- Sand Mountain (Alabama)
-
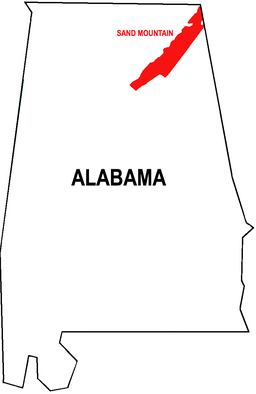
Sand Mountain (Alabama) Plateau Sand Mountain in AlabamaCountry United States Regions Georgia, Alabama, Tennessee Part of Appalachian Mountains Geology Sandstone Sand Mountain is a sandstone plateau in northeastern Alabama and (to a far lesser extent) northwestern Georgia. It is part of the southern tip of the Appalachian mountain chain. Geologically a continuation of Walden Ridge, Sand Mountain is part of the Cumberland Plateau, separated from the main portion of the plateau by the Tennessee River and Sequatchie Valley. The average elevation on Sand Mountain is around 1,500 feet (460 m) above sea level, compared to about 650 feet (200 m) in the surrounding area.[1] This elevation leads to it having the coolest climate in the state of Alabama.[2]
Contents
Geography
Sand Mountain runs in a diagonal northeast-southwest direction from the northeastern corner of Alabama, and includes parts of Jackson, DeKalb, Marshall, Etowah and Blount counties in Alabama, as well as part of Dade County, Georgia.[3]
Sand Mountain, especially the northern end, i.e. eastern Jackson County and northern DeKalb County, is mostly a rural,[4] agricultural area, with a mix of chicken, cow, and potato farms, as well as other assorted farms,[5] and large expanses of both rolling pastures and forests.[6] It contains many small towns (less than 1,000 people) and unincorporated communities.
History
Prehistory through the Colonial Period
The Sand Mountain area has been inhabited for at least 9000 years, as evidenced by archaeological finds at nearby Russell Cave National Monument, near Bridgeport, Alabama.[7] In historical times, Cherokee and Creek villages were located in the Tennessee Valley to the west of Sand Mountain, and in Wills Valley to the east. Sequoyah, creator of the Cherokee syllabary, lived in the Cherokee village of Wills Town, near present-day Fort Payne in Wills Valley.[8]
The first white visitors to Sand Mountain were possibly the party of Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto, who are believed to have crossed the mountain during their journey through southeastern North America between 1539 and 1543. One of the likely routes reconstructed for the expedition traces the party’s path across the mountain on their way from the Tennessee Valley to the Coosa Valley.[9]
Civil War
Union troops under Major General George H. Thomas crossed Sand Mountain in September 1863 in an attempt to cut off Confederate troops in Chattanooga. The Union mission was unsuccessful, and the opposing armies met at the Battle of Chickamauga on September 19–20, 1863.[10]
Jackson and DeKalb counties, along with the other north Alabama counties, had voted against secession in 1861, and pro-Union sentiment was high on Sand Mountain. In early 1861, as the secession debate heated up, several of the northern counties proposed breaking off from Alabama and joining with the counties of East Tennessee to create a new pro-Union state of Nickajack.[11] Industries such as mining, milling, and the railroads were accepted exemptions to military service for Southern unionists during the war, and some Sand Mountain men who did not wish to join the Confederate army worked in Sauta cave in the Tennessee Valley, mining potassium nitrate to make gunpowder, in lieu of military service.[12]
In September 1861, the "Paint Rock Rifles" were raised on Sand Mountain by Confederate Colonel Lemuel Green Mead of Jackson County. This unit became Company C of the 26th Alabama Infantry Regiment, which served at the Battle of Shiloh in April 1862. Colonel Mead resigned his commission in July 1862 after Union troops had invaded north Alabama, and organized an independent company of partisan rangers who carried out guerrilla raids on Union forces.[13]
In the summer of 1862, "Gunter's 1st Partisan Ranger Battalion" was formed on Sand Mountain in Jackson County by Major William T. Gunter. The unit was composed of five mounted companies and served under the command of Lieutenant General Nathan Bedford Forrest in skirmishes along the Tennessee River. In November 1862, the unit was merged with the 33rd Alabama Infantry Regiment.[14]
