- Portal (video game)
-
Portal 
Portal's box art displays a figure moving into a portal. Signs of this style are commonly used in the game's environment.Developer(s) Valve Corporation Publisher(s) Valve Corporation
Microsoft Game Studios (XBLA)Distributor(s) Electronic Arts (retail)
Steam (online)Writer(s) Erik Wolpaw
Chet FaliszekComposer(s) Kelly Bailey Series Half-Life Engine Source (Build 4295, 11 August 2010) Version 1.0.0.0 (12 November 2010)[1] Platform(s) Microsoft Windows[2]
Mac OS X[2]
PlayStation 3
Xbox 360Release date(s) October 9, 2007- Microsoft Windows and Xbox 360:
(The Orange Box retail)
- EU October 18, 2007
- AUS October 18, 2007
Steam October 9, 2007[5][6]
PlayStation 3:
Microsoft Windows:
(retail stand-alone):
Rest of WorldApril 11, 2008
Xbox Live Arcade:
October 22, 2008
Mac OS X:
May 12, 2010
Genre(s) Puzzle-platform game Mode(s) Single-player Rating(s) Media/distribution Optical disc, digital download System requirements Portal is a single-player first-person puzzle-platform sci fi video game developed by Valve Corporation. The game was released in a bundle package called The Orange Box for Microsoft Windows and Xbox 360 on October 9, 2007,[3][4] and for the PlayStation 3 on December 11, 2007.[7] The Windows version of the game is also available for download separately through Valve's content delivery system Steam[2] and was released as a standalone retail product on April 9, 2008.[9] A stand-alone version called Portal: Still Alive was released on the Xbox Live Arcade service on October 22, 2008; this version includes an additional 14 puzzles. A Mac OS X version was released as part of the Mac-compatible Steam platform on May 12, 2010.[11]
The game primarily comprises a series of puzzles that must be solved by teleporting the player's character and simple objects using "the handheld portal device", a device that can create inter-spatial portals between two flat planes. The player-character, Chell, is challenged by an artificial intelligence named GLaDOS (Genetic Lifeform and Disk Operating System) to complete each puzzle in the Aperture Science Enrichment Center using the portal gun with the promise of receiving cake when all the puzzles are completed. The game's unique physics allow momentum to be retained through portals, requiring creative use of portals to maneuver through the test chambers. This gameplay element is based on a similar concept from the game Narbacular Drop; many of the team members from the DigiPen Institute of Technology who worked on Narbacular Drop were hired by Valve for the creation of Portal.
Portal was acclaimed as one of the most original games of 2007, despite being considered short in length. The game received praise for its unique gameplay and darkly humorous story, created with the assistance of Erik Wolpaw and Chet Faliszek. It also received acclaim for the character of GLaDOS, voiced by Ellen McLain in the English-language version, and the end credits song "Still Alive" written by Jonathan Coulton for the game. Not counting sales through Steam, over four million copies of the game have been sold since its release. The game's popularity has led to official merchandise from Valve including plush Companion Cubes, as well as fan recreations of the cake and portal gun. A sequel, Portal 2, was released in 2011, adding several new gameplay mechanics and a cooperative multiplayer mode.[12]
Contents
Gameplay
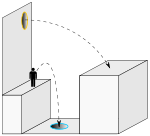
A representation of how the magnitude of linear momentum is conserved through portals. By jumping into the blue portal, the character is launched out of the orange portal and onto the platform on the right.In Portal, the player controls the protagonist, Chell, from a first-person perspective as she is challenged to navigate through a series of rooms using the Aperture Science Handheld Portal Device (portal gun or ASHPD). The portal gun can create two distinct portal ends, orange and blue. The portals create a visual and physical connection between two different locations in three-dimensional space. Neither end is specifically an entrance or exit; all objects that travel through one portal will exit through the other. An important aspect of the game's physics is momentum redirection.[13] As moving objects pass through portals, they come through the exit portal at the same direction as the exit portal is facing and with the same speed with which they passed through the entrance portal.[14] For example, a common maneuver is to jump down to a portal on the floor and emerge through a wall, flying over a gap or another obstacle. This allows the player to launch objects or Chell herself over great distances, both vertically and horizontally, referred to as 'flinging' by Valve.[13] As GLaDOS puts it, "In layman's terms: speedy thing goes in, speedy thing comes out". If portal ends are not on parallel planes, the character passing through is reoriented to be upright with respect to gravity after leaving a portal end.
Chell and all other objects in the game that can fit into the portal ends will pass through the portal. However, a portal shot cannot pass through an open portal; it will simply fail or create a new portal in an offset position. If a portal of the same color as an existing one is created, the previous portal is destroyed. Moving objects, glass, special wall surfaces, liquids, or areas that are too small will not accommodate portals. Chell is sometimes provided with cubes that she can pick up and use to climb on or to hold down large buttons that open doors or activate mechanisms. Particle fields known as emancipation grills exist at the end of all and within some test chambers that, when passed through, close any open portals and disintegrate any object carried through. The fields also block attempts to fire portals through them.[15]
Although Chell is equipped with mechanized heel springs to prevent damage from falling,[13] she can be killed by various other hazards in the test chambers, such as turret guns, bouncing balls of energy, and toxic liquid. She can also be killed by objects falling through portals, and by a series of crushers that appear in certain levels. Unlike most action games, there is no visible amount of health; Chell dies if she is dealt a certain amount of damage in a short time period, but returns to full health fairly quickly. Some obstacles, such as the energy balls and crushing pistons, will deal this necessary amount of damage with a single blow, thus causing instant death.
The portal gun allows several possible approaches to completing the various test chambers. In its initial preview of Portal, GameSpot noted that many solutions exist for completing each puzzle, and that the gameplay "gets even crazier, and the diagrams shown in the trailer showed some incredibly crazy things that you can attempt."[16] Two additional modes are unlocked upon the completion of the game that challenge the player to work out alternative methods of solving each test chamber. Challenge maps are unlocked near the halfway point and Advanced Chambers are unlocked when the game is completed.[17] In Challenge mode, levels are revisited with the added goal of completing the test chamber either with as little time, with the least number of portals, or with the fewest footsteps possible. In Advanced mode, certain levels are made more complex with the addition of more obstacles and hazards.[18][19]
The PC, Xbox 360 and Mac OS X versions of the game also feature a number of Achievements the player can earn by completing tasks. Achievements range from normal gameplay requirements, such as obtaining the Aperture Science Handheld Portal Device, to various tricks, such as using portals to jump a particular distance. As with other Source engine games since Half-Life 2, Portal can be played with commentary enabled; special icons will appear in the game that the player can activate to hear how certain parts of the game were developed.
