- Minié rifle
-
Minié rifle 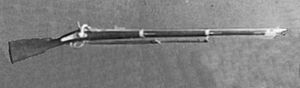
French Army P1851 Minié rifle.

British Army Pattern 1853 Enfield Minié rifle.

Springfield Model 1861 Minié rifle, the most widely used rifle during the American Civil War.

Württemberg, Baden and Hesse Vereinsgewehr 1857 rifled musket.

The Austrian Lorenz rifleType Service rifle Place of origin  France
FranceService history Used by France, Prussia, Austria, England, United States, Confederate States, Japan, Kingdom of the Two Sicilies Wars Crimean War, Indian Rebellion of 1857, Taiping Rebellion, Second Italian War of Independence, Austro-Prussian War, American Civil War, Boshin war, War of the Pacific. Specifications Weight 4 kilograms (8.8 lb) Barrel length 958 millimetres (37.7 in) Cartridge 18mm rimmed bullet Caliber 18 millimetres (0.71 in) Rate of fire 2-3 shots per minute Feed system muzzle-loading The Minié rifle was an important rifle in the 19th century, developed in 1849 following the invention of the Minié ball in 1847 by the French Army captains Claude-Étienne Minié of the Chasseurs d'Orléans and Henri-Gustave Delvigne. The rifle was designed to allow rapid muzzle loading of rifles, an innovation that brought about the widespread use of the rifle as a mass battlefield weapon. It was developed following difficulties encountered by the French army in Northern Africa, who were regularly outranged by the handcrafted but long-barreled weapons of their Algerian opponents. The Minié rifle belonged to the vast category of rifled muskets, which were developed following the invention of the Minié ball.
Contents
Mechanism
 Various types of Minié balls.
Various types of Minié balls.
 Training with the Minié rifle during the American Civil War, 1863. The caption reads: "Teaching the negro recruits the use of the Minié rifle".
Training with the Minié rifle during the American Civil War, 1863. The caption reads: "Teaching the negro recruits the use of the Minié rifle".
 In the Minié rifle a countersunk ramrod was necessary to force the ball without damaging its shape.
In the Minié rifle a countersunk ramrod was necessary to force the ball without damaging its shape.
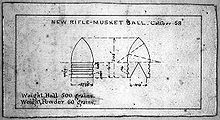
The rifle used a conical-cylindrical soft lead bullet, slightly smaller than the barrel bore, with three exterior grease-filled grooves and a conical hollow in its base. When fired, the expanding gas forcibly pushed on the base of the bullet, deforming it to engage the rifling. This provided spin for accuracy, a better seal for consistent velocity and longer range, and cleaning of barrel detritus.
Before this innovation, the smooth-bore gun was the only practical field weapon. A few rifled guns had been in use since the Renaissance, but they required hammering the munition inside the barrel, and created considerable cleaning problems. A short-lived system ("à tige") used a pin at the bottom of the barrel which would deform the bullet against the wall of the barrel when the bullet was pushed to the bottom. This system also was very problematic for cleaning, especially with the black powders of the period.
The Minié rifle had a percussion lock and weighed 10 lb 9 oz (4.8 kg). Having a reasonable accuracy up to 600 yards (550 metres), it was equipped with sights for effective aiming. It could penetrate 4 inches (10 cm) of soft pine at 1,000 yards (918 m). The hollow-based bullet had a .702 inch (17.8 mm) calibre, and weighed 500 grains (32.4 g ).
A test in Vincennes in 1849 demonstrated that at 15 yards the bullet was able to penetrate two boards of poplar wood, each two-thirds of an inch thick and separated by 20 inches. Soldiers of the time spread rumors that at 1,200 yards the bullet could penetrate a soldier and his knapsack and still kill anyone standing behind him, even killing every person in a line of 15.
The rifle saw limited distribution in the Crimean War and was the dominant infantry weapon in the American Civil War. The large caliber with high speed spin of these easily deformed bullets (13-18 mm) created terrible wounds.
Usage
The Pattern 1851 Minié rifle was in use by the British Army from 1851 to 1855. The Minié system was also used extensively by various manufacturers, such as Springfield (the Springfield Model 1861, the most widely used rifle of the American Civil War) and Enfield (the Pattern 1853 Enfield).
Minié rifles were also used extensively in the Boshin war (1868-1869) in Japan, where they had an important role in tipping the balance against the Tokugawa forces in encounters such as the Battle of Toba-Fushimi.
Obsolescence
The Minié rifle became obsolete in 1866 following the defeat of the Austrians, equipped with this type of rifle, against the Prussians, who were equipped with breech-loading Dreyse rifles. In France, the existing Minié rifles were then retooled to accommodate a breech-loading mechanism reminiscent of a snuff box, and thus became known as Tabatière rifles. Soon after, the breech-loading Chassepot system was then adopted by the French army.
Preceded by
Carabine à tigeFrench Army rifle
1851–1866Succeeded by
Tabatière rifleSee also
- French weapons in the American Civil War
References
- Nosworthy, Brent, The Bloody Crucible of Courage, Fighting Methods and Combat Experience of the Civil War, Carroll and Graf Publishers, 2003, ISBN 0-7867-1147-7.
- Smithsonian article
Small arms Charleville musket · Delvigne rifle (1826) · Thouvenin Carabine à tige (1846) · Lefaucheux M1858 revolver · Minié rifle (1849) · Tabatière rifle (1864) · Chassepot rifle (1866) · Gras rifle (1874) · Lebel rifle (1886) · Modèle 1892 revolver





Machine guns Cannons Year XI system (1803) · Paixhans gun (1823) · Valée system (1828) · Canon obusier de 12 (1853) · La Hitte system (1858) · de Reffye system (1870) · Lahitolle 95 mm (1873) · de Bange system (1875) · Canet 320 mm (1880) · Canon de 75 (1897)
Warships Ammunition Lepage fulminate (1807-10) · Pauly-Prélat integrated cartridge (1808) · Prélat percusion cap (1818) · Lefaucheux cartridge (1836) · Tamisier ball (1841) · Minié ball (1847) · 8 mm Lebel smokeless powder cartridge (1886)
Systems Lepage percussion system (1807) · Marié-Davy naval periscope (1854) · De Bange breech obturator (1872) · Du Temple high-circulation steam engine (1876) · Krebs naval electric gyrocompass (1880) · Smokeless powder Poudre B (1886)
Operational
usageNapoleonic Wars · French conquest of Algeria · Crimean War · French weapons in the American Civil War · Franco-Prussian war
Categories:- French rifles
- Early rifles
- American Civil War rifles
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.