A Union regiment, the 1st Tennessee and Alabama Vidette Cavalry, was raised at Stevenson, Alabama, in 1863, drawing men primarily from Sand Mountain.[15]
20th century
Sand Mountain was home, from 1903 to 1905, to a short-lived commune of forty Russian Jewish families attempting to form a collective farm and manufacturing concern. Due to the isolation of the area from other Jewish communities, the limestone soil of the area, and disharmony within the group, the project was abandoned and the inhabitants relocated after two years.[16]
Current issues and social characteristics
There are significant problems with methamphetamine manufacture and use in many communities on Sand Mountain, which was the subject of a recent documentary called Meth Mountain (a one-hour episode of A&E's Intervention).[17] There is very little violent crime on Sand Mountain.[18][19][20][21][22][23]
Politically and religiously, Sand Mountain is a fairly conservative place, consistently voting for conservative candidates in elections,[24] and with Baptists claiming the largest number of congregants of any church denomination.[25] Much of Sand Mountain is dry, with the sale of alcoholic beverages being forbidden.[26]
There is very little racial diversity on Sand Mountain, particularly the northern half, which is nearly all white.[27]
Sand Mountain is one of the last places in the country with churches which still use Sacred Harp singing in their Sunday morning church services, and is home to many of the largest and oldest continuous Sacred Harp singings in the country, as well as many important singers (i.e. editors of the Sacred Harp tunebook).[28][29]
Snake handling by some churches on Sand Mountain was the subject of Salvation on Sand Mountain, a 1996 book by Dennis Covington.[30] Those who live on Sand Mountain state that the book mostly took place in Scottsboro and that town is not on the mountain at all.
Sand Mountain has been home to chapters of the Ku Klux Klan in the past,[citation needed] though the SPLC's Hate Groups Map shows Sand Mountain to be free of known organized hate groups at the present.[31]
Climate
Sand Mountain, being located in the mid-South, has long hot humid summers, and winters which are short and mild by comparison to much of the rest of the country, with snow being a real rarity. Its elevation, however, leads to it being cooler than the rest of the state of Alabama.[32][33][34][35][36] On Sand Mountain, between 60 and 90 days per year are over 86 °F (30 °C), according to the Heat Zone Map published by the American Horticultural Society.[37] By comparison, the great majority of the upper Midwest and Northeast has less than 30 such days per year.[38] These hot days, combined with the South's high humidity, make it sweltering in the summer. The average daytime temperature is in the high 70s or above for at least 5 months out of the year (May through September).[32][33][34][35][36] Sand Mountain has higher rainfall than almost anywhere else in the South, including anywhere else in Alabama, with the exception of the Gulf Coast area.[39] Some areas of Sand Mountain get more than 66 inches (1,700 mm) of rainfall per year (though others get as little as 54 inches (1,400 mm)).[40]
The following is a general idea of Sand Mountain's climate, taken from Ider, Alabama:
Climate data for Sand Mountain, Alabama (spec. Ider, Ala.) Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year Average high °F (°C) 48
(9)53
(12)61
(16)70
(21)77
(25)84
(29)88
(31)87
(31)82
(28)72
(22)61
(16)51
(11)69.5
(20.8)Average low °F (°C) 26
(−3)28
(−2)35
(2)42
(6)52
(11)60
(16)65
(18)64
(18)57
(14)44
(7)36
(2)29
(−2)44.8
(7.1)Precipitation inches (mm) 6.06
(153.9)5.62
(142.7)6.57
(166.9)4.73
(120.1)4.70
(119.4)4.33
(110)5.18
(131.6)3.49
(88.6)4.27
(108.5)3.29
(83.6)5.00
(127)5.12
(130)58.36
(1,482.3)Source: Weather.com[41] Soil
Sand Mountain has, on average, a 2-to-4-foot (0.6 to 1.2 m) depth of soil - after which is solid sandstone bedrock. The soil is generally loam-based, and is a mixture of sandy loam and silty loam, drawing from such series as Apison, Atkins, Cotaco-Barbourville, Crossville, Hartsells, Lickdale, and Muskingum. It is extremely acidic, growing more so the deeper you go from the top. It is classified as "well-drained".
