- Coccolithophore
-
Coccolithaceae 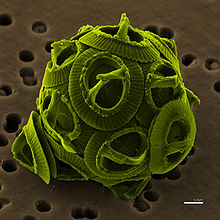
The coccolithophore Gephyrocapsa oceanica Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Chromalveolata Phylum: Haptophyta Class: Prymnesiophyceae Order: Isochrysidales,
CoccolithalesCoccolithophores (also called coccolithophorids) are single-celled algae, protists and phytoplankton belonging to the division of haptophytes. They are distinguished by special calcium carbonate plates (or scales) of uncertain function called coccoliths (calcareous nanoplankton), which are important microfossils. Coccolithophores are almost exclusively marine and are found in large numbers throughout the surface euphotic zone of the ocean. An example of a globally significant coccolithophore is Emiliania huxleyi.
The arrangement of coccolithophores are as spherical cells about 5–100 micrometres across, enclosed by calcareous plates, coccoliths, about 2–25 micrometres across. Coccolithophores that are alive today have two brown pigment chloroplasts in their cell with the nucleus located between them. The pigments are home to the chlorophyll which carry out photosynthesis. In order to obtain the sunlight needed for photosynthesis, coccolithophores live near the surface of the ocean. Although they have the capability to swim, coccolithophores dominant mode of transport is drifting with ocean current and circulation patterns. However, they may maneuver individually to remain in the euphotic zone during times of extremely favorable conditions.[1]
Due to their microscopic size and the broad distribution of many of their taxa, coccoliths have become very important as index fossils for solving various stratigraphic problems. Microfossils are sensitive indicators of changes in the temperature and salinity of the ocean and sea surface water. The quantitative analysis of calcareous nanoplankton assemblages is being employed to reveal such changes. They also produce alkenones, biomarkers of great utility in reconstructing ancient temperatures.
Coccolithophores have long been thought to respond to increased ocean acidity, caused by increasing CO2 levels, by becoming less calcified. In 2008, Iglesias-Rodriguez et al. were surprised to learn that in fact the opposite can happen in at least some circumstances, with the model species E. huxleyi becoming 40% heavier and more abundant in waters of higher CO2 concentration.[2]
-
Coccolithus pelagicus.
-
Satellite image of a large coccolithophore bloom in the Bering Sea in 1998.
-
The milky blue colour of this phytoplankton bloom strongly suggests that it contains coccolithophores.
See also
- CLAW hypothesis
- Dimethyl sulfide
- Dimethylsulfoniopropionate
- Emiliania huxleyi
- Emiliania huxleyi virus 86
- Ocean acidification
- Phytoplankton
- Pleurochrysis carterae
References
- ^ Prothero, D. R. (2004), Bringing fossils to life: an introduction to paleobiology (2nd ed.), Boston: McGraw Hill, pp. 210–213, ISBN 0073661708.
- ^ Iglesias-Rodriguez, M. Debora; Halloran, Paul R.; Rickaby, Rosalind E. M.; Hall, Ian R.; Colmenero-Hidalgo, Elena; Gittins, John R.; Green, Darryl R. H.; Tyrrell, Toby et al. (2008), "Phytoplankton Calcification in a High-CO2 World", Science 320 (5874): 336–340, doi:10.1126/science.1154122, PMID 18420926.
External links
- Cocco Express — Coccolithophorids Expressed Sequence Tags (EST) & Microarray Database
- University of California, Berkeley. Museum of Paleontology: "Introduction to the Prymnesiophyta".
- The Paleontology Portal: Calcareous Nanoplankton
- What is a Coccolithophore?
- Emiliania huxleyi Home Page
- BOOM — Biodiversity of Open Ocean Microcalcifiers
- INA — International Nannoplankton Association
- Nannotax – illustrated guide to Neogene coccolithophores and other nannofossils.
Chromalveolata: Hacrobia Cryptophyta/
CryptophyceaeCryptomonadaceaeHemiselmidaceaeCKHgc (Hemiselmis)Cryptophyte:
PyrenomonadalesChroomonadaceaeGeminigeraceaeGHgc (Guillardia, Hanusia) · GPTgc (Geminigera, Teleaulax) · other (Proteomonas)PyrenomonadaceaeRRSgc (Pyrenomonas, Rhinomonas, Rhodomonas, Storeatula)KatablepharidaceaeTelonemaHaptophyta/
HaptophyceaePrymnesiophyceaeCoccolithales (Pleurochrysis, Coccolithus) · Prymnesiales (Chrysochromulina, Prymnesium) · Isochrysidales (Chrysotila, Dicrateria, Emiliania, Gephyrocapsa, Isochrysis)PavlovophyceaeRelatedOther Categories:- Haptophytes
- Fossils
- Microbiology
-
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.