Synopsis
Characters
The game features two characters: the player-controlled silent protagonist named Chell, and GLaDOS (Genetic Lifeform and Disk Operating System), a computer artificial intelligence that monitors and directs the player. In the English-language version, GLaDOS is voiced by Ellen McLain, though her voice has been altered to sound more mechanical. The only background information presented about Chell is given by GLaDOS; the credibility of these facts, such as Chell being adopted, an orphan, and having no friends, is questionable at best, as GLaDOS is a liar by her own admission. In the "Lab Rat" comic created by Valve to bridge the gap between Portal and Portal 2, Chell's records reveal she was ultimately rejected as a test subject for having too much "tenacity", but was moved to the top of the test queue due to a "hunch" by Doug Rattman, a former employee of Aperture Science.[20][21]
Setting
Portal takes place in the Enrichment Center for Aperture Laboratories—also known as Aperture Science—which is the fictional research corporation responsible for the creation of the portal gun. According to information presented in Portal 2, the location of the complex is in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan. Information about the company, developed by Valve for creating the setting of the game, is revealed during the game and via the real-world promotional website.[22] According to the Aperture Science Web site, Cave Johnson founded the company in 1953 for the sole purpose of making shower curtains for the U.S. military. However, after becoming mentally unstable from mercury poisoning in 1978, Johnson created a three-tier research and development plan to make his organization successful. The first two tiers, the Counter-Heimlich Maneuver (a maneuver designed to ensure choking) and the Take-A-Wish Foundation (a program to give the wishes of dying children to unrelated, entirely healthy adults), were commercial failures and led to an investigation of the company by the U.S. Senate. However, when the investigative committee heard of the success of the third tier, a man-sized ad-hoc quantum tunnel through physical space with possible applications as a shower curtain, it recessed permanently and gave Aperture Science an open-ended contract to continue its research. The development of GLaDOS, an artificially intelligent research assistant and disk-operating system, began in 1986 in response to Black Mesa's work on similar portal technology.[23] A presentation seen during gameplay reveals that GLaDOS was also included in a proposed bid for de-icing fuel lines, incorporated as a fully functional disk-operation system that is arguably alive, unlike Black Mesa's proposal, which inhibits ice, nothing more.[24] Roughly thirteen years later, work on GLaDOS was completed and the untested AI was activated during the company's first ever bring-your-daughter-to-work day in May 200-.[22] Immediately after activation, the facility was flooded with deadly neurotoxin by the AI. Events of the first Half-Life game occur shortly thereafter, presumably leaving the facility forgotten by the outside world due to apocalyptic happenings. Wolpaw, in describing the ending of Portal 2, affirmed that the Combine invasion from Half-Life has occurred during Portal's events.[25]
The portions of the Aperture Science Enrichment Center that Chell explores suggest that it is part of a massive research installation. At the time of events depicted in Portal, the Aperture Science Enrichment Center facility seems to be long-deserted, although most of its equipment remains operational without human control.[26] Aperture Science exists in the Half-Life universe,[16][24] with the events of Portal occurring sometime between the story of Half-Life and Half-Life 2.[27] Aperture Science Inc. is also mentioned during Half-Life 2: Episode Two, in which the icebreaker ship Borealis, belonging to the corporation, is said to have disappeared under mysterious circumstances, along with the crew and part of its drydock. During its development, Half-Life 2 featured a chapter set on the Borealis, but this was abandoned and removed before release.[28]
Plot
Portal's plot is revealed to the player via audio messages from GLaDOS and side rooms found in the later levels. According to The Final Hours of Portal 2, the year is established to be "somewhere in 2010" — twelve years after its abandonment. The game begins with protagonist Chell waking up from a stasis bed and hearing instructions and warnings from GLaDOS about the upcoming test experience. This part of the game involves distinct test chambers that, in sequence, introduce players to the game's mechanics. GLaDOS's announcements serve not only to instruct Chell and help her progress through the game, but also to create atmosphere and develop the AI as a character.[13] Chell is promised cake and grief counseling as her reward if she manages to complete all the test chambers.[29]
Chell proceeds through the empty Enrichment Center, interacting only with GLaDOS. Over the course of the game, GLaDOS's motives are hinted to be more sinister than her helpful demeanor suggests. Although she is designed to appear helpful and encouraging, GLaDOS's actions and speech suggest insincerity and callous disregard for the safety and well-being of the test subjects. The test chambers become increasingly dangerous as Chell proceeds, and GLaDOS even directs Chell through a live-fire course designed for military androids as a result of "mandatory scheduled maintenance" in the regular test chamber. In another chamber, GLaDOS boasts about the fidelity and importance of the Weighted Companion Cube, a waist-high crate with a single large pink heart on each face, for helping Chell to complete the chamber. However, GLaDOS then declares that it "unfortunately must be euthanized" in an "emergency intelligence incinerator" before Chell can continue.[26] Some of the later chambers include automated turrets with child-like voices (also voiced by McLain) that fire at Chell, only to sympathize with her after being disabled ("I don't blame you" and "No hard feelings").[30][31]
After Chell completes the final test chamber, GLaDOS congratulates her and prepares her "victory candescence", maneuvering Chell into a pit of fire. As GLaDOS assures her that "all Aperture technologies remain safely operational up to 4,000 degrees [sic] kelvin", Chell escapes with the use of the portal gun and makes her way through the maintenance areas within the Enrichment Center.[32] GLaDOS becomes panicked and insists that she was only pretending to kill Chell, as part of testing. GLaDOS then asks Chell to assume the "party escort submission position", lying face-first on the ground, so that a "party associate" can take her to her reward. Chell, thinking that GLaDOS is trying to trick her into a vulnerable position, continues forward. Throughout this section, GLaDOS still sends messages to Chell and it becomes clear that she has become corrupt and may have killed everyone else in the center. Chell makes her way through the maintenance areas and empty office spaces behind the chambers, sometimes following graffiti messages which point in the right direction. These backstage areas, which are in an extremely dilapidated state, stand in stark contrast to the pristine test chambers. The graffiti includes statements such as "the cake is a lie" and pastiches of Emily Dickinson's poem "The Chariot," Henry Wadsworth Longfellow's "The Reaper and the Flowers," and Emily Brontë's "No Coward Soul Is Mine," mourning the death of the Companion Cube.[13]
GLaDOS attempts to dissuade Chell with threats of physical harm and misleading statements claiming that she is going the wrong way as Chell makes her way deeper into the maintenance areas. Eventually, Chell reaches a large chamber where GLaDOS's hardware hangs overhead. GLaDOS continues to plead with Chell, but during the exchange one of GLaDOS' personality core spheres falls off; Chell drops it in an incinerator. GLaDOS reveals that Chell has just destroyed the morality core, which the Aperture Science employees allegedly installed after GLaDOS flooded the enrichment center with a deadly neurotoxin, and goes on to state that now there is nothing to prevent her from doing so once again. A six-minute countdown starts as Chell dislodges and incinerates more pieces of GLaDOS, while GLaDOS attempts to discourage her both verbally with a series of taunts and increasingly juvenile insults and physically by firing rockets at Chell. After she has destroyed the final piece, a portal malfunction tears the room apart and transports everything to the surface. Chell is then seen lying outside the facility's gates amid the remains of GLaDOS. One of the final scenes is changed through a patch of the PC version that was made available a few days before Portal 2's announcement; in this retroactive continuity, Chell is dragged away from the scene by an unseen entity speaking in a robotic voice, thanking her for assuming the party escort submission position.[24][33]
The final scene, after a long and speedy zoom through the bowels of the facility, shows a mix of shelves surrounding a Black Forest cake[34] and the Weighted Companion Cube. The shelves contain dozens of other personality cores, some of which begin to light up before a robotic arm descends and extinguishes the candle on the cake.[35] As the credits roll, GLaDOS delivers a concluding report: the song "Still Alive", which declares the experiment to be a huge success.[36]
Development
System requirements Minimum Recommended Windows[2] Operating system Windows 7, Windows Vista, Windows XP, Windows 2000 CPU 1.7 GHz 3.0 GHz Memory 512 MB 1 GB Graphics hardware DirectX 8 video card DirectX 9 video card Network Internet Connection Mac[2] Operating system Leopard 10.5.8, Snow Leopard 10.6.3 Memory 1 GB Graphics hardware NVIDIA GeForce 8 / ATI X1600 or higher Network Internet Connection Concept
Portal is Valve's spiritual successor to the freeware game Narbacular Drop, the 2005 independent game released by students of the DigiPen Institute of Technology; the original Narbacular Drop team is now employed at Valve.[37][38] Valve had become interested in Narbacular Drop after seeing the game at DigiPen's annual career fair; Robin Walker, one of Valve's developers, saw the game at the fair, and later contacted the team, providing them with advice and offering them to show their game at Valve's offices. After their presentation, Valve's president Gabe Newell quickly offered the entire team jobs at Valve to develop the game further.[39] Newell later commented that he was impressed with the Digipen team as "they had actually carried the concept through", already having included the interaction between portals and physics, completing most of the work that Valve would have had to commit on their own.[39] Certain elements have been retained from Narbacular Drop, such as the system of identifying the two unique portal endpoints with the colors orange and blue. A key difference in the signature portal mechanic between the two games however is that Portal's portal gun cannot create a portal through an existing portal unlike in Narbacular Drop. The game's original setting, of a princess trying to escape a dungeon, was also dropped in favor of the Aperture Science approach.[39] Portal took approximately two years and four months to complete after the DigiPen team was brought into Valve,[40] and no more than ten people were involved with its development.[41] Portal writer Erik Wolpaw, who, along with fellow writer Chet Faliszek, was hired by Valve for the game, claimed that "Without the constraints, Portal would not be as good a game."[42]
The Portal team worked with Half-Life series writer Marc Laidlaw on fitting the game into the series' plot.[43] This was done, in part, due to the limited art capabilities of the small team; instead of creating new assets for Portal, they decided to tie the game to an existing franchise—Half-Life 2—to allow them to reuse the Half-Life 2 art assets.[24] Wolpaw and Faliszek were put to work on the dialogue for Portal.[38] The concept of a computer AI guiding the player through experimental facilities to test the portal gun was arrived at early in the writing process.[24] They drafted early lines for the yet-named "polite" AI with humorous situations, such as requesting the player's character to "assume the party escort submission position", and found this style of approach to be well-suited to the game they wanted to create, ultimately leading to the creation of the GLaDOS character.[24] GLaDOS was central to the plot, as Wolpaw notes "We designed the game to have a very clear beginning, middle, and end, and we wanted GLaDOS to go through a personality shift at each of these points."[44] Wolpaw further describes the idea of using cake as the reward came about as "at the beginning of the Portal development process, we sat down as a group to decide what philosopher or school of philosophy our game would be based on. That was followed by about 15 minutes of silence and then someone mentioned that a lot of people like cake."[24][44]
Design
 A typical Portal test chamber, with both of the player's colored portals opened. The Weighted Companion Cube can also be seen. The clean, spartan look to the chambers was influenced by the film The Island.