Settlements located on Sand Mountain
Jackson County
- Browntown, Alabama
- Bryant, Alabama
- Central, Alabama
- Davistown, Alabama
- Dutton, Alabama
- Eliza, Alabama
- Fabius, Alabama
- Fair View, Alabama
- Flat Rock, Alabama
- Higdon, Alabama
- Liberty Hill, Alabama
- Macedonia, Jackson County, Alabama
- Overlook, Alabama
- Pisgah, Alabama
- Rosalie, Alabama
- Section, Alabama
- Shrader, Alabama
DeKalb County
- Blake, Alabama
- Brooks Crossroads, Alabama
- Cartersville, Alabama
- Council Bluff, Alabama
- Crossville, Alabama
- Dawson, Alabama
- Elliott Crossroads, Alabama
- Five Forks, Alabama
- Fyffe, Alabama
- Geraldine, Alabama
- Grove Oak, Alabama
- Guest, Alabama
- Henagar, Alabama
- High Point, Alabama
- Horton, DeKalb County, Alabama
- Ider, Alabama
- Kilpatrick, Alabama
- Lakeview, Alabama
- Lathamville, Alabama
- Liberty, Alabama
- Old Blevins Mill, Alabama
- Plainview, Alabama
- Powell, Alabama
- Rainsville, Alabama
- Shiloh, DeKalb County, Alabama
- Skaggs Corner, Alabama
- Sylvania, Alabama
- Ten Broeck, Alabama
- Townsend Crossroads, Alabama
Marshall County
- Albertville, Alabama
- Guntersville, Alabama (only partially located on Sand Mountain)
- Boaz, Alabama
- Douglas, Alabama
- Asbury Community
See also
References
- ^ Google Earth
- ^ http://www.prism.oregonstate.edu/pub/prism/us_30s/graphics/tmax/Normals/us_tmax_1971_2000.14.png
- ^ https://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/us_2001/alabama_ref_2001.jpg
- ^ http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/14/Alabama_population_map.png
- ^ http://media.maps.com/magellan/Images/alland.gif
- ^ Google Earth
- ^ David Hurst Thomas, Exploring Ancient Native America, Routledge, 1999, pg 77.
- ^ Thomas E. Mails, The Cherokee People, Council Oak Books, 1992, pg 343.
- ^ Charles Hudson, Knights of Spain, Warriors of the Sun: Hernando de Soto and the South's Ancient Chiefdoms, University of Georgia Press, 1998, pg 460.
- ^ Victor Hicken, Illinois in the Civil War, University of Illinois Press; 1991, p. 194
- ^ Fleming, Walter L., Civil War and Reconstruction in Alabama. New York: Columbia University Press, 1905, pp 109-111.
- ^ Storey, Margaret M., Loyalty and Loss, Alabama's Unionists in the Civil War and Reconstruction, Louisiana State University Press, 2004.
- ^ "Lemuel Green Mead (1830-1878)". History-sites.com. http://history-sites.com/~kjones/mead.html. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ "Alabama Infantry Regiments, Histories of". History-sites.com. http://history-sites.com/~kjones/alinf.html#18th-Inf-Bn. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ Potter, Johnny, First Tennessee & Alabama Independent Vidette Cavalry Roster, 1863-1864, Mountain Press, 1995.
