- Comparison of memory cards
-
This table provides summary of comparison of various flash memory cards, as of 2011[update].
Contents
Common information
- unless otherwise indicated, all images to scale
Card family Standards organizations Varieties Entry date Picture[1] Main features CompactFlash SanDisk I 1994 
Thinner (3.3 mm), flash only, now up to 128 GiB, although standard goes up to 128 PiB since CF 5.0[2]) II Thicker (5.0 mm), older flash, but usually Microdrives, up to 128 PiB[2] SmartMedia Toshiba 3.3/5 V 1995 
Very slim (45.0×37.0×0.76 mm3), no wear leveling controller, up to 128MB. This particular example shows the write protect sticker (the silver disc). MultiMediaCard Siemens AG, SanDisk MMC 1997 
Slim and small (24×32×1.4 mm3), up to 16GB RS-MMC/MMC Mobile 2003/2005 
Compact (24×18×1.4 mm3), up to 16GB MMCplus 2005 
Compact (24×32×1.4 mm3), swifter, optional DRM, up to 16GB MMCmicro 2005 Subcompact (14×12×1.1 mm3), optional DRM, 16MB to 4GB Secure Digital Panasonic, SanDisk, Toshiba, Kodak SD 1999 
Small (32×24×2.1 mm3), DRM, up to 4GB. (2GB and 4GB cards use larger block sizes and may not be compatible with some host devices. See Article) miniSD 2003 
Compact (21.5×20×1.4 mm3), DRM, up to 4GB. (2GB and 4GB cards use larger block sizes and may not be compatible with some host devices. See Article) microSD 2005 
Subcompact (11×15×1 mm3), DRM, up to 4GB. (2GB and 4GB cards use larger block sizes and may not be compatible with some host devices. See Article) SDHC 2006 
Same build as SD but greater capacity and transfer speed, 4GB to 32GB. (not compatible with older host devices) miniSDHC 2008 
Same build as miniSD but greater capacity and transfer speed, 4GB to 32GB. 8GB is largest in early-2011. (not compatible with older host devices) microSDHC 2007 
Same build as microSD but greater capacity and transfer speed, 4GB to 32GB. 32GB is largest in mid-2011. (not compatible with older host devices) SDXC 2009 
Same build as SD, but greater capacity and transfer speed, 32GB and higher. Standard goes up to 2TB. (not compatible with older host devices) microSDXC 2009 
Same build as microSD, but greater capacity and transfer speed, 32GB and higher. Standard goes up to 2TB. (not compatible with older host devices) Memory Stick Sony/SanDisk Standard 1998 
Slim and narrow (50×21.5×2.8 mm3), optional DRM, up to 128MB PRO 2003 
(not to scale)Slim and narrow (50×21.5×2.8 mm3), swifter, optional DRM, up to 4GB Duo 2003 
Compact (31×20×1.6 mm3), optional DRM, up to 128MB PRO Duo 2002-06 Compact (31×20×1.6 mm3), optional DRM, up to 32GB PRO-HG Duo 2007-08 Compact (31×20×1.6 mm3), swifter, optional DRM, up to 32GB Micro (M2) 2006-02 Subcompact (15×12.5×1.2 mm3), optional DRM, up to 16GB xD Olympus, Fujifilm Standard 2002-07 
Slim and small (20×25×1.78 mm3), electrically identical to SmartMedia, no wear-leveling controller, up to 512MB[3] Type M 2005 
Slim and small (20×25×1.78 mm3) but slower read/write, no wear-leveling controller, up to 2GB[3] Type H 2005 
Slim and small (20×25×1.78 mm3) and swifter, no wear-leveling controller, up to 2GB[3] USB flash drive Various USB 1.1/2.0/3.0 2001 
(not to scale)Universally compatible across all computer platforms, but greater size suits them better to file transfer/storage instead of use in portable devices, up to 256GB Physical details
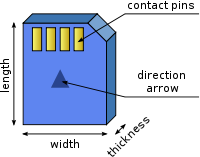
Note that a memory card's dimensions are determined while holding the card with contact pins upwards. The length of cards is often greater than their width. Most cards show a directional arrow to aid insertion; such an arrow should be upward.
