- Vanadium oxytrichloride
-
Vanadium oxytrichloride 
 Vanadium trichloride oxideOther namesVanadyl chloride
Vanadium trichloride oxideOther namesVanadyl chloride
Vanadyl trichlorideIdentifiers CAS number 7727-18-6 
PubChem 24410 RTECS number YW2975000 Properties Molecular formula VOCl3 Molar mass 173.30 g/mol Appearance Yellow to brown liquid Density 1.826 g/cm3, liquid Melting point -76.5 °C, 197 K, -106 °F
Boiling point 126.7 °C, 400 K, 260 °F
Solubility in water Decomposes Solubility in other solvents chlorinated solvents Vapor pressure 8.1 Pa (20 °C) Structure Molecular shape Tetrahedral Hazards EU Index Not listed Main hazards Toxic, hydrolysis to HCl NFPA 704 LD50 140 mg/kg (oral in rats) Related compounds Related vanadium compounds Vanadium(V) oxide
Vanadium tetrachloride
Vanadium oxytrifluorideRelated compounds Phosphoryl chloride  oxytrichloride (verify) (what is:
oxytrichloride (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Vanadium oxytrichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula VOCl3. This distillable liquid hydrolyzes readily in air and is a strong oxidant. It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis.[1]
Contents
Properties
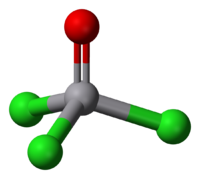
VOCl3 is a vanadium(V) compound and as such is diamagnetic. It is tetrahedral with O-V-Cl bond angles of 111° and Cl-V-Cl bond angles of 108°. The V-O and V-Cl bond lengths are 157 and 214 pm, respectively. VOCl3 is highly reactive toward water and evolves Cl2 upon standing. It is soluble in nonpolar solvents such as benzene, CH2Cl2, and hexane. In some aspects, the chemical properties of VOCl3 and POCl3 are similar. One distinction is that VOCl3 is a strong oxidizing agent, whereas the phosphorus compound is not.[2]
Preparation
VOCl3 is synthesized by the chlorination of V2O5. The reaction proceeds at ca. 600 °C:[3]
- 3 Cl2 + V2O5 → 2 VOCl3 + 1.5 O2
When the V2O5 is used as an intimate mixture with carbon, the synthesis proceeds at 200-400 °C; in this case the carbon serves as a deoxygenation agent akin to its use in the Kroll process for the manufacturing of TiCl4 from TiO2.
Vanadium(III) oxide can also be used as a precursor:
- 3 Cl2 + V2O3 → 2 VOCl3 + 0.5 O2
A more typical laboratory synthesis involves the chlorination of V2O5 using SOCl2.[4]
- V2O5 + 3 SOCl2 → 2 VOCl3 + 3 SO2
Reactions
Hydrolysis and alcoholysis
Vanadium oxytrichloride quickly hydrolyzes resulting in vanadium pentoxide and hydrochloric acid. In the picture, orange V2O5 can be seen forming on the walls of the beaker. An intermediate in this process is VO2Cl:
- 2 VOCl3 + 3 H2O → V2O5 + 6 HCl
VOCl3 reacts with alcohols especially in the presence of a proton-acceptor (e.g. Et3N) to give alkoxides:
- VOCl3 + 3 ROH → VO(OR)3 + 3 HCl (R = Me, Ph, etc.)
Interconversions to other V-O-Cl compounds
VOCl3 is also used in the synthesis of VOCl2.
- V2O5 + 3 VCl3 + VOCl3 → 6 VOCl2
Dioxovanadium monochloride can be prepared by an unusual reaction involving Cl2O.[5]
- VOCl3 + Cl2O → VO2Cl + 2 Cl2
At >180 °C, VO2Cl decomposes to V2O5 and VOCl3. Similarly, VOCl2 also decomposes to give VOCl3, together with VOCl.
Adduct formation
VOCl3 is strongly Lewis acidic, as demonstrated by its tendency to form adducts with various bases such as MeCN and amines. In forming the adducts, vanadium changes from four-coordinate tetrahedral geometry to six-coordinate octahedral geometry:
- VOCl3 + 2 H2NEt → VOCl3(H2NEt)2
VOCl3 in alkene polymerization
VOCl3 is used as a catalyst or precatalytst in production of ethylene-propylene rubbers (EPDM).
References
- ^ M. O'Brien, B. Vanasse (2001). Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis.
- ^ A. Earnshaw, N. Greenwood (1997). The Chemistry of the Elements - Second Edition. pp. 513–514.
- ^ A. Holleman, E. Wiberg (2001). Inorganic Chemistry.
- ^ S. Tyree (1967). Inorganic Syntheses Volume IX. p. 80.
- ^ H. Oppermann, "Gleichgewichte mit VOCl3, VO2Cl, VOCl2" Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie, vol. 331. 113-126 (1967)
Vanadium compounds Categories:- Vanadium compounds
- Oxochlorides
- Metal halides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