- ^ "Institute of Southern Jewish Life Digital Archive". Isjl.org. http://www.isjl.org/history/archive/al/sandMountain.html. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ "Intervention: Intervention In-Depth: Meth Mountain Episode Summary on". Tv.com. http://www.tv.com/intervention/intervention-in-depth-meth-mountain/episode/1224780/summary.html. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ "Powell, Alabama (AL 35971) profile: population, maps, real estate, averages, homes, statistics, relocation, travel, jobs, hospitals, schools, crime, moving, houses, sex offenders, news". City-data.com. http://www.city-data.com/city/Powell-Alabama.html. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ "Section, Alabama (AL 35771) profile: population, maps, real estate, averages, homes, statistics, relocation, travel, jobs, hospitals, schools, crime, moving, houses, sex offenders, news, sex offenders". City-data.com. http://www.city-data.com/city/Section-Alabama.html. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ "Pisgah, Alabama (AL 35765) profile: population, maps, real estate, averages, homes, statistics, relocation, travel, jobs, hospitals, schools, crime, moving, houses, sex offenders, news, sex offenders". City-data.com. http://www.city-data.com/city/Pisgah-Alabama.html. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ "Crossville, Alabama (AL 35962) profile: population, maps, real estate, averages, homes, statistics, relocation, travel, jobs, hospitals, schools, crime, moving, houses, sex offenders, news, sex offenders". City-data.com. http://www.city-data.com/city/Crossville-Alabama.html. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ "Fyffe, Alabama (AL 35971) profile: population, maps, real estate, averages, homes, statistics, relocation, travel, jobs, hospitals, schools, crime, moving, houses, sex offenders, news, sex offenders". City-data.com. http://www.city-data.com/city/Fyffe-Alabama.html. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ "Ider, Alabama (AL 35981) profile: population, maps, real estate, averages, homes, statistics, relocation, travel, jobs, hospitals, schools, crime, moving, houses, sex offenders, news, sex offenders". City-data.com. http://www.city-data.com/city/Ider-Alabama.html. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ The New York Times. http://elections.nytimes.com/2008/results/president/map.html.
- ^ "American FactFinder". Factfinder.census.gov. http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/DTSubjectShowTablesServlet?_ts=261390433391. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ http://www.abc.alabama.gov/images/Wet_Dry_Counties.gif
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ http://fasola.org/singings/sh_2004_map.png
- ^ The Sacred Harp, 1991 edition.
- ^ Dennis Covington, Salvation on Sand Mountain: Snake-Handling and Redemption in Southern Appalachia, Penguin (Non-Classics):March 1, 1996
- ^ "Hate Map | Southern Poverty Law Center". Splcenter.org. http://www.splcenter.org/intel/map/hate.jsp#s=AL. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ a b "PRISM Products". Prism.oregonstate.edu. http://www.prism.oregonstate.edu/products/viewer.phtml?file=/pub/prism/us_30s/graphics/tmax/Normals/us_tmax_1971_2000.05.png&year=1971_2000&vartype=tmax&month=05&status=final. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ a b "PRISM Products". Prism.oregonstate.edu. http://www.prism.oregonstate.edu/products/viewer.phtml?file=/pub/prism/us_30s/graphics/tmax/Normals/us_tmax_1971_2000.06.png&year=1971_2000&vartype=tmax&month=06&status=final. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ a b "PRISM Products". Prism.oregonstate.edu. http://www.prism.oregonstate.edu/products/viewer.phtml?file=/pub/prism/us_30s/graphics/tmax/Normals/us_tmax_1971_2000.07.png&year=1971_2000&vartype=tmax&month=07&status=final. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ a b "PRISM Products". Prism.oregonstate.edu. http://www.prism.oregonstate.edu/products/viewer.phtml?file=/pub/prism/us_30s/graphics/tmax/Normals/us_tmax_1971_2000.08.png&year=1971_2000&vartype=tmax&month=08&status=final. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ a b "PRISM Products". Prism.oregonstate.edu. http://www.prism.oregonstate.edu/products/viewer.phtml?file=/pub/prism/us_30s/graphics/tmax/Normals/us_tmax_1971_2000.09.png&year=1971_2000&vartype=tmax&month=09&status=final. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ http://www.ahs.org/pdfs/05_heat_map.pdf
- ^ http://www.ahs.org/pdfs/05_heat_map.pdf
- ^ [2][dead link]
- ^ http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys/namerica/usstates/weathermaps/al.gif
- ^ "Average Weather for Ider, AL". The Weather Channel. 2009. http://www.weather.com/outlook/health/achesandpains/wxclimatology/monthly/graph/35981. Retrieved 2009-05-24.
Coordinates: 32°51′17″N 86°54′45″W / 32.8548481°N 86.9124896°W
Categories:- Mountains of Alabama
- Geography of Jackson County, Alabama
- Geography of DeKalb County, Alabama
- Geography of Etowah County, Alabama
- Geography of Blount County, Alabama
- Geography of Dade County, Georgia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.