- Chlorine pentafluoride
-
Chlorine pentafluoride 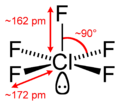
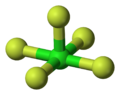
Identifiers CAS number 13637-63-3 PubChem 61654 RTECS number FO2975000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - FCl(F)(F)(F)F
- InChI=InChI=1S/ClF5/c2-1(3,4,5)6
Properties Molecular formula ClF5 Molar mass 130.445 g mol−1 Appearance colorless gas Density 4.5 g/cm3 Melting point −103 °C
Boiling point −13.1 °C
Solubility in water hydrolyzes Structure Molecular shape Square pyramidal Thermochemistry Std enthalpy of
formation ΔfHo298−238.49 kJ mol−1 Standard molar
entropy So298310.73 J K−1 mol−1  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Chlorine pentafluoride is an interhalogen compound with formula ClF5. It was first synthesized in 1963.[1]
Its square pyramidal structure with C4v symmetry was confirmed by its high resolution19F NMR spectrum.[2]
Contents
Preparation
Initially, a common method for synthesis of this hypervalent molecule was to react ClF3 with F2 at high temperatures and high pressures. Also, reacting metal fluorides, MClF4 (i.e. KClF4, RbClF4, CsClF4) with F2 produced ClF5 and the corresponding MF.[1] In 1981, researchers found that NiF2 is an excellent catalyst for generating ClF5.[3]
Reactions
ClF5 reacts violently with water to produce FClO4 and HF.[4] It is also a strong fluorinating agent. While unreactive with first row nonmetals except carbon and boron, it reacts readily with second and third row nonmetals at room temperature except chlorine.[2]
See also
References
- ^ Smith D. F. (1963). "Chlorine Pentafluoride". Science 141 (3585): 1039–1040. doi:10.1126/science.141.3585.1039. PMID 17739492.
- ^ a b Pilipovich, D., Maya, W., Lawton, E.A., Bauer, H.F., Sheehan, D. F., Ogimachi, N. N., Wilson, R. D., Gunderloy, F. C., Bedwell, V. E. (1967). "Chlorine pentafluoride. Preparation and Properties". Inorganic Chemistry 6 (10): 1918. doi:10.1021/ic50056a036.
- ^ Šmalc, A., Žemva, B., Slivnik, J., and Lutar K. (1981). "On the Synthesis of Chlorine Pentafluoride". Journal of Fluorine Chemistry 17 (4): 381–383. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(00)81783-2.
- ^ Pradyot Patnaik (2007). A comprehensive guide to the hazardous properties of chemical substances (3rd ed.). Wiley-Interscience. pp. 478–479. ISBN 0471714585.
External links
Chlorine compounds Categories:- Fluorides
- Inorganic chlorine compounds
- Interhalogen compounds
- Rocket oxidizers
- Fluorinating agents
- Oxidizing agents
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