A typical Portal test chamber, with both of the player's colored portals opened. The Weighted Companion Cube can also be seen. The clean, spartan look to the chambers was influenced by the film The Island.
The austere settings in the game came about because testers spent too much time trying to complete the puzzles using decorative but non-functional elements. As a result, the setting was minimized to make the usable aspects of the puzzle easier to spot, using the clinical feel of the setting in the film The Island as reference.[45] While there were plans for a third area, an office space, to be included after the test chambers and the maintenance areas, the team ran out of time to include it.[45] They also dropped the introduction of the Rat Man, a character who left the messages in the maintenance areas, to avoid creating too much narrative for the game,[46] though the character was developed further in a tie-in comic "Lab Rat", that ties Portal and Portal 2's story together.[20][21] According to Swift, the final battle with GLaDOS went through many iterations, including having the player chased by James Bond lasers, which was partially applied to the turrets, Portal Kombat where the player would have needed to redirect rockets while avoiding turret fire, and a chase sequence following a fleeing GLaDOS. Eventually, they found that playtesters enjoyed a rather simple puzzle with a countdown timer near the end; Swift noted, "Time pressure makes people think something is a lot more complicated than it really is," and Wolpaw admitted, "It was really cheap to make [the neurotoxin gas]" in order to simplify the dialogue during the battle.[41]
Chell's face and body are modeled after Alésia Glidewell, an American freelance actress and voice-over artist, selected by Valve from a local modeling agency for her face and body structure.[40][47] Ellen McLain provided the voice of the antagonist GLaDOS. Erik Wolpaw noted, "When we were still fishing around for the turret voice, Ellen did a sultry version. It didn't work for the turrets, but we liked it a lot, and so a slightly modified version of that became the model for GLaDOS's final incarnation."[44] Mike Patton performed the growling and snarling voice of GLaDOS's final personality core, named the Anger Sphere.
The Weighted Companion Cube inspiration was from project lead Kim Swift with additional input from Wolpaw from reading some "declassified government interrogation thing" whereby "isolation leads subjects to begin to attach to inanimate objects";[41][44] Swift commented, "We had a long level called Box Marathon; we wanted players to bring this box with them from the beginning to the end. But people would forget about the box, so we added dialogue, applied the heart to the cube, and continued to up the ante until people became attached to the box. Later on, we added the incineration idea. The artistic expression grew from the gameplay."[45] Wolpaw further noted that the need to incinerate the Weighted Companion Cube came as a result of the final boss battle design; they recognized they had not introduced the idea of incineration necessary to complete the boss battle, and by training the player to do it with the Weighted Companion Cube, found the narrative "way stronger" with its "death".[48] Swift noted that reported psychological comparisons to both the Milgram experiment and 2001: A Space Odyssey are happenstance.[45]
The portal gun's full name, Aperture Science Handheld Portal Device, can be abbreviated as ASHPD, which resembles a shortening of the name Adrian Shephard, the protagonist of Half-Life: Opposing Force. This similarity was noticed by fans before the game's release; as a result, the team placed a red herring in the game by having the letters of Adrian Shephard highlighted on keyboards found within the game.[45] According to Kim Swift, the cake is a Black Forest cake that she thought looked the best at the nearby Regent Bakery and Café in Redmond, Washington, and, as an easter egg within the game, its recipe is scattered among various screens showing lines of binary code.[34][49] The Regent Bakery has stated that since the release of the game, its Black Forest cake has been one of its more popular items.[49]
Soundtrack
Most of the game's soundtrack is non-lyrical ambient music composed by Kelly Bailey and Mike Morasky, somewhat dark and mysterious to match the mood of the environments. The closing credits song, "Still Alive," was written by Jonathan Coulton and sung by Ellen McLain (a classically trained operatic soprano) as the GLaDOS character. Wolpaw notes that Coulton was invited to Valve a year before the release of Portal, though it was not yet clear where Coulton would contribute. "Once Kim [Swift] and I met with him, it quickly became apparent that he had the perfect sensibility to write a song for GLaDOS."[36][44] The song was released as a free downloadable song for the music video game Rock Band on April 1, 2008.[50][51][52] The soundtrack for Portal was released as a part of The Orange Box Original Soundtrack[53] and includes both GLaDOS's in-game rendition and Coulton's vocal mix of "Still Alive." A brief instrumental version done in an uptempo Latin style can be heard playing over radios in-game.
Merchandise
 The popularity of the Weighted Companion Cube has led Valve to create merchandise based on it, including fuzzy dice.
The popularity of the Weighted Companion Cube has led Valve to create merchandise based on it, including fuzzy dice.
The popularity of the game and of its characters has led Valve to develop merchandise for Portal made available through its online Steam store. Some of the more popular items were the Weighted Companion Cube plush toys and fuzzy dice.[54] When first released, both were sold out in under 24 hours.[55] Other products available through the Valve store include t-shirts and Aperture Science coffee mugs and parking stickers, and merchandise relating to the phrase the cake is a lie, which has become an internet meme. Wolpaw noted they did not expect certain elements of the game to be as popular as they were, while other elements they had expected to become fads were ignored, such as a giant hoop that rolls on-screen during the final scene of the game that the team had named Hoopy.[24]
Distribution
Demo
In January 2008, Valve released a special demo version titled Portal: The First Slice, free for any Steam user using Nvidia graphics hardware as part of a collaboration between the two companies.[56] It also comes packaged with Half-Life 2: Deathmatch, Peggle Extreme, and Half-Life 2: Lost Coast. The demo includes test chambers 00 to 10 (eleven in total). Valve has since made the demo available to all Steam users.[57]
Portal
Portal was first released as part of The Orange Box for Microsoft Windows and Xbox 360 on October 9, 2007,[3][4] and for the PlayStation 3 on December 11, 2007.[7] The Windows version of the game is also available for download separately through Valve's content delivery system Steam[2] and was released as a standalone retail product on April 9, 2008.[9] In addition to Portal, the Box also included Half-Life 2 and its two add-on episodes, as well as Team Fortress 2. Portal's inclusion within the Box was considered an experiment by Valve; having no idea of the success of Portal, the Box provided it a "safety net" via means of these other games. Portal was kept to a modest length in case the game did not go over well with players.[35] Since then, a standalone version of the game was released for Microsoft Windows users.
