- Cortical bone
-
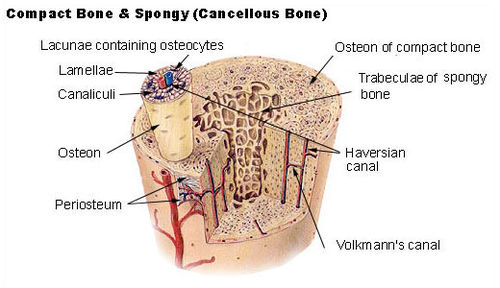
Cortical bone, synonymous with compact bone, is one of the two types of osseous tissue that form bones. Cortical bone facilitates bone's main functions: to support the whole body, protect organs, provide levers for movement, and store and release chemical elements, mainly calcium. As its name implies, cortical bone forms the cortex, or outer shell, of most bones. Again, as its name implies, compact bone is much denser than cancellous bone, which is the other type of osseous tissue. Furthermore, it is harder, stronger and stiffer than cancellous bone. Cortical bone contributes about 80% of the weight of a human skeleton. The primary anatomical and functional unit of cortical bone is the osteon.
References
- Netter, Frank H. (1987), Musculoskeletal system: anatomy, physiology, and metabolic disorders. Summit, New Jersey: Ciba-Geigy Corporation ISBN 0-914168-88-66
External links
- Cortical+bone at eMedicine Dictionary
Musculoskeletal system · connective tissue: bone and cartilage (TA A02.0, TH H3.01, GA 2.86–95) Cartilage perichondrium · fibrocartilage callus · metaphysis
cells (chondroblast · chondrocyte)
types (hyaline · elastic · fibrous)Bone CycleTypescancellous · corticalRegionsStructureosteon / Haversian system · Haversian canals · Volkmann's canals · connective tissue (endosteum · periosteum) · Sharpey's fibres · enthesis · lacunae · canaliculi · trabeculae · medullary cavity · bone marrowShapesCategories:- Musculoskeletal system stubs
- Skeletal system
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.