- Tellurium dioxide
-
Tellurium dioxide 
 Other namesTellurium(IV) oxide
Other namesTellurium(IV) oxideIdentifiers CAS number 7446-07-3 
PubChem 62638 ChemSpider 56390 
UNII 397E9RKE83 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=[Te]=O
Properties Molecular formula TeO2 Molar mass 159.60 g/mol Appearance white solid Density 5.670 g/cm3 (tetragonal)
6.04 g/cm3 (orthorhombic) [1]Melting point 733 °C
Boiling point 1245 °C
Solubility in water negligible Solubility soluble in acid and alkali Hazards EU Index Not listed Flash point Non-flammable Related compounds Other cations Sulfur dioxide
Selenium dioxideRelated tellurium oxides Tellurium trioxide  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Tellurium dioxide (TeO2) is a solid oxide of tellurium. It is encountered in two different forms, the yellow orthorhombic mineral tellurite, β-TeO2, and the synthetic, colourless tetragonal (paratellurite), α-TeO2.[2] Most of the information regarding reaction chemistry has been obtained in studies involving paratellurite, α-TeO2.[3]
Contents
Preparation
Paratellurite, α-TeO2, is produced by reacting tellurium with O2:[2]
- Te + O2 → TeO2
An alternative preparation is to dehydrate tellurous acid, H2TeO3, or to thermally decompose basic tellurium nitrate,Te2O4.HNO3 above 400°C.[2]
Chemical properties
TeO2 is highly insoluble in water and soluble in concentrated sulfuric acid. It is also incompatible with strong acids and strong oxidizing agents. It is an amphoteric substance and therefore can act both as an acid or as a base depending on the solution it is in.[4] It reacts with acids to make tellurium salts and bases to make tellurites. It can be oxidized to telluric acid or tellurates.
Structure
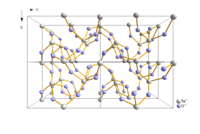
Paratellurite, α-TeO2, converts at high pressure into the β-, tellurite form.[5] Both the α-, (paratellurite) and β- (tellurite forms) contain four coordinate Te with the oxygen atoms at four of the corners of a trigonal bipyramid. In paratellurite all vertices are shared to give a rutile-like structure, where the O-Te-O bond angle is 140°. α-TeO2 In tellurite pairs of trigonal pyramidal, TeO4 units, sharing an edge, share vertices to then form a layer.[5] The shortest Te-Te distance in tellurite is 317 pm, compared to 374 pm in paratellurite.[5] Similar Te2O6 units are found in the mineral denningite.[5]
TeO2 melts at 732.6 °C, forming a red liquid.[6]
Uses
It is used as an acousto-optic material.
Tellurium dioxide is also a conditional glass former, which means it will form a glass with small molar% additions of a second compound such as an oxide or halide. TeO2 glasses have high refractive indices and transmit into the mid-infrared part of the electromagnetic spectrum, therefore they are of technological interest for optical waveguides. Tellurite glasses have also been shown to exhibit Raman gain up to 30 times that of silica, useful in optical fibre amplification.[7]
Safety
TeO2 is a possible teratogen.[8]
Exposure to tellurium compounds produces a garlic-like odour on the breath, caused by the formation of ethyl telluride.[9]
References
- ^ Pradyot Patnaik (2002). Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0070494398.
- ^ a b c Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, A. (1984). Chemistry of the Elements. Oxford: Pergamon. p. 911. ISBN 0-08-022057-6.
- ^ W.R.McWhinnie (1995) Tellurium - Inorganic chemistry Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry Ed. R. Bruce King (1994) John Wiley & Sons ISBN 0 471 93620 0
- ^ K. W. Bagnall (1966). The Chemistry of Selenium, Tellurium and Polonium. London: Elsevier. pp. 59–60. ISBN 0080188559.
- ^ a b c d Wells, A. F. (1984), Structural Inorganic Chemistry (5th ed.), Oxford: Clarendon Press, ISBN 0-19-855370-6
- ^ Egon Wiberg; Nils Wiberg; Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001). Inorganic chemistry. Academic Press. pp. 592–593. ISBN 0123526515.
- ^ Stegeman R, Jankovic L, Kim H, Rivero C, Stegeman G, Richardson K, Delfyett P, Guo Y, Schulte A, Cardinal T (2003). "Tellurite glasses with peak absolute Raman gain coefficients up to 30 times that of fused silica". Optics Letters 28 (13): 1126–8. doi:10.1364/OL.28.001126. PMID 12879929.
- ^ Perez-D'Gregorio RE, Miller RK, Baggs RB (1988). "Maternal toxicity and teratogenicity of tellurium dioxide in the Wistar rat: relationship to pair-feeding". Reprod. Toxicol. 2 (1): 55–61. doi:10.1016/S0890-6238(88)80009-1. PMID 2980402.
- ^ Atta-ur-Rahman (2008). Studies in Natural Products Chemistry, Volume 35. Elsevier. p. 905. ISBN 0444531815. http://books.google.com/?id=8Ugmrew2EqEC.
External links
Tellurium compounds Categories:- Oxides
- Tellurium compounds
- Nonlinear optical materials
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