Card Width (mm) Length (mm) Thickness (mm) Volume (mm³) Mass (g)[4] CompactFlash, Type I 43.0 36.0 3.3 5,108 3.3 CompactFlash, Type II 43.0 36.0 5.0 7,740 SmartMedia 37.0 45.0 0.76 1,265 2.0 MMC, MMCplus 24.0 32.0 1.4 1,075 1.3[5] RS-MMC, MMCmobile 24.0 18.0 1.4 605 1.3 MMCmicro 14.0 12.0 1.1 185 SD, SDHC, SDXC, SDIO 24.0 32.0 2.1 1,613 2.0 miniSD, miniSDHC, miniSDIO 20.0 21.5 1.4 602 1.0 microSD, microSDHC, microSDXC 11.0 15.0 1.0 165 0.27 Memory Stick Standard, PRO 21.5 50.0 2.8 3,010 4.0 Memory Stick Duo, PRO Duo, PRO-HG , XC 20.0 31.0 1.6 992 2.0 Memory Stick Micro (M2), XC 12.5 15.0 1.2 225 2.0 xD 25.0 20.0 1.78 890 2.8 USB varies varies varies varies varies Technical details
Card Varieties Actual max. storage capacity (mebibyte, or MiB) Theoretical max. capacity Max. Read Speed (MByte/s) Max. Write Speed (MByte/s) Read/write cycles Low-level access Operating voltage (V)[6] Controller chip[7] # of pins CompactFlash I 131,072 128 PiB[2] 167[8] 167[8] NOR/NAND 3.3 and 5 Yes 50 II 12,288 128 PiB[2] (due to LBA-48) 167[8] 167[8] SmartMedia 128 2 1,000,000 NAND 3.3 or 5 No 22 MMC MMC 8,192 128 GB 2 2 1,000,000[9] 3.3 Yes 7 RS-MMC 2,048 2[10] 2[10] 3.3 7 MMCmobile 2,048 15[11] 8[11] 1.8 and 3.3 13 MMCplus 4,096[12] 52[13] 52[13] 3.3 13 MMCmicro 2,048 1.8 and 3.3 13 eMMC 2 TiB 104 104 1.8 and 3.3 Yes 13 Secure Digital SD 4 GiB 133 133 3.3 Yes 9 miniSD 8,192 133 133 11 microSD 4,096 133 133 8 SDHC 32,768[14] 2 TiB 12.5/25(HS) 12.5/25(HS) 1.8 and 3.3 Yes 9 miniSDHC 4,096[15] 12 12 11 microSDHC 32,768[16] 10 10 8 SDXC 32,768 2 TiB 104 104 1.8 and 3.3 Yes 9 Memory Stick Standard 128 128 MiB 2.5 1.8 3.3 Yes 10 PRO 4,096 2 TiB 20 20 3.3 PRO Duo 32 ,000[17] 20 20 3.3 PRO-HG Duo 32, 000[18] Actual: 30[19]
Theoretical: 60[20]Actual: 30[19]
Theoretical: 60[20]3.3 Micro (M2) 16,384[21] 32 GiB 20 20 1.8 and 3.3 xC 2 TiB 60 60 3.3 Yes 10 xD 512 512 MiB 5 3 3.3 No 18 Type M 2,048 8 GiB 4 2.5 Type H 2,048 8 GiB 5 4 Type M+ 2,048 8 GiB 6 3.75 USB Full speed 131,072 (2009) 262,144 (2010) No Limit 1 1 5 Yes 4 High speed 40 40 Consumer details
Card Write protection switch[22] DRM CompactFlash No No SmartMedia Partial, sticker Partial (optional) MMC, RS-MMC No No MMCMobile Yes, secureMMC SD Yes[23][24] Yes, CPRM miniSD No microSD No Memory Stick Standard, PRO Yes Optional, MagicGate Memory Stick Duo, PRO Duo No Optional, MagicGate Memory Stick PRO-HG Duo No Optional, MagicGate Memory Stick Micro (M2) No Optional, MagicGate xD No Partial [25] USB Sometimes No Compatibility
The following chart gives details on availability of adapters to put a given card (horizontal) in a given slot or device (vertical). This table does not take into account protocol issues in communicating with the device.
