- N-Ethylmaleimide
-
N-Ethylmaleimide[1]  1-Ethylpyrrole-2,5-dioneOther namesEthylmaleimide
1-Ethylpyrrole-2,5-dioneOther namesEthylmaleimideIdentifiers Abbreviations NEM CAS number 128-53-0 
PubChem 4362 ChemSpider 4209 
UNII O3C74ACM9V 
DrugBank DB02967 KEGG C02441 
ChEBI CHEBI:44485 
ChEMBL CHEMBL8211 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C1\C=C/C(=O)N1CC
Properties Molecular formula C6H7NO2 Molar mass 125.12528 Melting point 43-46 °C
Boiling point 210 °C, 483 K, 410 °F
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references N-Ethylmaleimide (NEM) is an organic compound that is derived from maleic acid. It contains the imide functional group, but more importantly it is an alkene that is reactive toward thiols and is commonly used to modify cysteine residues in proteins and peptides.[2]
Contents
Organic chemistry
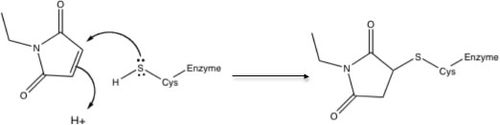
In the jargon of organic chemistry, NEM is a Michael acceptor, which means that it adds nucleophiles such as thiols. The resulting thioether features a strong C-S bond and the reaction is virtually irreversible. Reaction with thiols occur in the pH range 6.5–7.5, NEM may react with amines or undergo hydrolysis at a more alkaline pH. NEM has been widely used to probe the functional role of thiol groups in enzymology. NEM is an irreversible inhibitor of all cysteine peptidases, with alkylation occurring at the active site thiol group (see schematic).[3][4]
Case studies
NEM blocks vesicular transport. In lysis buffers, 20 to 25 mM of NEM is used to inhibit de-sumoylation of proteins for Western Blot analysis. NEM has also been used as an inhibitor of deubiquitinases.
N-Ethylmaleimide was used by Arthur Kornberg and colleagues to knock out DNA polymerase III in order to compare its activity to that of DNA polymerase I (pol III and I, respectively). Kornberg had been awarded the Nobel Prize for discovering pol I, then believed to be the mechanism of bacterial DNA replication, although in this experiment he showed that pol III was the actual replicative machinery.
References
- ^ N-Ethylmaleimide at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ Thiol reactive probes at Invitrogen
- ^ Nelson, D. L.; Cox, M. M. "Lehninger, Principles of Biochemistry" 3rd Ed. Worth Publishing: New York, 2000. ISBN 1-57259-153-6.
- ^ Gregory, J. D. (1955) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 77, 3922-3923
External links
Categories:- Maleimides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.