- Osseous tissue
-
Osseous tissue, or bone tissue, is the major structural and supportive connective tissue of the body. Osseous tissue forms the rigid part of the bone organs that make up the skeletal system.
Contents
Formation
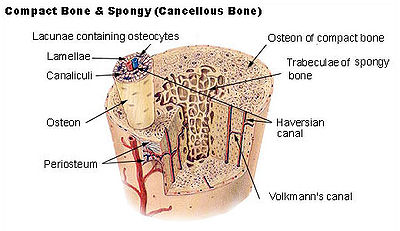
Bone tissue is a mineralized connective tissue. It is formed by cells, called osteoblasts, that deposit a matrix of Type-I collagen and also release calcium, magnesium, and phosphate ions that ultimately combine chemically within the collagenous matrix into a crystalline mineral, known as bone mineral, in the form of hydroxyapatite. The combination of hard mineral and flexible collagen makes bone harder and stronger than cartilage without being brittle. Compact bone consists of a repeating structure called a Haversian system, or osteon, which is the primary anatomical and functional unit. Each osteon has concentric layers of mineralized matrix, called concentric lamellae, which are deposited around a central canal, also known as the Haversian canal, each containing a blood and nerve supply.
Types
There are two types of osseous tissue: compact and spongy. Compact tissue is synonymous with cortical bone, and spongy tissue is synonymous with trabecular and cancellous bone. Compact bone forms the extremely hard exterior while spongy bone fills the hollow interior. The tissues are biologically identical; the difference is in how the microstructure is arranged.
Functions
Osseous tissue performs numerous functions including:
Directly:
- Support for muscles, organs, and soft tissues.
- Leverage and movement.
- Protection of vital organs, e.g., the heart. (Note: not all vital organs are protected by bones, e.g., the intestines.)
- Calcium phosphate storage.
Indirectly:
- Hemopoiesis - formation of blood cells by the bone marrow interspersed within the spongy bone.
Osseous tissue versus bones
Bone tissue is different from bones themselves — bones are organs made up of bone tissue as well as marrow, blood vessels, epithelium and nerves, while bone tissue refers specifically to the mineral matrix that form the rigid sections of the organ.
See also
- Periosteum
- Bone healing
- Osseointegration
- Osteocyte
- Osteoblast
- Osteoclast
- Red bone marrow
- Hydroxylapatite
Sources
- Henry Gray: Anatomy of the human body (Bartleby.com; Great Books Online)
- Eldra P. Solomon - Richard R. Schmidt - Peter J. Adragna : Human anatomy & physiology ed. 2nd 1990 (Sunders College Publishing, Philadelphia) ISBN 0 03 011914 6
External links
Categories:- Skeletal system
- Tissues
- Musculoskeletal system stubs
- Cell biology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.