Following labels are used:
- + (native) - a slot is native for such card.
- D (Directly compatible) - a card may be used in such a slot directly, without any adapters. Best possible compatibility.
- M (requires a Mechanical adapter) - such adapter is only a physical enclosure to fit one card sized into another; all electrical pins are exactly the same.
- EM (requires an Electro-Mechanical adapter) - such adapter features both physical enclosure and pins re-routing as terminals are sufficiently different. No powered elements in such adapter exists, thus they're very cheap and easy to manufacture and may be supplied as a bonus for every such card.
- E (requires an Electronic adapter enclosure) - these adapters are the most advanced ones with some chips (may be requiring external power) that transform signals, as well as physical enclosure and pin routing.
- X (requires an eXternal adapter) - technically the same as E, but such adapter usually consists of 2 parts: a pseudo-card with pin routing and physical enclosure size that perfectly match the target slot and a break-out box (a card reader) that holds a real card. Such adapter is the least comfortable to use.
- Empty cell - card can't be used in such slot, no single adapter is known to exist. Sometimes a chain of adapters can help (for example, miniSD→CF as miniSD→SD→CF)
Cards → CF SM MMC Memory Stick SD xD ↓ Slots I II MMC RS-MMC, MMCmobile Std PRO PRO Duo Micro SD mini micro Std M H ExpressCard E[26] E[26] E[27] E[28] E[28] E[27] E[27] E[27] E[29] E[27] E[27] E[27] PC card EM[30] EM[30] E[31] E[32] E[32] E[32] E[32] CF I + E E[33] E[34] E[34] E[35] E[33] E[36] E[36] E[36] CF II + + E E[33] E[34] E[34] E[33] E[36] E[36] E[36] SM + X[37] X[37] X[37] xD E[38] + + + MMC + M D[39] MS X[40] + + M M X[40] X[40] E[41] SD D M + EM EM IDE PATA EM[42] EM[42] E[43][44] Serial ATA E[45] E[45] USB X[46] X[46] X[46] X[46] X[46] X[46] E[47] E[47] E[48] E[49] X[46] X[46] X[46] Floppy E[50] Nintendo DS Slot-1 E[51] Nintendo DS Slot-2 E[52] E[52] E[52] References
- ^ Pictures are given in relative scales; they're sized to be WYSIWYG when viewing using 81PPI monitor.
- ^ a b c d Compact Flash Association announces CF 5.0 standard supporting up to 128 PiB of storage
- ^ a b c FUJIFILM Global | xD-Picture Card and Adapters
- ^ Plexus Outbursts specifications
- ^ Apacer's MMC specifications
- ^ Voltage table at All Memory Cards, note that some cards support both voltages (and), and some cards are available in distinct versions (or)
- ^ Explanation of controller chip at All Memory Cards
- ^ a b c d CompactFlash Specification Rev. 6.0
- ^ ACP-EP Specifications
- ^ a b ACP-EP RS-MMC card features list
- ^ a b ACP-EP MMCmobile card features list
- ^ Transcend MMCplus 4 GiB
- ^ a b MMC transferred at up to 52 MiB/s
- ^ Toshiba Adds New High Density SDHC Cards and microSDHC Card to Extensive Memory Card Line-up
- ^ New 4 GiB miniSDHC card
- ^ [1]
- ^ Sony 32 GB Memory Stick PRO Duo
- ^ [2]
- ^ a b Sony Introduces Faster MS Pro HG Duo Card
- ^ a b Sony Memory Stick PRO-HG, up to 32 GB, 8-bit parallel transfer
- ^ SanDisk announces world's largest mobile phone card capacity with 16GB M2
- ^ Write protection switch at All Memory Cards
- ^ Some early SD cards may not have a write protection switch.
