- Tellurate
-
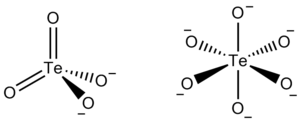
The tellurate ion is TeO42− or TeO66−.
Unlike sulfate, tellurate is a somewhat good oxidizer; it can be reduced to tellurite or tellurium.
Tellurate exists in two forms, metatellurate ion, TeO42−, and orthotellurate ion, TeO66−.
Compounds include metatellurates and orthotellurates. Metatellurates are analogous to sulfates, but they are rare. Orthotellurates are much more common and this forms most of the chemistry of tellurates.
In neutral conditions, pentahydrogen orthotellurate ion, H5TeO6−, is most common; in basic conditions, tetrahydrogen orthotellurate ion, H4TeO62−, is found; in acid conditions, the orthotelluric acid, H6TeO6 is formed.[1]
Contents
Properties
The metatellurate anion, TeO42−, has a molecular weight of 191.60 g/mole. It belongs to the Td molecular point group, thus it has a tetrahedral shape even though two of its oxygen atoms are double bonded.
- TeO42− → TeO32− + 1/2O2 (E0= −1.042 V)
The E0 or standard reduction potential value is significant as it gives an indication of the strength of the tellurate ion as an oxidizing agent.[1]
The orthotellurate anion, TeO66−, has a molecular weight of 223.6 g/mole. It belongs to the Oh molecular point group, thus it has an octahedral shape.
NMR spectroscopy
Tellurium has two NMR active nuclei, 123Te and 125Te. 123Te has an abundance of 0.9% and a nuclear spin (I) of 1/2. 125Te has an abundance of 7% and an equivalent nuclear spin.[2] 125Te is more commonly performed because it has a higher sensitivity.[3] The metatellurate anion has a chemical shift around 610 ppm when analyzed using 125Te NMR at 25°C at a frequency of 94.735 MHz and referenced externally against aqueous 1.0 M telluric acid.[4]
List of some known salts involving metatellurate anions
Na2TeO4*2H2O
K2TeO4*2H2O
Rb2TeO4
Cs2TeO4
CaTeO4
Al2(TeO4)3
(NH4)2TeO4
References
- ^ a b Frost, R.L. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2009, 72, 903.
- ^ Housecroft, C. E.; Sharpe, A. G. (2008). Inorganic Chemistry (3rd ed.). Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0131755536.
- ^ Drago, R. S. Physical Methods for Chemists 2nd ed.; Surfside Scientific Publishers: Gainesville, FL 1992.
- ^ Konaka, S.; Ozawa, Y.; Yagasaki, A. Inorg. Chem., 2008, 47, 1244.
External links
Categories:- Oxoanions
- Tellurates
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.