Portal was the first Valve-developed game to be added to the Mac OS X-compatible list of games available on the launch of the Steam client for Mac on May 12, 2010,[11] supporting Steam Play, in which players that had bought the game either on a Macintosh or Windows computer could also play it on the alternate system. As part of the promotion, Portal was offered as a free title for any Steam user during the two weeks following the Mac client's launch.[58] Within the first week of this offer, over 1.5 million copies of the game were downloaded through Steam.[59] A similar promotion was held in September 2011, near the start of a traditional school year, encouraging the use of the game as an educational tool for science and mathematics.[60][61] Valve wrote that they felt that Portal "makes physics, math, logic, spatial reasoning, probability, and problem-solving interesting, cool, and fun", a necessary feature to draw children into learning.[62] This was tied to Digital Promise, an United States Department of Education initiative to help develop new digital tools for education, and which Valve is part of.[63]
Portal: Still Alive
Portal: Still Alive was announced as an exclusive Xbox Live Arcade game at the 2008 E3 convention, and was released on October 22, 2008.[64] It features the original game, 14 new challenges, and new achievements.[65] The additional content was based on levels from the map pack "Portal: The Flash Version" created by We Create Stuff and contains no additional story-related levels.[66] According to Valve spokesman Doug Lombardi, Microsoft had previously rejected Portal on the platform due to its large size.[67] Portal: Still Alive was well-received by reviewers.[68] 1UP's Andrew Hayward stated that, with the easier access and lower cost than paying for The Orange Box, Portal is now "stronger than ever".[69] IGN editor Cam Shea ranked it fifth on his top 10 list of Xbox Live Arcade games. He stated that it was debatable whether an owner of The Orange Box should purchase this, as its added levels do not add to the plot. However, he praised the quality of the new maps included in the game.[70] The game ranked 7th in a later list of top Xbox Box Live titles compiled by IGN's staff in September 2010.[71]
Sequel
Main article: Portal 2Swift stated that future Portal developments would depend on the community's reactions, saying, "We're still playing it by ear at this point, figuring out if we want to do multiplayer next, or Portal 2, or release map packs."[18] Some rumors regarding a sequel arose due to casting calls for voice actors.[72][73] On March 10, 2010, Portal 2 was officially announced for a release late in that year;[74] the announcement was preceded by an alternate reality game based on unexpected patches made to Portal that contained cryptic messages in relation to Portal 2's announcement, including one that changed the fate of Chell at the end of the game. Though Portal 2 was announced for a Q4 2010 release, the game was eventually released on April 19, 2011.[33][75][76][77]
Critical reception
See also: Critical reception of The Orange BoxReception Aggregate scores Aggregator Score GameRankings 89.15%[78] Metacritic 90/100[79] Review scores Publication Score 1UP.com A[26] Eurogamer 9/10[30] GameSpot 9.0/10 GameSpy 4.5/5.0[29] IGN 8.2/10[31] Portal was very well-received by critics. It was a favorite of The Orange Box, often earning more praise than either Half-Life 2: Episode Two or Team Fortress 2. It was praised for its unique gameplay and dark, deadpan humor.[80] Eurogamer cited that "the way the game progresses from being a simple set of perfunctory tasks to a full-on part of the Half-Life story is absolute genius",[81] while GameSpy noted that "What Portal lacks in length, it more than makes up for in exhilaration."[82] The game was criticized for sparse environments, and both criticized and praised for its short length.[83] Aggregate reviews for the stand-alone PC version of Portal gave the game an average rating of 89% based on 27 reviews through Game Rankings,[78] and 90% through 28 reviews on Metacritic.[79] Upon release of Portal 2, Valve stated that Portal has sold more than four million copies through the retail versions, including the standalone game and The Orange Box, and from the Xbox Live Arcade version. This figure does not include sales figures for Valve's own Steam digital download service.[84]
The game also generated a fan-following for the Weighted Companion Cube[85]—even though the cube itself does not talk or act in the game. Fans have created plush[86] and papercraft versions of the cube and the various turrets,[87] as well as PC case mods[88] and models of the Portal cake and portal gun.[89][90][91] Jeep Barnett, a programmer for Portal, noted that players have told Valve that they had found it more emotional to incinerate the Weighted Companion Cube than to harm one of the "Little Sisters" from BioShock.[45] Both GLaDOS and the Weighted Companion Cube were nominated for the Best New Character Award on G4, with GLaDOS winning the award for "having lines that will be quoted by gamers for years to come."[92][93][94]
Portal's story has been stated to be well-established in the context of Erving Goffman's dissemination on dramaturgy, The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life, which equates one's persona to the front and back stage areas of a theater. In the case of Portal, the story carefully establishes the front stage, the pretense of the Enrichment Center, and hints at problems in the back stage through various technical faults, and then slowly reveals more and more of the back stage to the player throughout the game.[95] Due to this, the video game was made part of the required course material among other classical and contemporary works, including Goffman's work, for a freshman course "devoted to engaging students with fundamental questions of humanity from multiple perspectives and fostering a sense of community" for Wabash College in 2010.[96][97] Portal has also been cited as a strong example of instructional scaffolding that can be adapted for more academic learning situations, as the player, through careful design of levels by Valve, is first hand-held in solving simple puzzles with many hints at the correct solution, but this support is slowly removed as the player progresses in the game, and completely removed when the player reaches the second half of the game.[98] Portal will also be exhibited at the Smithsonian Art Exhibition in America. Portal won the "Action" section for the platform "Modern Windows."[99]
Mods and ports
A modding community has developed around Portal with users creating their own test chambers and other in-game modifications.[100][101] The group "We Create Stuff" created an Adobe Flash version of Portal, entitled Portal: The Flash Version, just prior to release of The Orange Box that was well received by the community[102] which they have since converted to a map pack for the published game.[103] Many of the levels in this map pack have been incorporated into the standalone Xbox Live Arcade game Portal: Still Alive. Another map pack, Portal: Prelude, is an unofficial prequel developed by an independent team of three that focuses on the pre-GLaDOS era of Aperture Science, and contains nineteen additional "crafty and challenging" test chambers.[104][105] An ASCII version of Portal was created by Joe Larson.[106][107] An unofficial port of Portal to the iPhone using the Unity game engine was created but only consisted of a single room from the game.[108][109]
Awards
Portal has won several awards:
- At the 2008 Game Developers Choice Awards, Portal won Game of the Year, along with the Innovation Award and Best Game Design.[110]
- IGN.com honored Portal with several awards, for Best Puzzle Game for PC[111] and Xbox 360,[112] Most Innovative Design for PC,[113] and Best End Credit Song (for "Still Alive") for Xbox 360,[114] along with overall honors for Best Puzzle Game[115] and Most Innovative Design.[116]
- In its Best of 2007, GameSpot honored The Orange Box with 4 awards in recognition of Portal, giving out honors for Best Puzzle Game,[117] Best New Character(s) (for GLaDOS),[118] Funniest Game,[119] and Best Original Game Mechanic (for the portal gun).[120]
- Portal was awarded Game of the Year (PC), Best Narrative (PC), and Best Innovation (PC and console) honors by 1UP.com in its 2007 editorial awards.[121]
- GamePro honored the game for Most Memorable Villain (for GLaDOS) in its Editors' Choice 2007 Awards.[122]
- Portal was awarded the Game of the Year award in 2007 by Joystiq,[123] Good Game,[124] and Shacknews.[125]
- The Most Original Game award by X-Play.[126]
- In Official Xbox Magazine's 2007 Game of the Year Awards, Portal won Best New Character (for GLaDOS), Best Original Song (for "Still Alive"), and Innovation of the Year.[127]
- In GameSpy's 2007 Game of the Year awards, Portal was recognized as Best Puzzle Game,[128] Best Character (for GLaDOS), and Best Sidekick (for the Weighted Companion Cube).[128]
- A.V. Club called it the Best Game of 2007.[129]
- The Web comic Penny Arcade awarded Portal Best Soundtrack, Best Writing, and Best New Game Mechanic in its satirical 2007 We're Right Awards.[130]
- Eurogamer gave Portal first place in its Top 50 Games of 2007 rankings.[131]
- IGN.com also placed GLaDOS, (from Portal) as the #1 Video Game Villain on its Top-100 Villains List.[132]
- Gamesradar named it the best game of all time.[133]
Wired considered Portal to be one of the most influential games of the first decade of the 21st century, believing it to be the prime example of quality over quantity for video games.[134]
See also
- Narbacular Drop
- Portals in fiction
- Portal 2
References
- Footnotes
- ^ "Portal Update Released". Steam. Valve Corporation. http://store.steampowered.com/news/4639/. Retrieved 2011-08-02.
