- Vanadium(II) chloride
-
Vanadium(II) chloride 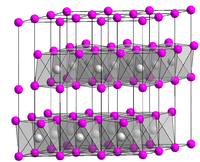 Vanadium(II) chlorideOther namesVanadous chloride
Vanadium(II) chlorideOther namesVanadous chlorideIdentifiers CAS number 10580-52-6 PubChem 66355 ChemSpider 59733 
RTECS number YW1575000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - Cl[V]Cl
Properties Molecular formula VCl2 Molar mass 121.847 g/mol Appearance pale green solid Density 3.230 g/cm3 Melting point 1027 °C, 1300 K, 1881 °F
Boiling point 1506 °C, 1779 K, 2743 °F
Solubility in water soluble Structure Crystal structure CdI2 Coordination
geometryoctahedral Hazards R-phrases 20/21/22-34 S-phrases 26-27-36/37/39-45 Main hazards Reacts with oxygen rapidly Related compounds Other anions vanadium(II) fluoride, vanadium dibromide Other cations titanium dichloride, chromium(II) chloride Related compounds vanadium trichloride  chloride (verify) (what is:
chloride (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Vanadium(II) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula VCl2. This purple solid is the most reduced vanadium chloride. Like other metal dihalides, it is a polymer. Vanadium(II) chloride dissolves in water to give purple solutions.
It is prepared by thermal decomposition of VCl3, which leaves a residue of VCl2:[1]
- 2 VCl3 → VCl2 + VCl4
VBr2 and VI2 are structurally and chemically similar to the dichloride. All have the d3 configuration, with a quartet ground state, akin to Cr(III).[2]
Vanadium dichloride is a powerful reducing species, being able to reduce sulfoxides to sulfides, organic azides to amines, as well as reductively coupling some alkyl halides. VCl2 dissolves in water to give the hexaaquo ion [V(H2O)6]2+. Evaporation of such solutions produces crystals of [V(H2O)6]Cl2.
References
- ^ Young, R. C.; Smith, M. E. "Vanadium(II) Chloride" Inorganic Syntheses, 1953 volume IV, page 126-127.doi:10.1002/9780470132357.ch42
- ^ Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. "Inorganic Chemistry" Academic Press: San Diego, 2001. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
Vanadium compounds Categories:- Vanadium compounds
- Chlorides
- Metal halides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
