- County of Edessa
-
County of Edessa
Comitatus Edessanus← 
1098–1150  →
→
 →
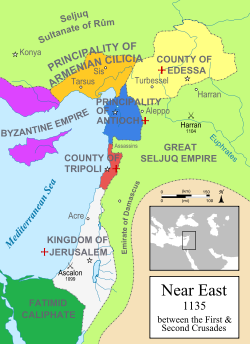
→The County of Edessa in the context of the other states of the Near East in 1135. Capital Edessa (1098-1144; 1146)
Turbessel (1144-1146; 1146-1150)Language(s) Latin, Old French, Italian, Armenian (also Arabic, Greek) Religion Roman Catholicism, Armenian Apostolic Church, Greek Orthodoxy, Syrian Orthodoxy, Islam, Judaism Government Monarchy Count - 1098–1100 Baldwin I - 1131-1150 Joscelin II Historical era High Middle Ages - First Crusade 1098 - Conquered by Nur ad-Din Zengi, and the rest sold to Manuel I Komnenos 1150 The County of Edessa was one of the Crusader states in the 12th century, based around Edessa, a city with an ancient history and an early tradition of Christianity.
Unlike the other Crusader states, the County was landlocked; it was remote from the other states and was not on particularly good terms with its closest neighbor, the Principality of Antioch. Half of the county, including its capital, was located east of the Euphrates, far to the east of the others, rendering it particularly vulnerable. The part west of the Euphrates was controlled from the stronghold of Turbessel.
Contents
Foundation
Baldwin of Boulogne entering Edessa in February 1098. He is shown being welcomed by the Armenian clergy, who welcomed the end of tutelage to Constantinople.[1]
In 1098, Baldwin of Boulogne left the main Crusading army, which was travelling south towards Antioch and Jerusalem, and went first south into Cilicia, then east to Edessa. There, he convinced its lord, Thoros, to adopt him as a son and heir. Thoros was a Christian of Armenian origin but of Greek Orthodox religion and was largely disliked by his Armenian Orthodox subjects; in March 1098 he was assassinated or abdicated (here historians conflict), although it is unknown if Baldwin had any part in whichever of the two options did happen. Nonetheless, Baldwin succeeded Thoros as ruler, taking the title of Count (having been Count of Verdun as a vassal of his brother in Europe).
In 1100, Baldwin became King of Jerusalem when his brother Godfrey of Bouillon died. The County of Edessa passed to his cousin Baldwin of Bourcq. He was joined by Joscelin of Courtenay, who became lord of the fortress of Turbessel on the Euphrates, an important outpost against the Seljuk Turks.
The Frankish lords formed a good rapport with their Armenian subjects, and there were frequent intermarriages; the first three counts all married Armenians. Count Baldwin's wife had died in Maraş in 1097, and after he succeeded to Edessa he married Arda, a granddaughter of the Armenian Roupenid chief Constantine. Baldwin of Bourcq married Morphia, a daughter of Gabriel of Melitene, and Joscelin of Courtenay married a daughter of Constantine.
Conflicts with Muslim neighbours
 Baldwin of Boulogne receiving the hommage of the Armenians in Edessa.
Baldwin of Boulogne receiving the hommage of the Armenians in Edessa.
Baldwin II quickly became involved in the affairs of northern Syria and Asia Minor. He helped secure the ransom of Bohemond I of Antioch from the Danishmends in 1103, and, with Antioch, attacked the Byzantine Empire in Cilicia in 1104. Later in 1104, Edessa was attacked by Mosul, and both Baldwin and Joscelin were taken prisoner when they were defeated at the Battle of Harran. Bohemond's cousin Tancred became regent in Edessa (although Richard of Salerno actually governed the territory), until Baldwin and Joscelin were ransomed in 1108. Baldwin had to fight to regain control of the city; Tancred was eventually defeated, though Baldwin had to ally with some of the local Muslim rulers.
In 1110, all lands east of the Euphrates were lost to Mawdud of Mosul. This was not followed by an assault on Edessa itself as the Muslim rulers were more concerned with consolidating their own power.
Baldwin II became King of Jerusalem (also as Baldwin II) when Baldwin I died in 1118. Although Eustace of Boulogne had a better claim as the late Baldwin's brother, he was in France and did not want the title. Edessa was given to Joscelin in 1119. Joscelin was taken prisoner once again in 1122; when Baldwin came to rescue him, he too was captured, and Jerusalem was left without its king. Joscelin escaped in 1123, and obtained Baldwin's release the next year.