- ^ a b c d e f "Portal". Steam. Valve Corporation. http://store.steampowered.com/app/400/. Retrieved 2010-08-11.
- ^ a b c "The Orange Box (PC)". Metacritic. http://www.metacritic.com/games/platforms/pc/halflife2theorangebox?q=The%20Orange%20Box. Retrieved 2008-02-25.
- ^ a b c "The Orange Box (Xbox 360)". Metacritic. http://www.metacritic.com/games/platforms/xbox360/halflife2theorangebox?q=The%20Orange%20Box. Retrieved 2008-02-25.
- ^ "Pre-Purchase The Orange Box, Play Team Fortress 2 Next Week". Steam. Valve. 2007-09-06. http://store.steampowered.com/news/1186/. Retrieved 2010-08-11.
- ^ "Valve Uncrates The Orange Box". Steam. Valve. 2007-10-10. http://store.steampowered.com/news/1237/. Retrieved 2010-08-11.
- ^ a b c "The Orange Box (PS3)". Metacritic. http://www.metacritic.com/games/platforms/ps3/halflife2theorangebox?q=The%20Orange%20Box. Retrieved 2008-02-25.
- ^ "IGN The Orange Box (PS3)". IGN. http://au.ps3.ign.com/objects/743/743925.html. Retrieved 2008-03-29.
- ^ a b c Kiestmann, Ludwig (2008-03-06). "Individual Orange Box games hit retail April 9". Joystiq. http://www.joystiq.com/2008/03/05/individual-orange-box-games-hit-retail-april-9/. Retrieved 2008-03-06.
- ^ VALVE (2008-04-14). "Classification Database - PORTAL (M)". Classification.gov.au. http://www.classification.gov.au/www/cob/find.nsf/5c2433d416948a0bca25759f00820d25/660d1c735dac8c89ca25767100785fe4!OpenDocument. Retrieved 2010-08-23.[dead link]
- ^ a b Hollister, Sean (2010-04-29). "Steam for Mac Opens a Portal to May 12, steps through". Engadget. http://www.engadget.com/2010/04/29/steam-for-mac-opens-a-portal-to-may-12-steps-through/. Retrieved 2010-05-11.
- ^ "Portal 2 delay sarcastically confirmed by Valve". Inquisitr.com. 2010-11-19. http://www.inquisitr.com/90702/portal-2-delay-sarcastically-confirmed-by-valve/. Retrieved 2010-11-19.
- ^ a b c d e Valve Corporation. (In-game developer commentary) Portal. 2007.
- ^ Alessi, Jeremy (2008-08-26). "Games Demystified: Portal". Gamasutra. http://www.gamasutra.com/view/feature/3770/games_demystified_portal.php. Retrieved 2008-08-28.
- ^ The Orange Box manual (Xbox 360 version). Valve Corporation. 2007. pp. 12–17.
- ^ a b Ocampo, Jason (2006-07-13). "Half-Life 2: Episode Two — The Return of Team Fortress 2 and Other Surprises". GameSpot. http://gamespot.com/pc/action/halflife2episode2/news.html?sid=6154006. Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- ^ Craddock, David (2007-10-03). "Portal: Final Hands-on". IGN. http://au.pc.ign.com/articles/824/824756p2.html. Retrieved 2007-10-05.
- ^ a b Bramwell, Tom (2007-05-15). "Portal: First Impressions". Eurogamer. http://www.eurogamer.net/article.php?article_id=76374&page=2. Retrieved 2007-10-05.
- ^ Francis, Tom (2007-05-09). "PC Preview: Portal— PC Gamer Magazine". ComputerAndVideoGames.com. http://www.computerandvideogames.com/article.php?id=162968. Retrieved 2007-10-05.
- ^ a b Esposito, Joey (2011-04-08). "Portal 2: Lab Rat - Part 1". IGN. http://comics.ign.com/articles/116/1160605p1.html. Retrieved 2011-04-11.
- ^ a b Esposito, Joey (2011-04-11). "Read Portal 2: Lab Rat - Part 2". IGN. http://comics.ign.com/articles/116/1161043p1.html. Retrieved 2011-04-11.
- ^ a b VanBurkleo, Meagan (2010-03-24). "Aperture Science: A History". Game Informer. http://gameinformer.com/b/features/archive/2010/03/24/Aperture-Science_3A00_-A-History.aspx. Retrieved 2010-03-24.
- ^ "Aperture Science Web Site (login: cjohnson password: tier3)". Valve. http://www.aperturescience.com.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Reeves, Ben (2010-03-10). "Exploring Portal’s Creation And Its Ties To Half-Life 2". Game Informer. http://gameinformer.com/b/features/archive/2010/03/10/opening-the-portal-exploring-portal-s-creation-and-its-ties-to-half-life-2.aspx. Retrieved 2010-03-10.
- ^ Stanton, Rich (2011-04-26). "Erik Wolpaw on Portal 2’s ending: "the [spoiler] is probably lurking out there somewhere"". PC Gamer. http://www.pcgamer.com/2011/04/26/erik-wolpaw-on-portal-2s-ending-the-spoiler-is-probably-lurking-out-there-somewhere/. Retrieved 2011-04-26.
- ^ a b c Elliot, Shawn (2007-10-10). "Portal (PC)". 1UP. http://www.1up.com/do/reviewPage?cId=3163578. Retrieved 2008-08-03.
- ^ Totilo, Stephan (2011-03-11). "Valve Plans To Bridge Portal And Portal 2 With A Surprise, Keep Gordon Freeman Out Of It". Kotaku. http://kotaku.com/5781121/valve-plans-to-bridge-portal-and-portal-2-with-a-surprise-keep-gordon-freeman-out-of-it. Retrieved 2011-03-11.
- ^ Valve Corp. (2004). Raising the Bar. Roseville: Prima Games. p. 117. ISBN 0-7615-4364-3. http://www.worldcat.org/oclc/57189955.
- ^ a b Accardo, Sal (2007-10-09). "Portal (PC)". Gamespy. http://pc.gamespy.com/pc/portal/826434p1.html. Retrieved 2008-02-25.
- ^ a b Bradwell, Tom (2007-10-10). "Portal". Eurogamer. http://www.eurogamer.net/article.php?article_id=85005. Retrieved 2008-02-25.
- ^ a b Adams, Dan (2007-10-09). "Portal Review". IGN. http://pc.ign.com/articles/825/825987p1.html. Retrieved 2008-02-25.
- ^ Montfort, Nick (2009). "Portal of Ivory, Passage of Horn". In Drew Davidson et al.. Well Played 1.0: Video Game, Value and Meaning. ETC Press. ISBN 978-0-557-06975-0. http://www.etc.cmu.edu/etcpress/content/portal-passage-nick-montfort.
- ^ a b Faylor, Chris (2010-03-03). "Portal Mystery Deepens with Second Update". Shacknews. http://www.shacknews.com/onearticle.x/62622. Retrieved 2010-03-03.
- ^ a b Geoff, Keighley (2008-03-01). "GameTrailers Episode 106". GameTrailers.com. http://www.gametrailers.com/gametrailerstv_player.php?ep=10&sd=1&ch=4. Retrieved 2008-03-25.
- ^ a b VanBurkleo, Meagan (April 2010). "Portal 2". Game Informer: pp. 50–62.
- ^ a b Coulton, Jonathan (2007-10-15). "Portal: The Skinny". Jonathan Coulton's blog. http://www.jonathancoulton.com/2007/10/15/portal-the-skinny/. Retrieved 2007-11-01.
