- Tellurium tetrachloride
-
Tellurium tetrachloride  Tellurium(IV) chloride
Tellurium(IV) chloride
Tetratellurium hexadecachlorideOther namesTellurium chlorideIdentifiers CAS number 10026-07-0 PubChem 61443 ChemSpider 55367 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - Cl[Te](Cl)(Cl)Cl
Properties Molecular formula [TeCl4]4 Molar mass 1077.64 g/mol Appearance hygroscopic pale yellow solid
(if fused, maroon liquid)Density 3.26 g/cm³, solid Melting point 224 °C
Boiling point 380 °C
Structure Crystal structure Monoclinic, mS80 Space group C12/c1, No. 15 Coordination
geometryDistorted octahedral (Te) Molecular shape Seesaw (gas phase) Dipole moment 2.59 D (gas phase) Hazards Main hazards Toxic, corrosive,
respiratory irritantRelated compounds Other anions Tellurium tetrafluoride
Tellurium tetrabromide
Tellurium tetraiodideOther cations Selenium tetrachloride
Polonium tetrachlorideRelated compounds Tellurium dichloride  tetrachloride (verify) (what is:
tetrachloride (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Tellurium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the empirical formula TeCl4. The compound is volatile, subliming at 200 °C at 0.1 mm Hg[1]. Molten TeCl4 is ionic, dissociating into ions TeCl3+ and Te2Cl102−.[1]
Contents
Structure
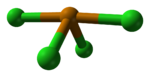
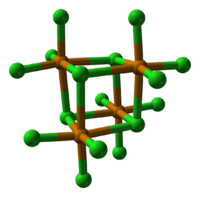
TeCl4 is monomeric in the gas phase, with a structure similar to that of SF4.[2]. In the solid state, it is a tetrameric cluster, Te4Cl16. The cluster with a Te4Cl4 core and three terminal chloride ligands for each Te. Alternatively it can be considered as a Te4 tetrahedron with face-capping chlorines and three terminal chlorines per tellurium atom, giving each tellurium atom a distorted octahedral environment
Synthesis
TeCl4 is prepared by chlorination of tellurium powder:
- Te + 2 Cl2 → TeCl4
The reaction is initiated with heat. The product is isolated by distillation.[3]
Applications
TeCl4 has proven of occasional interest in organic synthesis.[4] It adds to alkenes to give Cl-C-C-TeCl3 derivatives, wherein the Te can be subsequently removed with sodium sulfide. Electron-rich arenes react to give aryl Te compounds. Thus anisole give TeCl2(C6H4OMe)2, which can be reduced to the diaryl telluride.
Safety considerations
As is the case for other tellurium compounds, TeCl4 is toxic. It also releases HCl upon hydrolysis.
References
- ^ a b Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0080379419.
- ^ Cotton, F. Albert; Wilkinson, Geoffrey; Murillo, Carlos A.; Bochmann, Manfred (1999), Advanced Inorganic Chemistry (6th ed.), New York: Wiley-Interscience, ISBN 0-471-19957-5
- ^ Suttle, J. F.; Smith, C. R. F. (1950). "Tellurium(IV) chloride". Inorganic Syntheses 3: 140–2. doi:10.1002/9780470132340. ISBN 9780470131626.
- ^ Petragnani, N.; Comasseto, J. V. Synthesis 1991, 793, 897
Tellurium compounds Categories:- Tellurium compounds
- Chlorides
- Nonmetal halides
- Deliquescent substances
- Chalcohalides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.