- Ulaid
-
The Ulaid (Old Irish, pronounced [ˈʊləðʲ]) or Ulaidh (modern Irish, pronounced [ˈʊləɣʲ]) were a people of early Ireland who gave their name to the modern province of Ulster (modern Irish: Cúige Uladh, pronounced [/ˈkuːiɡʲə ˈʊləɣ/], meaning "fifth-part of the Ulaidh"). The the English word Ulster derives from Irish Ulaidh and Old Norse staðr (meaning "place, territory").
In medieval texts they are also referred to as the Clanna Rudraige (modern spelling: Clanna Rudhraighe, anglicization: Clanna Rury) meaning "descendants of Rudraige" – whence the modern Irish term Rúraíocht (the Ulster Cycle of Irish mythology).[1]
Contents
History of the name
Ulaid is a plural noun, indicating an ethnonym rather than a geographic term.[2] The Ulaid are probably mentioned in Ptolemy's 2nd century Geographia, as the Ούολουντοι (Uolunti),[3] probably a corruption of Ούλουτοι (Uluti). The name is probably derived from ul, "beard".[4] The general scholarly consensus since as early as the time of Eoin MacNeill has been that the Ulaid were apparently kin to the so-called Érainn,[5] or at least to their royal families, sometimes called the Clanna Dedad, and perhaps not their nebulous subject populations.[6] T. F. O'Rahilly notably believed the Ulaid were an actual branch of the Érainn.[7] In any case, certainly related to the Ulaid are the less widely known Dáirine, also another name for the Érainn royalty, and both were related to or derived from the Darini of Ptolemy.[8]
Artifacts
Although Francis John Byrne describes the few La Tène artifacts discovered in Ireland as 'rather scanty',[9] most of the artifacts (mostly weapons and harness pieces) have been found in the North of Ireland, suggesting 'small bands of settlers (warriors and metalworkers) arrived' from Britain in the 3rd century BC, and may have been absorbed into the Ulaid population.[10]
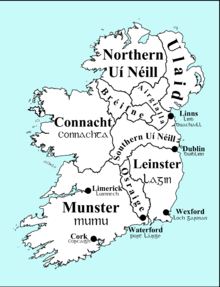
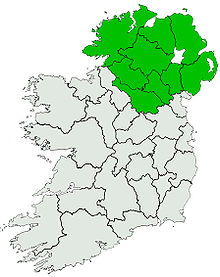
Territories
The use of the word cuige, earlier cóiced, literally "fifth", to mean "province", implies the existence at some point in prehistory of a pentarchy, whose five members are believed to have been population groups the Ulaid, the Connachta (Connacht) and the Laigin (Leinster), the region Mumu (Munster), and the central kingdom of Mide.[11] At their height, Ulaid territory extended south as far as the River Boyne and as far west as County Leitrim. However, that pentarchy no longer existed by the 5th century, when documentary history in Ireland begins. The Ulaid still held significant territory, primarily in Counties Antrim, Down and Louth, although the boundaries of their territories were fluid. Their primary ruling dynasty was the Dál Fiatach, based in Downpatrick, County Down. The name Ulaid developed an additional geographical sense, so that the term rí Ulad, "king of the Ulaid", could refer to the king of the Dál Fiatach, or to the over-king of the north-east, many of whom came from dynasties of the Cruithne such as the Dál nAraide and the Uí Echach Cobo (the Dál nAraide even claimed in their altered genealogies to be na fir Ulaid, "the true Ulaid"). The rest of the ancient fifth fell under the control of the Airgíalla and the northern dynasties of the Uí Néill. The Ulaid as a distinct people, as represented by the Dál Fiatach, survived until their conquest in 1177 by the Anglo-Norman knight John de Courcy.[12][13]
Descent
Medieval Irish genealogists traced the Ulaid's descent from the legendary High King Rudraige mac Sithrigi.[14] The Ulaid feature in Irish legends and historical traditions of prehistoric times, most notably in the group of sagas known as the Ulster Cycle. These stories are set during the reign of the Ulaid king Conchobar mac Nessa at Emain Macha (Navan Fort, near Armagh) and tell of his conflicts with the Connachta, led by queen Medb and her husband Ailill mac Máta. The chief hero is Conchobar's nephew Cú Chulainn, and the central story is the proto-epic Táin Bó Cúailnge, "The Cattle Raid of Cooley".