- ^ "Things are heating up!". Narbacular Drop official site. 2006-07-17. Archived from the original on 2007-09-28. http://web.archive.org/web/20070928221628/http://www.nuclearmonkeysoftware.com/news.html?46. Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- ^ a b Berghammer, Billy (2006-08-25). "GC 06:Valve's Doug Lombardi Talks Half-Life 2 Happenings". Game Informer. Archived from the original on 2007-10-02. http://web.archive.org/web/20071002110610/http://www.gameinformer.com/News/Story/200608/N06.0825.1923.12789.htm. Retrieved 2007-09-27.
- ^ a b c Dudley, Breir (2011-04-17). "'Portal' backstory a real Cinderella tale". Seattle Times. http://seattletimes.nwsource.com/html/businesstechnology/2014794592_brier18.html. Retrieved 2011-04-17.
- ^ a b Pratt (2007-09-30). "Pratt and Chief interview the Portal team at VALVe headquarters". Planet Half-Life. http://planethalflife.gamespy.com/View.php?view=Interviews.Detail&id=80. Retrieved 2008-02-07.
- ^ a b c Faylor, Chris (2008-02-23). "GDC 08: Portal Creators on Writing, Multiplayer, Government Interrogation Techniques". Shacknews. http://www.shacknews.com/featuredarticle.x?id=784. Retrieved 2008-02-23.
- ^ Irwin, Mary Jane (2008-02-23). "GDC: A Portal Postmortem". Next-Gen Biz. http://www.next-gen.biz/news/gdc-portal-postmortem. Retrieved 2008-02-26.
- ^ Leone, Matt (2006-09-08). "Portal Preview". 1UP.com. http://www.1up.com/do/previewPage?pager.offset=0&cId=3153489. Retrieved 2006-09-11.
- ^ a b c d e Walker, John (2007-10-31). "RPS Interview: Valve's Erik Wolpaw". Rock, Paper, Shotgun. http://www.rockpapershotgun.com/?p=518. Retrieved 2007-10-31.
- ^ a b c d e f Elliot, Shawn (2008-02-06). "Beyond the Box: Orange Box Afterthoughts". 1UP. http://www.1up.com/do/feature?cId=3165930. Retrieved 2008-02-14.
- ^ McWhertor, Michael (2008-02-23). "Portal Devs Reveal the GLaDOS That Never Was, Inspiration Behind Weighted Companion Cube". Kotaku. http://kotaku.com/359961/portal-devs-reveal-the-glados-that-never-was-inspiration-behind-weighted-companion-cube. Retrieved 2008-02-26.
- ^ Glidewell, Alésia. "On-Camera — Alésia Glidewell — Voice Over Artist". AlesiaGlidewell.com. http://www.alesiaglidewell.com/oncamera.php. Retrieved 2008-04-13.
- ^ Graff, Kris (2009-11-02). "Valve's Writers And The Creative Process". Gamasutra. http://www.gamasutra.com/view/feature/4151/valves_writers_and_the_creative_.php?page=1. Retrieved 2009-11-02.
- ^ a b VanBurkleo, Meagan (2010-03-31). "Let There Be Cake". Game Informer. http://gameinformer.com/b/features/archive/2010/03/31/Let-There-Be-Cake.aspx. Retrieved 2010-03-31.
- ^ Baptiste, Sean (2008-02-21). "Valve Party at GDC + Special Preview of an Upcoming DLC Song". Harmonix. Archived from the original on 2008-02-25. http://web.archive.org/web/20080225131915/http://www.rockband.com/rockers_blog_entry/hmxsean/216671?redir=1. Retrieved 2008-02-21.
- ^ Baptiste, Sean. "DLC April 1st! Huge success!". Rockband.com forums. http://www.rockband.com/forums/showthread.php?t=40092. Retrieved 2008-03-31.
- ^ Faylor, Chris (2008-03-31). "'Still Alive' Hits Rock Band X360 Tomorrow for Free, PlayStation 3 Edition Due Mid-April". Shacknews. http://www.shacknews.com/onearticle.x/51991. Retrieved 2008-03-31.
- ^ "The Orange Box Original Soundtrack". Valve Corporation. Archived from the original on December 25, 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20071225055453/http://store.valvesoftware.com/productshowcase/productshowcase_TOBSoundtrack.html. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ "Steam Updates: Friday, November 9, 2007". Valve. 2007-11-09. http://www.steampowered.com/Steam/Marketing/message/1301/. Retrieved 2007-11-09.
- ^ De Marco, Flynn (2007-12-15). "Official Plush Weighted Companion Cube Sells Out". Kotaku. http://kotaku.com/gaming/sold-out/official-plush-weighted-companion-cube-sells-out-334413.php. Retrieved 2008-02-21.
- ^ "Valve and NVIDIA Offer Portal: First Slice Free to GeForce Users". Steam. Valve. 2008-01-09. http://store.steampowered.com/news/1398/. Retrieved 2010-08-11.
- ^ "Everyday Shooter Makes PC Debut on Steam Today". Valve. 2008-05-08. http://store.steampowered.com/news/1570/. Retrieved 2008-05-15. "In other Steam news, Portal: First Slice -- the official demo for the title named Game of the Year by over 30 publications -- is now available for free to all gamers via Steam."
- ^ Caolli, Eric (2010-05-12). "Steam Launched For Mac, Portal Offered For Free". Gamasutra. http://www.gamasutra.com/view/news/28529/Steam_Launched_For_Mac_Portal_Offered_For_Free.php. Retrieved 2010-05-13.
- ^ Remo, Chris (2010-05-19). "Portal Racks Up 1.5M Free Downloads On PC, Mac". Gamasutra. http://www.gamasutra.com/view/news/28626/Portal_Racks_Up_15M_Free_Downloads_On_PC_Mac.php. Retrieved 2010-05-19.
- ^ Purchase, Robert (2011-09-16). "Portal free on Steam until 20th Sept". Eurogamer. http://www.eurogamer.net/articles/2011-09-16-portal-free-on-steam-until-20th-sept. Retrieved 2011-09-16.
- ^ "Learn With Portals". learningwithportals.com. Valve Corporation. 2011-09-15. http://www.learningwithportals.com. Retrieved 2011-09-16.
- ^ Kuchera, Ben (2011-09-16). "Portal is used to teach science as Valve gives game away for limited time". Ars Technica. http://arstechnica.com/gaming/news/2011/09/portal-is-used-to-teach-science-as-valve-gives-game-away-for-limited-time.ars. Retrieved 2011-09-16.
- ^ Toppo, Greg (2011-09-19). "Valve teams with White House in digital learning program". USA Today. http://content.usatoday.com/communities/gamehunters/post/2011/09/valve-teams-with-white-house-in-digital-learning-program/1. Retrieved 2011-09-20.
- ^ Faylor, Chris (2008-10-16). "Portal: Still Alive Hits Xbox Live Arcade Next Wed; Promises Cake and Companionship". Shacknews. http://www.shacknews.com/onearticle.x/55376. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ^ Faylor, Chris (2008-07-14). "Portal: Still Alive Coming Exclusively to Xbox 360". Shacknews. http://www.shacknews.com/onearticle.x/53605. Retrieved 2008-07-14.
- ^ Remo, Chris (2008-07-20). "Portal: Still Alive Explained". GameSetWatch. http://www.gamesetwatch.com/2008/07/portal_still_alive_explained_1.php. Retrieved 2008-07-21.
- ^ Lee, James (2008-04-28). "Portal was offered to XBLA, but rejected". GamesIndustry.biz. http://www.gamesindustry.biz/articles/portal-was-offered-to-xbla-but-rejected. Retrieved 2008-06-14.
- ^ "Portal: Still Alive (xbox360: 2008)". MetaCritic. http://www.metacritic.com/games/platforms/xbox360/portalstillalive. Retrieved 2008-10-27.
