- Rigvedic rivers
-
Rivers, such as the Sapta Sindhu ("seven rivers"),[1] play a prominent part in the hymns of the Rigveda, and consequently in early Vedic religion. It is likely that they are derived from older Proto-Indo-Iranian or Proto-Indo-European hydronyms as cognate names exist in Avestan language and other Indo-European languages.
Contents
Mythology
A recurring theme in the Rigveda is that of Indra slaying Vritra (literally "the obstacle"), liberating the rivers; in a variant of the myth, Indra smashes the Vala cave, releasing the cows that were within. The two myths are separate[2] however, rivers and cows are often poetically correlated in the Rigveda, for example in 3.33, a notable hymn describing the crossing of two swollen rivers by the chariots and wagons of the Bharata tribe,
- 3.33.1cd Like two bright mother cows who lick their youngling, Vipas and Sutudri speed down their waters. (trans. Griffith) [3]
Sapta Sindhu
The Sapta Sindhu are a group of seven chief rivers of uncertain or fluctuating identification (the number seven is of greater importance than the exact members of the group, compare the Saptarishi, and also the (later) seven seas and the seven climes) of the Avesta. The Avesta's hapta həndu are generally equated with the Vedic Sapta Sindhavaḥ: in Vendidad 1.18 these are described to be the fifteenth of the sixteen lands created by Mazda.[4]
Identity of the seven rivers
It is not entirely clear how the seven rivers were intended to be enumerated. They are often located in the in northtern India / eastern Pakistan. If the Sarasvati and the five major rivers of the Punjab are included (Sutudri, Parusni, Asikni, Vitasta, Vipas(Vipāś), the latter all tributaries of Sindhu), one river is missing probably the Kubha. (The Sindhu is a special case, having feminine or masculine gender). Other possiblilities include the Arjikiya or Sushoma; compare also the list of ten rivers, both east and west of the Indus, in the Nadistuti sukta, RV 10.75. In 6.61.10, Sarasvati is called "she with seven sisters" (saptasvasā) indicating a group of eight rivers, the number seven being more important than the individual members (see also saptarshi, hapta karšuuar /haft keshvar in Avestan), so that the list of the Sapta Sindhu may not have been fixed or immutable. In RV 10.64.8 and RV 10.75.1, three groups of seven rivers are referred to (tríḥ saptá sasrâ nadíyaḥ "thrice seven wandering rivers"), as well as 99 rivers.
Geography of the Rigveda
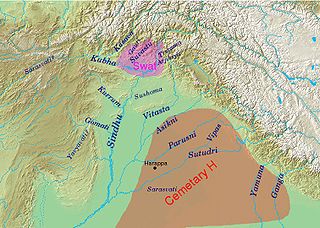 Geography of the Rigveda; the extent of the Swat and Cemetery H cultures are indicated.
Geography of the Rigveda; the extent of the Swat and Cemetery H cultures are indicated.
Identification of Rigvedic rivers is the single most important way of establishing the geography of the early Vedic civilization. Rivers with certain identifications stretch from eastern Afghanistan to the western Gangetic plain, clustering in the Punjab. Some river names appear to go back to common Indo-Iranian rivers, with cognate river names in Avestan, notably the Sarasvati (Avestan Haraxvaiti, Old Persian Hara(h)uvati) and the Sarayu (Iran. Harayu, Avestan acc. Harōiiūm, mod. Persian Harē).
A number of names can be shown to have been re-applied to other rivers as the center of Vedic culture moved eastward. It is possible to establish a clear picture for the latest phase of the Rigveda, thanks to the Nadistuti sukta (10.75), which contains a geographically ordered list of rivers. The most prominent river of the Rigveda is the Sarasvati, next to the Indus. The Sarasvati river of the Rigveda is commonly identified with the present-day Ghaggar-Hakra, although the Helmand River as a possible locus of early Rigvedic references has been discussed. This is mostly ascribed to the movement of Vedic Aryans from their early seats in Seistan (Arachosia, Avestan Haraēuua), Gandhara and eastern Afghanistan into the Indus plains and beyond. On the other hand archaeologists like B.B. Lal have shown the possibility of reverse westward movements of some Indo-aryan clans from indus basin as well as the absence of the certain archaeological trace for any outside intrusion to the subcontinent[5].
List
In the geographical organization of the following list, it has to be kept in mind that some names appearing both in early and in late hymns may have been re-applied to new rivers during the composition of the Rigveda.
Northwestern Rivers (western tributaries of the Indus):
- Trstama (Gilgit)?
- Susartu
- Anitabha (listed once, in 5.53.9, with the Afghan rivers Rasa (Avestan Rangha/Raŋhā), Kubha, Krumu, Sarayu (Avest. Harōiiu)
- Rasa (on the upper Indus (often a mythical river, Avestan Rangha, Scythian Rha)
- Svetya
- Kubha (Kabul), Greek Kophēn
- Krumu (Kurrum)
- Gomati (Gomal)
- Sarayu (modern Hari River of Herat)
- Mehatnu (along with the Gomati and Krumu)
- Suvastu (Swat) in RV 8.19.37)
- Gauri (Panjkora)??
- Kusava (Kunar)??
The Indus and its minor eastern tributaries:
Central Rivers (rivers of the Punjab):
East-central Rivers (rivers of Haryana):
- Sarasvati (References to the Sarasvati river in the Rigveda are identified with the present-day Ghaggar River, although the Arghandāb River (a tributary of the great Helmand River) as a possible locus of early Rigvedic references has been discussed.)
- Drsadvati, Apaya (RV 3.23.4, Mahabharata Apaga.)
Eastern Rivers:
- Asmanvati (Assan)?
- Yamuna
- Ganges
Uncertain / other
- Silamavati?
- Urnavati?
- Yavyavati (Zhob river?)
Notes
- ^ e.g. RV 2.12; RV 4.28; RV 8.24
- ^ H.-P. Schmidt, Brhaspati and Indra, Wiesbaden 1968
- ^ http://www.sacred-texts.com/hin/rigveda/rv03033.htm
- ^ Gnoli 1989 pp.44–46
- ^ http://www.archaeologyonline.net/artifacts/19th-century-paradigms.html
See also
- River goddess
- Samudra
- Nadistuti sukta
- Ap (water)
- Rigvedic deities
- Aryan migration
- Out of India theory
- Old European hydronymy
References
- S.C. Sharma. 1974. The description of the rivers in the Rig Veda. The Geographical Observer, 10: 79-85.
- Michael Witzel, Tracing the Vedic dialects in Dialectes dans les litteratures Indo-Aryennes ed. Caillat, Paris, 1989, 97–265.
- Gherardo Gnoli, De Zoroastre à Mani. Quatre leçons au Collège de France (Travaux de l’Institut d’Études Iraniennes de l’Université de la Sorbonne Nouvelle 11), Paris (1985)
- Shrikant G. Talageri, The Rigveda, a historical analysis, Aditya Prakashan, New Delhi (chapter 4)
The five rivers of the Punjab Punjabi names 

Greek names Hydaspes · Hydraotes · Acesines · Hyphasis · HesidrosSanskrit names Vitasta · Parushani · Ashikini · Vipasa · ShatadruRigveda Mandalas Deities Rivers Rishis Saptarishi (Gritsamada · Vishvamitra · Vamadeva · Atri · Angiras · Bharadvaja · Vasishta)
Categories:- Rigvedic rivers
- Rig Veda
- History of India
- Rivers of Sindh
- Hydronymy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