In some stories Conchobar's birth and death are synchronised with those of Christ, which creates an apparent anachronism in the presence of the Connachta. The historical Connachta were a group of dynasties who traced their descent to the legendary king Conn Cétchathach, whose reign is traditionally dated to the 2nd century.[15] However, the chronology of early Irish historical tradition is inconsistent and highly artificial.[16] One early saga makes Fergus mac Léti, one of Conchobar's predecessors as king of the Ulaid, a contemporary of Conn,[17] and Tírechán's 7th century memoir of Saint Patrick says that Cairbre Nia Fer, Conchobar's son-in-law in the sagas, lived only 100 years before the saint, i.e. in the 4th century.[18]
Origins
Kenneth Jackson, based on his estimates on the survival of oral tradition, also suggested that the Ulster Cycle originated in the 4th century.[19] Other scholars, following T. F. O'Rahilly, propose that the sagas of the Ulster Cycle derive from the wars between the Ulaid and the midland dynasties of the Connachta and the nascent Uí Néill in the 4th and 5th centuries, at the end of which the Ulaid lost much of their territory, and their capital, to the new kingdoms of the Airgíalla.[20] Traditional history credits this to the Three Collas, three great great great grandsons of Conn, who defeated the Ulaid king Fergus Foga at Achad Lethderg in County Monaghan, seized all Ulaid territory west of the Newry River and Lough Neagh, and burned Emain Macha. Fergus Foga is said to have been the last king of the Ulaid to reign there. The Annals of the Four Masters dates this to AD 331.[21] O'Rahilly and his followers believe the Collas are literary doublets of the sons of Niall Noígiallach, eponymous founder of the Uí Néill, who they propose were the true conquerors of Emain in the 5th century.[11]
Ancestry
It should be noted that the Kings of Tara in the Ulster Cycle are the kindred of the Ulaid, the Érainn, and are generally portrayed sympathetically, especially Conaire Mór. It was remembered that the Connachta and Uí Néill had not yet taken the kingship. Tara was later occupied by the Laigin, who are to some extent strangely integrated with the Connachta in the Ulster Cycle.[22] The latter later took the midlands from the Laigin and their historical antagonism is legendary. The Érainn, led by Cú Roí, also rule in distant Munster and, while presented as deadly rivals of the Ulaid, are again portrayed with unusual interest and sympathy.
See also
References
- ^ Price, Glanville. The Celtic Connection. Rowman & Littlefield, 1992. p.73
- ^ Francis J. Byrne, Irish Kings and High Kings, Four Courts Press, 2001, p. 46
- ^ Ptolemy, Geographia 2.1
- ^ Karl Horst Schmidt, "Insular P- and Q-Celtic", in Martin J. Ball and James Fife (eds.), The Celtic Languages, Routledge, 1993, p. 67
- ^ Eoin MacNeill, "Early Irish Population Groups: their nomenclature, classification and chronology", in Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy (C) 29. (1911): 59–114
- ^ Eoin MacNeill, Phases of Irish History. Dublin: M. H. Gill & Son. 1920.
- ^ T. F. O'Rahilly, Early Irish History and Mythology, 1946, p. 81
- ^ Discussed at length by O'Rahilly 1946
- ^ Byrne, Francis John, Irish Kings and High-Kings. Four Courts Press. 2nd revised edition, 2001.
- ^ Connolly, S.J, The Oxford companion to Irish history. Oxford University Press. 2nd edition, 2007.
- ^ a b Dáibhí Ó Cróinín, "Ireland, 400-800", in Dáibhí Ó Cróinín (ed.), A New History of Ireland Vol 1, 2005, pp. 182-234
- ^ Byrne 2001, pp. 106-129
- ^ Michael Richter, Medieval Ireland, Gill & McMillan, 2005
- ^ O'Rahilly 1946, p. 480
- ^ R. A. Stewart Macalister (ed. & trans.), Lebor Gabála Érenn: The Book of the Taking of Ireland Part V, Irish Texts Society, 1956, p. 331-333
- ^ Byrne 2001, p. 50-51.
- ^ D. A. Binchy (ed. & trans.), "The Saga of Fergus mac Léti", Ériu 16, 1952, pp. 33-48
- ^ Ludwig Bieler (ed. & trans.), The Patrician Texts in the Book of Armagh, Tírechán 40
- ^ Kenneth Hurlstone Jackson, The Oldest Irish Tradition: a Window on the Iron Age, Cambridge University Press, 1964
- ^ O'Rahilly 1946, pp. 207-234
- ^ Annals of the Four Masters M322-331
- ^ Apparently the Laigin had a prehistoric presence in Connacht and may once have been its sovereigns. See Byrne, pp. 130 ff.
External links
Towns Dunon • Eblana • Iuernis • Labiros • Makolikon • Manapia • Nagnata • Raiba • Regia • Regia EteraRivers Argita • Auoba • Birgos • Buuinda • Dabrona • Dur • Iernos • Libnios • Logia • Modonnos • Oboka •Rauios •Senos • Uidua • UinderiosPromontories Isamnion • Northern • Robogdion • Sacron • Southern • UennicnionIslands Adros • Ebuda • Epidion • Erimnos • Limnos • Malaios • Mona • Monaoida • RikinaCategories:- Ancient Ireland
- Medieval Ireland
- Kingdoms of ancient Ireland
- Ulster Cycle
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.