- ^ Hayward, Andrew (2008-10-27). "Portal: Still Alive (Xbox 360)". 1UP. http://www.1up.com/do/reviewPage?cId=3170852&p=4. Retrieved 2008-10-27.
- ^ "IGN's Top 10 Xbox Live Arcade Games". IGN. 2009-05-07. http://xbox360.ign.com/articles/980/980538p1.html. Retrieved 2009-08-07.
- ^ "The Top 25 Xbox Live Arcade Games". IGN. 2010-09-16. http://xboxlive.ign.com/articles/112/1120887p1.html. Retrieved 2010-09-16.
- ^ Plunkett, Luke (2008-06-10). "Casting call reveals Portal 2 details". Kotaku. http://kotaku.com/5014851/rumor-casting-call-reveals-portal-2-details. Retrieved 2008-07-18.
- ^ Plunkett, Luke (2008-06-10). "More details on Portal 2's bad guy". Kotaku. http://kotaku.com/5015122/more-details-on-portal-2s-bad-guy. Retrieved 2008-07-18.
- ^ Webster, Andrew (2010-03-05). "Portal 2 is official, first image inside". Ars Technica. http://arstechnica.com/gaming/news/2010/03/portal-2-is-official-first-image-inside.ars. Retrieved 2010-03-05.
- ^ Leahy, Brian (2010-03-01). "Portal Patch Adds Morse Code, Achievement - Portal 2 Speculation Begins". Shacknews. http://www.shacknews.com/onearticle.x/62575. Retrieved 2010-03-02.
- ^ Mastrapa, Gus (2010-03-02). "Geeky Clues Suggest Portal Sequel Is Coming". Wired. http://www.wired.com/gamelife/2010/03/portal-viral/. Retrieved 2010-03-02.
- ^ Gaskill, Jake (2010-03-03). "Rumor: Valve To Make Portal 2 Announcement During GDC 2010". X-Play. http://g4tv.com/thefeed/blog/post/702963/Rumor-Valve-To-Make-Portal-2-Announcement-During-GDC-2010.html. Retrieved 2010-03-03.
- ^ a b "Portal Reviews (PC)". Game Rankings. http://www.gamerankings.com/htmlpages2/934386.asp. Retrieved 2009-07-05.
- ^ a b "Portal (pc: 2007): Reviews". Metacritic. http://www.metacritic.com/games/platforms/pc/portal. Retrieved 2007-10-22.
- ^ Keil, Matt. "G4 Review — The Orange Box". G4TV. http://www.g4tv.com/xplay/reviews/1629/The_Orange_Box.html. Retrieved 2007-10-19.
- ^ Reed, Kristen (2007-10-10). "The Orange Box". Eurogamer. http://www.eurogamer.net/article.php?article_id=85044. Retrieved 2008-02-14.
- ^ McGarvey, Sterline (2007-10-10). "The Orange Box (X360)". GameSpy. http://xbox360.gamespy.com/xbox-360/half-life-2/826174p1.html. Retrieved 2008-02-14.
- ^ Adams, Dan. "IGN: Portal Review". IGN. http://pc.ign.com/articles/825/825987p2.html. Retrieved 2007-10-19.
- ^ Rose, Mike (2011-04-20). "Portal Sells 4 Million Excluding Steam Sale". Gamasutra. http://www.gamasutra.com/view/news/34204/Portal_Sells_4_Million_Excluding_Steam_Sales.php. Retrieved 2011-04-20.
- ^ Alexander, Leigh (2007-12-19). "Gamasutra's Best Of 2007: Top 5 Poignant Game Moments". Gamasutra. http://www.gamasutra.com/php-bin/news_index.php?story=16712. Retrieved 2007-12-19.
- ^ Jetlogs (2007-10-29). "Companion Cube Plushie Sewing Pattern". Jetlogs. http://jetlogs.org/2007/10/29/companion-cube-plushie-sewing-pattern. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ Jetlogs (2007-10-14). "Portal: Weighted Companion Cube Papercraft". Jetlogs. http://jetlogs.org/2007/10/14/weighted-companion-cube-papercraft/. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ Persson, Magnus (2008-01-28). "Weighted Companion Cube PC case mods.". Bit-tech.net. http://www.bit-tech.net/modding/2008/01/21/the_weighted_companion_pc/1. Retrieved 2008-02-25.
- ^ Lizzie (2008-01-01). "How to Make a Weighted Companion Cube Cake". http://carina.org.uk/WeightedCompanionCubeCake.shtml. Retrieved 2008-02-07.
- ^ de Marco, Flynn (2007-10-21). "The Weighted Companion Cube Cake". Kotaku. http://kotaku.com/gaming/cake/the-weighted-companion-cube-cake-313286.php. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ Cavali, Earnest (2009-01-21). "Fan Crafts Gorgeous Replica Portal Gun". Wired. http://www.wired.com/gamelife/2009/01/portal-fans-cra/. Retrieved 2010-05-20.
- ^ "Winners of X-Play Best of 2007 Awards Announced—BioShock is Video Game of the Year". G4TV. 2007-12-17. http://www.g4tv.com/g4/press/200/Winners_of_XPlay_Best_of_2007_Awards_Announced__BioShock_is_Videogame_of_the_Year.html. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ Neuls, Johnathan (2007-11-12). "Valve to sell official Weighted Companion Cube plushies". Ars Technica. http://arstechnica.com/journals/thumbs.ars/2007/11/12/in-the-event-that-the-weighted-companion-cube-does-speak-please-give-it-a-hug. Retrieved 2008-04-18.
- ^ Kurchera, Ben (2008-01-02). "Kiss Me, Kill Me, Thrill Me: ups and downs in gaming 2007". Ars Technica. http://arstechnica.com/reviews/hardware/2007-games-review.ars/3. Retrieved 2008-04-18.
- ^ Johnson, Daniel (2009-06-01). "Column: 'Lingua Franca' – Portal and the Deconstruction of the Institution". GameSetWatch. http://www.gamesetwatch.com/2009/06/column_lingua_franca_portal_an.php. Retrieved 2009-06-01.
- ^ Goldman, Tom (2010-08-22). "College Professor Requires Students to Study Portal". The Escapist. http://www.escapistmagazine.com/news/view/102951-College-Professor-Requires-Students-to-Study-Portal. Retrieved 2010-08-22.
- ^ Klepek, Patrick (2011-05-18). "Intro to GLaDOS 101: A Professor's Decision to Teach Portal". Giant Bomb. http://www.giantbomb.com/news/intro-to-glados-101-a-professors-decision-to-teach-portal/3206/. Retrieved 2011-05-18.
- ^ Schiller, Nicholas (2008) (PDF). A Portal to Student Learning: What Instruction Librarians can Learn from Video Game Design. http://research.wsulibs.wsu.edu:8080/dspace/handle/2376/1468. Retrieved 2009-06-25.
- ^ [1]
- ^ Zitron, Ed (2008-01-05). "Portal Maps Investigated". CVG. http://www.computerandvideogames.com/article.php?id=178414. Retrieved 2008-01-05.
- ^ "Thinking With Portals". ThinkingWithPortals.com. http://www.thinkingwithportals.com/. Retrieved 2008-06-21.
- ^ Peckham, Matt (2007-10-11). "Portal: The Flash Version". PC World. http://blogs.pcworld.com/gameon/archives/005669.html. Retrieved 2008-05-05.
- ^ Breckon, Nick (2008-05-05). "Flash Version of Portal Converted to Actual Map Pack". Shacknews. http://www.shacknews.com/onearticle.x/52522. Retrieved 2008-05-05.
- ^ Cavalli, Earnest (2008-10-08). "Portal: Prelude Now Available". Wired. http://blog.wired.com/games/2008/10/portal-prelude.html. Retrieved 2008-10-09.
- ^ Phillips, John (2009-09-22). "Portal: Prelude". Gamespy. http://planethalflife.gamespy.com/View.php?view=Reviews.Detail&id=65. Retrieved 2008-12-18.
- ^ Plunkett, Luke (2009-07-08). "It's Portal, Running In ASCII". Kotaku. http://kotaku.com/5309667/its-portal-running-in-ascii. Retrieved 2009-07-16.
