- Diethylene glycol dinitrate
-
Diethylene glycol dinitrate 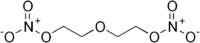 Nitric acid 2-(2-nitrooxyethoxy)ethyl esterOther namesDiethyleneglycol dinitrate
Nitric acid 2-(2-nitrooxyethoxy)ethyl esterOther namesDiethyleneglycol dinitrate
Diethyl glycol dinitrate
Oxydiethylene dinitrateIdentifiers CAS number 693-21-0 PubChem 61198 ChemSpider 55142 
UN number 0075 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C(CO[N+](=O)[O-])OCCO[N+](=O)[O-]
Properties Molecular formula C4H8N2O7 Molar mass 196.12 g/mol Density 1.4092 (0 °C)
1.3846 (20 °C)Melting point -11.5 °C, 262 K, 11 °F
Boiling point 197 °C (decomposes)
Solubility in water 4.1 g/L (24 °C)  glycol dinitrate (verify) (what is:
glycol dinitrate (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Diethylene glycol dinitrate is a nitrated alcohol ester produced by the action of concentrated nitric acid, normally admixed with an excess of strong sulfuric acid as a dehydrating agent, upon diethylene glycol.
Diethylene glycol dinitrate is a colorless, odorless, viscous, oily liquid, specific gravity 1.4092 at 0 °C and 1.3846 at 20 °C; freezing point −11.5 °C under a standard atmosphere, the theoretical boiling point of approximately 197 °C difficult to confirm as the compound begins to decompose and spontaneously inflames at or slightly below this temperature. Partial pressure is reported as 0.007 mmHg (930 mPa) at 22.4 °C and 760 mmHg (101 kPa). It is readily miscible in most non-polar solvents, methanol, and cold acetic acid. Solubility in water (4.1 gm/L at 24 °C) and ethanol is very low. While chemically similar to a number of powerful high explosives, pure diethylene glycol dinitrate is extremely hard to initiate and will not propagate a detonation wave. It inflames only with difficulty (requiring localized heating to decomposition point) unless first atomized, and burns placidly even in quantity.
Mixed with nitrocellulose and extruded under pressure, diethylene glycol dinitrate forms a tough colloid whose characteristics (good specific impulse, moderate burn rate and temperature, great resistance to accidental ignition and casual handling) make it well suited as a solid propellant for rocketry. It was widely used in this capacity, by both sides, during World War II. It also found use as a "productive" desensitizer (one that contributes to the overall power of the explosion rather than having a neutral or negative effect) in nitroglycerine and nitroglycol based explosives such as dynamite and blasting gelatin. It is also used as plasticizer for energetic materials.
If ingested, like nitroglycerine, it produces rapid vasodialation through the release of nitrogen monoxide, NO. Popularly-termed nitric oxide, NO is a physiological signaling molecule that relaxes smooth muscle. Consequently, diethylene glycol dinitrate has occasionally been used medically to relieve angina, substernal chest pain associated with impaired cardiac circulation. The rational is that the concurrent headache it induces is somewhat less severe than other nitro compounds.
At present, interest in the chemical seems to be mostly historical: more potent perchlorate–metal mixtures have long since supplanted it as a solid propellant; safer explosives have replaced nitroglycerine, true dynamites (the term is often used generically, even by experienced field technicians, to refer to almost any explosive supplied in small, discrete packages) retaining only a few specialist uses. The medical application was never widespread, the standard nitroglycerine being faster acting and almost literally dirt cheap; oral nitrates in any case being only palliative, not an effective treatment.
Triethylene glycol dinitrate, diethylene glycol dinitrate, and trimethyloleate trinitrate are being considered as replacements for nitroglycerin in propellants. [1]
References
- W. H. Rinkenbach, Industrial Engineering Chemistry v19 p925 (1927) Note: the present author has transliterated some terminology and notation in line with modern practice.
- Military applications referenced in Encyclopedia of Weapons of World War 2; Gen. Ed. Chris Bishop, c.2003 Friedman/Fairfax NYNY, ISBN 1-58663-762-2
Categories:- Alkyl nitrates
- Propellants
- Monopropellants
- Explosive chemicals
- Liquid explosives
- Plasticizers
- Antianginals
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