- ^ The write protect switch signals to the host, which is responsible for write protection. The write protect switch is not connected to the internal circuitry of the card. SD Card Simplified Physical Layer Specification
- ^ Fujifilm accessories xD-Picture Card
- ^ a b DataFab EXP-CF
- ^ a b c d e f g DataFab EXP 12 in 2
- ^ a b DataFab exp 12 in 1
- ^ DataFab exp M2+microSD
- ^ a b Transcend CompactFlash-to-PC Card adapter
- ^ Transcend SmartMedia-to-PC Card adapter
- ^ a b c d Transcend 5-in-1 Adapter
- ^ a b c d Minolta SD-CF1 SD-to-CompactFlash adapter
- ^ a b c d Transcend MemoryStick-to-CompactFlash adapter
- ^ Sony MSAC-MCF1N and AD-MSCF1 PRO Duo to CF adapters
- ^ a b c d e f Olympus MACF-10 xD-to-CompactFlash adapter
- ^ a b c Hama xD-to-SM adapter
- ^ In March 2008, Olympus started shipping the MASD-1 microSD-to-xD adapter along with its latest compact digital cameras, with a shape designed to fit only in those latest cameras. The physical adapter is in fact purely electromechanical, although the xD and SD protocols are completely incompatible. This demonstrates that the cameras themselves must understand the SD protocol, and thus the adapter is more properly termed an electronic adapter, with the electronic logic contained in the camera rather than the physical accessory.
- ^ SD cards are usually thicker than MMC ones, and although it uses perfectly compatible pins, not every MMC slot may allow thick SD card to be inserted
- ^ a b c Dragon SD/miniSD/MMC to MS PRO Duo Adapter
- ^ KingMax microSD to MS PRO Duo Adapter
- ^ a b PC Engines IDE to CompactFlash adapters
- ^ Star Empery PT110 SD Card To ATA IDE 3.5 inch Hard Drive Adapter
- ^ 4× SD to SSD IDE Adapter
- ^ a b Accelerated Compact Flash: The Addonics SATA CF Adapter
- ^ a b c d e f g h i There are many USB-connected "n-in-1" memory card readers, for example Belkin's "Hi-Speed USB 2.0 15-in-1 Media Reader & Writer".
- ^ a b MS Duo and M2 adapters have appeared in the last 12 months which look like USB memory sticks
- ^ SanDisk @ CES - SD card with built-in USB adapter
- ^ A-Data microSD to USB Adapter
- ^ DCRP Special Report: FlashPath Adapter by Tom Beardmore
- ^ R4 microSD to NDS Slot-1 Adapter
- ^ a b c Supercard to NDS Slot-2 Adapter
External links
- GumstixDocsWiki Frequently Asked Questions: Are SD cards interchangeable with MMC cards?
- Types of Memory Cards
- USB mass storage device class: Mass Storage device class specification — on the site of the USB Implementers Forum.
Memory cards Main articles 
Types CompactFlash (CF) • Express Card • JEIDA • MultiMediaCard (MMC) • Memory Stick (MS/MS-PRO) • miCard • Microdrive (MD) • MiniCard • P2 • PC Card (PCMCIA, CardBus, CardBay) • Secure Digital (SD) • SmartMedia (SM) • SxS • Universal Flash Storage (UFS) • USB • xD-PictureCategories:- Computing comparisons
- Solid-state computer storage media
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.