Blackburn Pellet
- Blackburn Ripon
- Blackburn Velos
- Boulton Paul Atlantic
- Boulton Paul Bodmin
- Boulton Paul Bolton
- English Electric Kingston flying boat (prototype)
- Fairey III
- Fairey Fawn
- Gloster Gorcock
- Gloster Guan
- Handley Page H.P.31 Harrow
- Handley Page Hyderabad
- Mitsubishi B1M
- Parnall Pike
- Parnall Possum
- Parnall Puffin
- Supermarine S.4
- Supermarine S.5
- Supermarine Seagull
- Supermarine Southampton
- Tarrant Tabor
- Vickers Vernon
- Vickers Valparaiso
- Vickers Victoria
- Vickers Virginia
- Vickers Vixen
- Westland Walrus
Other applications
- British Power Boat Company Type Two 63 ft HSL
- British Power Boat Company 60 ft 4 in[3]
Engines on display
Preserved Napier Lion engines are on static display at the following museums:
- Brooklands Museum
- Canada Aviation Museum
- Imperial War Museum Duxford
- Solent Sky
Specifications (Lion II)
Data from Lumsden[4]
General characteristics
- Type: 12-cylinder water-cooled W-block (3 banks of 4 cylinders) aircraft piston engine
- Bore: 5.5 in (139.7 mm)
- Stroke: 5.125 in (130.17 mm)
- Displacement: 1,461.6 in³ (23.9 L)
- Length: 57.5 in (1460 mm)
- Width: 42.0 in (1067 mm)
- Height: 43.5 in (1105 mm)
- Dry weight: 960 lb (435 kg)
Components
- Valvetrain: Two intake and two exhaust valves per cylinder actuated via double overhead camshafts per cylinder block.
- Cooling system: Water-cooled
Performance
- Power output: 480 hp (358 kW) at 2,200 rpm at 5,000 ft
- Specific power: 0.32 hp/in³ (15.0 kW/L)
- Compression ratio: 5.8:1
- Power-to-weight ratio: 0.5 hp/lb (0.82 kW/kg)
See also
- Napier-Bentley
- Vehicles powered by Napier Lion engines
- Related lists
References
Notes
- ^ Vessey 1997
- ^ Napier aero-engines. "Lion" (PDF). Flight. 27 June 1958. http://www.flightglobal.com/pdfarchive/view/1958/1958%20-%200877.html.
- ^ www.mwadui.com/HonKong/The 2nd MTB Flotilla.pdf
- ^ Lumsden 2003, p.166.
Bibliography
- Lumsden, Alec. British Piston Engines and their Aircraft. Marlborough, Wiltshire: Airlife Publishing, 2003. ISBN 1-85310-294-6.
- Vessey, Alan. Napier Powered. Stroud: Tempus (Images of England series), 1997. ISBN 0-7524-0766-X.
External links
- "The Napier Lion Aeromotor" (PDF). Flight XI (13): 397–402. March 27, 1919. No. 535. http://www.flightglobal.com/pdfarchive/view/1919/1919%20-%200397.html. Retrieved January 12, 2011. Contemporary technical description of the Lion with photographs and drawings.
Napier aero engines Piston engines Turboprop / Turboshaft Coupled Naiad · Eland · Gazelle · Naiad
Turbo-compound Gas-generator Rocket Lists relating to aviation General Aircraft (manufacturers) · Aircraft engines (manufacturers) · Airlines (defunct) · Airports · Civil authorities · Museums · Registration prefixes · Rotorcraft (manufacturers) · TimelineMilitary Accidents/incidents Records Categories:- Napier aircraft engines
- Aircraft piston engines 1910-1919
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.