- Dynamite
-
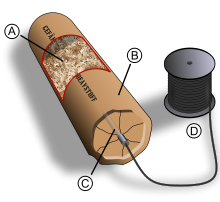 Diagram of dynamite.
Diagram of dynamite.
- Sawdust (or any other type of absorbent material) soaked in nitroglycerin.
- Protective coating surrounding the explosive material.
- Blasting cap.
- Electrical cable (or fuse) connected to the blasting cap.
Dynamite is an explosive material based on nitroglycerin, initially using diatomaceous earth (kieselgur: American spelling; kieselguhr: British spelling), or another absorbent substance such as powdered shells, clay, sawdust, or wood pulp. Dynamites using organic materials such as sawdust are less stable and such use has been generally discontinued. Dynamite was invented by the Swedish chemist and engineer Alfred Nobel in Krümmel (Geesthacht, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany), and patented in 1867. Its name is derived from Greek roots that literally mean "connected with power."
Dynamite is usually sold in the form of sticks about 8 in (20 cm) long and about 1.25 in (3.2 cm) in diameter, with a weight of about 0.5 lb (0.23 kg).[1] Other sizes also exist. The maximum shelf life of nitroglycerin-based dynamite is recommended as one year from the date of manufacture under good storage conditions.[1]
Dynamite is a high explosive, which means it detonates rather than deflagrates. While trinitrotoluene is used as the standard for gauging explosive power, dynamite has more than a 60% greater energy density than TNT.
Another form of dynamite consists of nitroglycerin dissolved in nitrocellulose and a small amount of ketone. This form of dynamite is similar to cordite, and is much safer than the simple mix of nitroglycerin and diatomaceous earth. Military dynamite achieves greater stability by avoiding the use of nitroglycerin and uses much more stable chemicals.[2] Public knowledge of dynamite led to metaphoric uses, such as saying that a particular issue "is political dynamite" (for example at this link).
Contents
Uses
Dynamite is mainly used in the mining, quarrying, construction, and demolition industries, and it has had some historical usage in warfare. However the unstable nature of nitroglycerin, especially if subjected to freezing, has rendered it obsolete for military uses.
History
Dynamite was invented by Alfred Nobel and was the first safely manageable explosive stronger than black powder. Nobel obtained patents for his invention: in England on 7 May 1867 and in Sweden on 19 October 1867.[3] He originally sold dynamite as "Nobel's Blasting Powder". After its introduction, dynamite rapidly gained wide-scale use as a safe alternative to gunpowder and nitroglycerin. Nobel tightly controlled the patents, and unlicensed duplicating companies were quickly shut down. However, a few American businessmen got around the patent by using a slightly different formula.[4] The invention was celebrated by anarchists, who recognized its suitability for propaganda by the deed.[5]
Manufacture
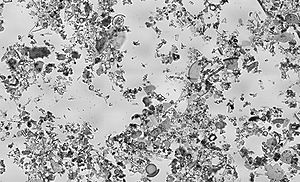 Diatomaceous earth as viewed under bright field illumination on a light microscope. Diatomaceous earth is a soft, siliceous, sedimentary rock made up of the cell walls/shells of single cell diatoms and which readily crumbles to a fine powder. It is also very absorbent. This image of diatomaceous earth particles in water is at a scale of 6.236 pixels/micrometer, the entire image covers a region of approximately 1.13 by 0.69 millimeter.
Diatomaceous earth as viewed under bright field illumination on a light microscope. Diatomaceous earth is a soft, siliceous, sedimentary rock made up of the cell walls/shells of single cell diatoms and which readily crumbles to a fine powder. It is also very absorbent. This image of diatomaceous earth particles in water is at a scale of 6.236 pixels/micrometer, the entire image covers a region of approximately 1.13 by 0.69 millimeter.
Classic dynamite consists of three parts nitroglycerin, one part diatomaceous earth and a small admixture of sodium carbonate. This mixture is formed into short sticks and wrapped in paper. Nitroglycerin by itself is a very strong explosive, and in its pure form it is extremely shock-sensitive. (That is, physical shock can cause it to explode.), degrading over time to even more unstable forms. This makes it highly dangerous to transport or use in its pure form. Absorbed into diatomaceous earth or more commonly sawdust, nitroglycerin is less shock-sensitive. Over time, the dynamite will "weep" or "sweat" its nitroglycerin, which can then pool in the bottom of the box or storage area. (For that reason, explosive manuals recommend the repeated turning over boxes of dynamite in storage.) Crystals will form on the outside of the sticks causing them to be even more shock, friction or temperature sensitive. This creates a very dangerous situation. While the actual possibility of explosion without a blasting cap is minimal, old dynamite is still dangerous.