Fall of the county
Joscelin was gravely injured during a siege in 1131 and was succeeded by his son Joscelin II. By this time, Zengi had united Aleppo and Mosul and began to threaten Edessa; meanwhile, Joscelin II paid little attention to the security of his county, and argued with the counts of Tripoli who then refused to come to his aid. Zengi besieged the city in 1144, capturing it on December 24 of that year. Joscelin continued to rule his lands west of the Euphrates, and he also managed to take advantage of the death of Zengi in September 1146 to regain and hold briefly his old capital. The city was again lost in November, and Joscelin barely escaped. In 1150 he was captured by Zengi's son Nur ad-Din, and was kept a prisoner in Aleppo until he died in 1159. His wife sold Turbessel and what was left of the County to the Byzantine Emperor Manuel I Comnenus, but these lands were conquered by Nur ad-Din and the Sultan of Rum within the year. Edessa was the first Crusader state to be created, and also the first to be lost.
Population and demographics
Edessa was one of the largest of the Crusader states in terms of territory but had one of the smallest populations. Edessa itself had about 10,000 inhabitants. The rest of the county consisted mostly of fortresses. The county's territory extended from Antioch in the west to across the Euphrates in the east at its greatest extent. It also often occupied land as far north as Armenia proper. To the south and east were the powerful Muslim cities of Aleppo and Mosul, and the Jazira (northern Iraq). The inhabitants were mostly Assyrian Syriac Orthodox, and Armenian Orthodox Christians, with some Greek Orthodox and Arab Muslims. Although the numbers of Latins always remained small, there was a Roman Catholic Patriarch. The fall of the city was the catalyst for the Second Crusade in 1146.
Vassals of Edessa
Lordship of Turbessel
Turbessel was firstly the lordship of Joscelin I when he was not yet the Count of Edessa. It controlled the area west of the Euphrates, and held the border against Antioch. It then was a special holding of Courtenay counts of Edessa, and again became their seat after the loss of the city of Edessa. It was sold with the remaining parts of the County to the Byzantines just before it was conquered by Muslims. After the sale, the wife and family of Joscelin II moved with the proceeds to the Kingdom of Jerusalem, near Acre.
Counts of Edessa, 1098–1150
- Baldwin I 1098–1100
- Baldwin II 1100–1118
- Tancred, Prince of Galilee regent (with Richard of Salerno as governor, 1104–1108)
- Joscelin I 1118–1131
- Joscelin II 1131–1150 (d.1159)
- Joscelin III, titular Count from 1159
References
- ^ "Les Croisades, Origines et consequences", Claude Lebedel, p.50
Crusader States Levant Kingdom of Jerusalem · Principality of Antioch · County of Edessa · County of Tripoli · Kingdom of Cilicia · Kingdom of CyprusLatin Greece Baltic Crusades Portal Medieval states in Anatolia Ahis • Aq Qoyunlu • Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia • Alaiye • Artuqids • Aydinids • Isfendiyarids • Tzachas • Chobanids • Beylik of Çubukoğulları • Danishmends • Beylik of Demleç • Dulkadirids • Eretnids • Beylik of Erzincan • Eshrefids • Germiyanids • Hamidids • Beylik of İnal • Kadi Burhan al-Din • Karamanids • Karasids • Beylik of Lâdik • Mengujekids • Menteşe • Pervâneoğlu • Ramadanids • Sahib Ataids • Saltukids • Sarukhanids • Ahlatshahs • Beylik of Tanrıbermiş • Beylik of Teke • Beyliks of Canik • Byzantine Empire • County of Edessa • Emirate of Armenia • Empire of Nicaea • Empire of Trebizond • Kara Koyunlu • Latin Empire • Ottoman Empire • Principality of Antioch • Sultanate of RumCategories:- Former monarchies
- Former countries in the Middle East
- States and territories established in 1098
- States and territories disestablished in 1150
- Counts of Edessa
- County of Edessa
- 1st house of Courtenay
- Byzantine Empire successor states in Anatolia
- States in medieval Anatolia
- Crusader states
- History of Şanlıurfa Province
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.