- Northrop Switchblade
-
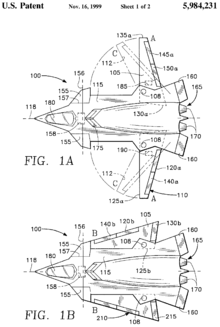
"Switchblade" Role Concept jet fighter Manufacturer Northrop First flight Never flown Primary user United States Air Force Number built Never built The Northrop "Switchblade" is a concept fighter jet which is a potential development of a utility patent filed by Grumman (U.S. Patent 5,984,231) in November 1999.
Contents
Design and development
As far back as 1989 the buzz inside aviation circles was that The Pentagon was developing a variable-sweep wing aircraft to replace the aging fleet of F-111s which were retired by the USAF in 1998. The F-111 was a medium sized bomber also capable of defending itself as a fighter and then speeding away at over 1600 MPH. In the mid-90s reports began to surface concerning a new swing-wing aircraft sighted near Cannon Air Force Base, NM and at Langley Air Force Base in Virginia. In September 1994, that aircraft was observed circling high over Amarillo, TX for several minutes at midday.[dubious ][citation needed] The plane was not a standard variable swing-wing aircraft as first reported, rather employing a unique forward-swept swing wing mechanism that enables the jet to become an advanced attack aircraft capable of precision weapons delivery, super maneuverability (for air combat) and Mach 3 "dash" capability. It is a bomber, fighter and high-speed aircraft all-in-one.
For a time it was concluded that this top-secret project by Northrop was officially named Bird of Prey on account of the squadron patch worn by pilots involved in the covert BoP project, though it is now known that the Bird of Prey was in fact another Black project stealth aircraft altogether, by Boeing. It is possible that this ATF/B -type "Switchblade" craft is a stealth concept plane from back in the Multi-Role Fighter [MRF] competition days, given its aptitude. Multi-mission aircraft of the past have invariably had to make design sacrifices in one area or another, never really coming close to becoming true flying Swiss Army knives. The Northrop design seems to meets all the design criteria for an advanced multi-regime tactical bomber/fighter aircraft. Northrop Grumman have considerable expertise in designing advanced aircraft. Northrop was the chief contractor on the stealth B-2 Spirit, the YF-23 Black Widow II and the Tacit Blue. Grumman has experience designing forward swept wing and variable-swept wing aircraft, the X-29 and F-14 Tomcat, respectively.
The wings are attached to the fuselage (body) at a pivot point toward the rear of the aircraft. With the wings fully swept aft the aircraft can slow to drop precision weapons or land on short unimproved runways. Swept forward twenty degrees and the aircraft takes advantage of the maneuverability that forward-swept wings offer becoming a highly agile air combat platform. Sweep the wings fully forward and they become flush with the aircraft with the trailing edge becoming the leading edge, forming a highly swept 75-degree stealthy delta ideal for high-speed Mach 3 exits. Or as it is understated in the U.S. Patent 5,984231 abstract, "the aforementioned apparatus may be used in a method to configure the aircraft for flight in a desired flight regime".
Geometry Function 
Wings fully extendedLong wingspan increases lift, enabling slower flight speeds for precision bombing and
landing on short runways.
Wings swept forwardForward sweep provides a good balance of lift and drag; efficient airflow over the wings
and control surfaces enhances the fighter's maneuverability for air-to-air combat.
Wings fully sweptLow aspect ratio provides the least drag, enabling the aircraft to speed up to Mach 3. In
this configuration the trailing edge becomes the leading edge, a section of the wing root
becomes the new trailing edge. Ace Combat's X-02 Wyvern's blueprint. The outer wing will fold inside the inner wing at high speeds.
Ace Combat's X-02 Wyvern's blueprint. The outer wing will fold inside the inner wing at high speeds.
Disadvantages
Though the concept of the "Switchblade" is extremely good for different combat situations, the mechanism that would be used to operate the wings would be quite heavy and bulky, and would have to be placed very close to the middle of the plane in order to aid balance of center of gravity. Fly-by-wire may compensate for these problems but the aircraft must still keep from being too unstable because computers are unable to compensate for too radical a problem.
Additionally, when the wings are at their fully swept angle, the wing shape presented to the oncoming air will not be a proper airfoil [aerofoil] shape, creating an inconsistent one which increases drag with negative effects on speed and control. The shape presented would be an airfoil (from the canard) plus the side cross section of the wing. This would encourage very small wings. Flat plate airfoils are one possible solution, but they are not a perfect solution, given their easier stall, higher drag and smaller lift. Wings with adaptable surfaces are one possible way of resolving problems.
Popular culture
The fictional F/A-37 Talon (shown), which starred in the 2005 film Stealth, had the "Switchblade's" swing-wing design. The Talon was capable of at least Mach 4, and used a pair of scramjets/pulse detonation engines for all flight speeds from subsonic to hypersonic.
Also in the 2002 film I-Spy (film), there is a plane which looks incredibly similar to the Northrop Switchblade and is called "Switchblade" or "the Switchblade" (though Eddie Murphy's character calls it "The Leafy Bug"), it has the technology to turn invisible.
The designers of Ace Combat incorporated the design into the similar X-02 Wyvern, an experimental fighter which has featured in Ace Combat 04: Shattered Skies, Ace Combat 5: The Unsung War, Ace Combat Zero: The Belkan War and Ace Combat X: Skies of Deception.
See also
References
External links
- Switchblade at Area51ZONE.com
- Switchblade at Air-Attack.com
Lists relating to aviation General Aircraft (manufacturers) · Aircraft engines (manufacturers) · Airlines (defunct) · Airports · Civil authorities · Museums · Registration prefixes · Rotorcraft (manufacturers) · TimelineMilitary Accidents/incidents Records Categories:- Research projects
- Aircraft configurations
- Aircraft wing design
- Variable-sweep wing aircraft
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.