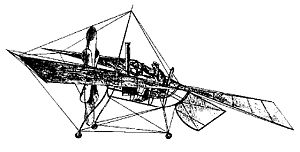
- Du Temple Monoplane
-
Monoplane The Du Temple Monoplane. Role National origin France Manufacturer Félix du Temple First flight 1874 Number built 1 The du Temple Monoplane was a large aeroplane made of aluminium, built in Brest, France, by naval officer Félix du Temple in 1874.
The plane had a wingspan of 13 m (43 ft) and weighed of only 80 kg (180 lb) without the pilot.
Several trials were made with the plane, and it is generally recognized that it achieved lift-off (from a combination of its own power and running down an inclined ramp)[1][2], glided for a short time and returned safely to the ground, making it the first successful powered flight in history, although the flight was only a short distance and a short time.
The plane was displayed at the 1878 Exposition Universelle ("World Fair") in Paris.
Contents
Steam engine
The plane used a very compact, high-speed circulation steam engine for which Félix du Temple applied for a patent on 28 April 1876. The engine used very small pipes packed together "to obtain the highest possible contact surface for the smallest possible volume" [3]
- "When he began with the aid of his brother, M. Louis du Temple, to experiment on a large scale, the inadequacy of all motors then known became apparent. They first tried steam at very high pressures, then a hot-air engine, and finally built and patented, in 1876 a very light steam boiler weighing from 39 to 44 lb. to the horse power, which appears to have been the prototype of some of the light boilers which have since been constructed. It consisted in a series of very thin tubes less than 1/8 in. in internal diameter, through which water circulated very rapidly, and was flashed into steam by the surrounding flame."[4]
This type of boiler, which boils the water instantly, has come to be known as a flash boiler. The engine design was later adopted by the French Navy for the propulsion of the first French torpedo boats:
- "Officers and engineers have now made up their opinion regarding Du Temple's steam engine. Everybody proclaims the superiority of its qualities… orders are pouring in from our commercial harbours and from the French government."[5]
See also
- List of early flying machines
- First flying machine
- Timeline of aviation - 19th century
- History of aviation
Notes
- ^ Gibbs-Smith
- ^ "So what's new?" Flight International 21 January 1984 p216
- ^ The patent describes "une demande pour une chaudière à vapeur à circulation rapide donnant la plus grande surface de chauffe possible sous le plus petit volume et le moindre poids."
- ^ Octave Chanute, Aeroplanes : Part III, August 1892
- ^ Revue Maritime 1888 according to (in French) (pdf) Felix du Temple, http://www.mairie-tourlaville.fr/fr/tourisme/tourisme_et_patrimoine/dossiers_en_consultation/fichiers/felix_du_temple.pdf, "L’opinion est faite aujourd’hui sur la chaudière Du Temple parmi les officiers et les ingénieurs. Tout le monde proclame ses qualités supérieures… les commandes affluent de nos ports de commerce et de la part du gouvernement français"[dead link]
References
- Gibbs-Smith, Charles H. (1959), "Hops and Flights: A Roll Call of Early Powered Take-offs", Flight 75: 468, http://www.flightglobal.com/pdfarchive/view/1959/1959%20-%200939.html, retrieved 2011-03-03
External links
Lists relating to aviation General Aircraft (manufacturers) · Aircraft engines (manufacturers) · Airlines (defunct) · Airports · Civil authorities · Museums · Registration prefixes · Rotorcraft (manufacturers) · TimelineMilitary Accidents/incidents Records Small arms Charleville musket · Delvigne rifle (1826) · Thouvenin Carabine à tige (1846) · Lefaucheux M1858 revolver · Minié rifle (1849) · Tabatière rifle (1864) · Chassepot rifle (1866) · Gras rifle (1874) · Lebel rifle (1886) · Modèle 1892 revolver





Machine guns Cannons Year XI system (1803) · Paixhans gun (1823) · Valée system (1828) · Canon obusier de 12 (1853) · La Hitte system (1858) · de Reffye system (1870) · Lahitolle 95 mm (1873) · de Bange system (1875) · Canet 320 mm (1880) · Canon de 75 (1897)
Warships Ammunition Lepage fulminate (1807-10) · Pauly-Prélat integrated cartridge (1808) · Prélat percusion cap (1818) · Lefaucheux cartridge (1836) · Tamisier ball (1841) · Minié ball (1847) · 8 mm Lebel smokeless powder cartridge (1886)
Systems Lepage percussion system (1807) · Marié-Davy naval periscope (1854) · De Bange breech obturator (1872) · Du Temple high-circulation steam engine (1876) · Krebs naval electric gyrocompass (1880) · Smokeless powder Poudre B (1886)
Operational
usageNapoleonic Wars · French conquest of Algeria · Crimean War · French weapons in the American Civil War · Franco-Prussian war
Categories:- 19th-century French experimental aircraft
- Propeller aircraft
- Single-engine aircraft
- Steam-powered aircraft
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.