- ^ Larson, Joseph (2011-01-12). "ASCIIportal". Joesph Larson. http://cymonsgames.com/asciiportal. Retrieved 2011-01-12.
- ^ Spenser, Spanner (2009-07-15). "Valve's Portal opened on the iPhone". Pocket Gamer. http://www.pocketgamer.co.uk/r/iPhone/Portal/news.asp?c=14397. Retrieved 2009-07-16.
- ^ Boyer, Brandon (2009-07-16). "Chell's bells: Portal on the iPhone". Boing Boing Offworld. http://www.offworld.com/2009/07/chells-bells-portal-on-the-iph.html. Retrieved 2009-07-17.
- ^ "Portal BioShocks GDC Awards". GameSpot. http://uk.gamespot.com/news/6186460.html?action=convert&om_clk=latestnews&tag=latestnews;title;3. Retrieved 2008-02-21.
- ^ "IGN Best of 2007: PC Best Puzzle Game". IGN.com. http://bestof.ign.com/2007/pc/7.html. Retrieved 2008-02-18.
- ^ "IGN Best of 2007: Xbox 360 - Best Puzzle Game". IGN.com. http://bestof.ign.com/2007/xbox360/5.html. Retrieved 2008-02-18.
- ^ "IGN Best of 2007: PC — Most Innovative Design". IGN.com. http://bestof.ign.com/2007/pc/18.html. Retrieved 2008-02-18.
- ^ "IGN Best of 2007: Xbox 360 - Best End Credit Song". IGN.com. http://bestof.ign.com/2007/xbox360/13.html. Retrieved 2007-12-26.
- ^ "IGN Best of 2007: Overall — Best Puzzle Game". IGN.com. http://bestof.ign.com/2007/overall/7.html. Retrieved 2008-02-18.
- ^ "IGN Best of 2007: Overall — Most Innovative Design". IGN.com. http://bestof.ign.com/2007/overall/21.html. Retrieved 2008-02-18.
- ^ "GameSpot's Best of 2007: Best Puzzle Game Genre Awards". GameSpot. http://www.gamespot.com/best-of/genreawards/index.html?page=8. Retrieved 2008-02-18.
- ^ "GameSpot's Best of 2007: Best New Character(s) Special Achievement". GameSpot. http://www.gamespot.com/best-of/specialachievement/index.html?page=11. Retrieved 2008-02-18.
- ^ "GameSpot's Best of 2007: Funniest Game Special Achievement". GameSpot. http://www.gamespot.com/best-of/specialachievement/index.html?page=12. Retrieved 2008-02-18.
- ^ "GameSpot's Best of 2007: Best Original Game Mechanic Special Achievement". GameSpot. http://www.gamespot.com/best-of/specialachievement/index.html?page=16. Retrieved 2008-02-18.
- ^ "2007 1UP Network Editorial Awards from 1UP.com". 1UP.com. http://www.1up.com/do/feature?cId=3165432. Retrieved 2008-02-18.
- ^ The GamePros (2007-12-27). "GamePro Editors' Choice *2007* (Pg. 2/5)". GamePro. http://www.gamepro.com/gamepro/domestic/games/features/154428.shtml. Retrieved 2008-02-18.
- ^ Kietzmann, Ludwig (2008-01-01). "Joystiq's Top 10 of 2007: Portal". Joystiq. http://www.joystiq.com/2008/01/01/game-of-the-year-portal/. Retrieved 2008-02-18.
- ^ "Game of the Year". Good Game Stories. 2007-12-12. http://www.abc.net.au/tv/goodgame/stories/s2115530.htm. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ Shack Staff (2008-01-04). "Game of the Year Awards 2007". Shacknews. http://www.shacknews.com/featuredarticle.x?id=725. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ "X-Play Best of 2007: Most Original Game". G4. 2007-12-18. http://www.g4tv.com/xplay/videos/19476/Best_of_2007_Most_Original_Game.html?videoCategory_key=8. Retrieved 2008-02-25.
- ^ "OXM's 2007 Game of the Year Awards". Official Xbox Magazine. 2008-03-17. http://www.oxmonline.com/article/features/mag/oxm-2007-game-year-awards?page=0%2C0. Retrieved 2008-03-21.
- ^ a b "GameSpy's Game of the Year 2007: Special Awards". GameSpy. http://goty.gamespy.com/2007/special/29.html. Retrieved 2008-04-06.
- ^ Dahlen, Chris; Mastrapa, Gus (2007-12-24). "A. V. Club Best Games of 2007". A. V. Club. http://www.avclub.com/content/feature/best_games_of_2007. Retrieved 2007-12-24.
- ^ "Penny Arcade! We're Right Returns". Penny Arcade. 2007-12-28. http://www.penny-arcade.com/comic/2007/12/28. Retrieved 2007-12-28.
- ^ "Eurogamer's Top 50 Games of 2007". Eurogamer. http://www.eurogamer.net/article.php?article_id=89793&page=3. Retrieved 2008-01-01.
- ^ "IGN's top 100 villains". IGN. http://video.ign.com/dor/articles/1089926/igns-1-videogame-villain/videos/top10villain_spc_051410.html. Retrieved 2010-05-18.
- ^ GamesRadar US & UK (2011-03-31). "The 100 best games of all time". GamesRadar. p. 12. http://www.gamesradar.com/f/the-100-best-games-of-all-time/a-20110330182119708031/p-12. Retrieved 2011-04-01.
- ^ Kohler, Chris (2009-12-24). "The 15 Most Influential Games of the Decade". Wired. http://www.wired.com/gamelife/2009/12/the-15-most-influential-games-of-the-decade/. Retrieved 2009-12-24.
- Bibliography
- Jeep Barnett, Kim Swift & Erik Wolpaw (2008-11-04). "Thinking With Portals: Creating Valve's New IP". Gamasutra. CMP Media. http://www.gamasutra.com/view/feature/3839/thinking_with_portals_creating_.php. Retrieved 2008-11-21.
External links
- Official homepage — The Orange Box’’
- Information portal
- ApertureScience.com (Viral advertising, Alternate reality game)
- Portal at the Internet Movie Database
Portal series Video games Portal · Portal 2Characters Related articles Half-Life · The Orange Box · Potato Sack · "Still Alive" · Music of Portal 2 · Narbacular Drop · Tag: The Power of PaintValve games Half-Life series Half-Life (Opposing Force · Blue Shift · Decay) · Half-Life 2 (Episode One · Episode Two · Episode Three)Portal series Portal · Portal 2Counter-Strike series Day of Defeat series Team Fortress series Left 4 Dead series Other games Source engine games Valve Half-Life seriesHalf-Life 2 · Half-Life 2: Deathmatch · Half-Life Deathmatch: Source · Half-Life: Source · Half-Life 2: Lost Coast · Half-Life 2: Episode One · Half-Life 2: Episode Two · Half-Life 2: Episode ThreeOtherAlien Swarm · Counter-Strike: Global Offensive · Counter-Strike: Source · Day of Defeat: Source · Dota 2 · Left 4 Dead · Left 4 Dead 2 · Portal · Portal 2 · Team Fortress 2Other Bloody Good Time · E.Y.E.: Divine Cybermancy · The Crossing · Dark Messiah of Might and Magic · Dear Esther · Garry's Mod · Hybrid · Kuma Reality Games (Kuma\War 2, others) · Nuclear Dawn · Postal III · SiN Episodes · Sting: The Secret Operations · Tactical Intervention · The Ship · Vampire: The Masquerade – Bloodlines · Vindictus · VR Worlds 2 · Zeno ClashCategories:- 2007 video games
- First-person shooters
- Comedy video games
- PlayStation 3 games
- Portal (series)
- Puzzle video games
- Science fiction video games
- Valve Corporation games
- Mac OS X games
- Windows games
- Xbox 360 games
- Xbox 360 Live Arcade games
- Source engine games
- Video games with commentaries
- Art games
- Microsoft Windows and Xbox 360:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.