South Africa
For several decades beginning in the 1940s, the largest producer of dynamite in the world was the Republic of South Africa. There the De Beers company established a factory in 1902 at Somerset West. The explosives factory was later operated by AECI (African Explosives and Chemical Industries). The demand for the product came mainly from the country's vast gold mines, centered on the Witwatersrand. The factory at Somerset West was in operation in 1903 and by 1907 it was already producing 340,000 cases [22 kilograms (50 pounds) each] annually. In addition, a rival factory at Modderfontein was producing another 200,000 cases per year.[6]
One of the drawbacks of dynamite was that it was dangerous to manufacture. There were two large explosions at the Somerset West plant during the 1960s. Some workers died, but the loss of life was limited by the modular design of the factory and its earth works, and the planting of trees that directed the blasts upward. There were also several less notable but still newsworthy explosions at the Modderfontein factory. After 1985, pressure from trade unions forced AECI to phase out the production of dynamite. The factory then went on to produce ammonium nitrate emulsion-based explosives that are far safer to manufacture and to handle.[7]
United States
In the United States, in 1885, the chemist Russell S. Penniman invented "ammonium dynamite", a form of explosive that used ammonium nitrate as a substitute for the more costly nitroglycerin. These dynamites were marketed with the trade name "Extra". Ammonium nitrate contains 85% of the chemical energy of nitroglycerin. Dynamite was manufactured by the E. I du Pont de Nemours Company until the mid-1970s. Other American dynamite makers of that time period included the Hercules Corporation, Atlas, Trojan-US Powder, Austin, and several other smaller firms. Dynamite has been mostly phased out in favor of water gel explosives, which are cheaper to manufacture, and in many ways are safer to handle.[8]
Difference from TNT
It is a common misconception that trinitrotoluene (TNT) and dynamite are the same thing, or that dynamite contains TNT. Though both substances are high explosives, there is little similarity between them. Dynamite is an absorbent mixture soaked in nitroglycerin then compacted into a cylindrical shape and wrapped in paper. TNT is a specific chemical compound called 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. (Military dynamite is a dynamite substitute, also formulated without nitroglycerin, containing 75% RDX, 15% TNT, 5% SAE 10 motor oil, and 5% cornstarch to be the equivalent of dynamite composed of 60% nitroglycerin, but much safer to store and handle.[9])
A stick of dynamite contains roughly 2.1 MJ of energy.[10] The energy density (joules/kilogram or J/kg) of dynamite is approximately 7.5 MJ/kg, compared to 4.7 MJ/kg of TNT[citation needed].
See also
References
Notes
- ^ a b Austin Powder Guide, Dynamite series page 2.
- ^ Ledgard, Jared (2007), A Soldiers Handbook, Volume 1: Explosives Operations, ISBN 0615147941, http://books.google.com/books?id=U6f-Qlmm6zIC&pg=PA498&lpg=PA498&dq=Military+dynamite+TNT
- ^ Schück & Sohlman (1929), p. 101.
- ^ US Patent 234489 issued to Morse 16 November 1880
- ^ Palmer, Brian (2010-12-29) What do anarchists want from us?, Slate.com
- ^ An MBendi Profile: South Africa - History of the Chemical Industry.
- ^ Historical Highlights 1980's.
- ^ DuPont Heritage: Explosives.
- ^ Unexploded Ordnance Information: Ordnance Fillers
- ^ Classroom Energy.
Sources
- Cartwright, A. P. (1964). The Dynamite Company: The Story of African Explosives and Chemical Industries Limited. Cape Town: Purnell & Sons (S.A.) (Pty) Ltd.
- Schück, H. and Sohlman, R.(1929). The Life of Alfred Nobel. London: William Heinemann Ltd.
External links
- Alfred Nobel
- Oregon State Police - Arson and Explosives Section (Handling instructions and photos)
- Big bang
- Detonator cables
- US patent 78317, Alfred Nobel, "Improved explosive compound", issued 1868-05-26
Categories:- Explosives
- 1866 introductions
- Swedish inventions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.





