- North Reef Light
-
North Reef Light 
North Reef Light from the air, 2007 Location North Reef, Queensland, Australia Coordinates 23°11′07.36″S 151°54′13.67″E / 23.1853778°S 151.9037972°ECoordinates: 23°11′07.36″S 151°54′13.67″E / 23.1853778°S 151.9037972°E Year first constructed 1878 Construction timber frame clad with galvanised wrought iron Tower shape conical Markings / pattern white, red dome Height 80 feet (24 m)[1] Focal height 75 feet (23 m) Current lens VRB-25 Intensity 35,050 cd Range 17 nautical miles (31 km; 20 mi) Characteristic Fl.(2)W. 15s Racon Q Admiralty number K3014 NGA number 111-10312 ARLHS number AUS-122 North Reef Light is an active lighthouse located on North Reef, a 5.6 square kilometres (2.2 sq mi) planar reef,[2] about 120 kilometres (75 mi) northeast of Gladstone, Queensland, Australia. The lighthouse was constructed on a migratory patch of sand inside a fringing coral reef, which over the years disappeared and reappeared, as sand was washed away and accumulated, and is now a vegetated sandy island. Its construction is unique, having a hollow concrete base that both gives it resistance to the shifting nature of the sandbar and serves as a fresh water tank.[3] As such, it is considered one of the major achievement in Australian lighthouse construction.[4] It is also notable in that due to the harsh conditions, only bachelors were allowed to serve as lighthouse keepers.[3] At 24 metres (79 ft) it is also the tallest of Queensland's timber framed iron clad lighthouses.[5]
Contents
History
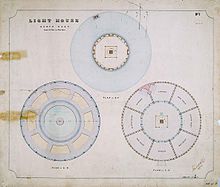
The recommendation to establish a lighthouse on North Reef was made by a select parliamentary committee in 1864. The site was then a small sandbank on a coral reef. The proposal called for a cast iron cylindrical tower, 12 metres (39 ft) in diameter and 15 metres (49 ft) tall, which would rest on the coral, penetrating the sand. A hollow base would be formed by pouring concrete into the cylinder, which would also serve as a fresh water tank, and the residence will surround it.[4] Tenders were called in January 1876, and the winning offer was for £7,964 by Walker and Company of Maryborough. Construction was to be completed in by July 1877 but delays, first in approval of the money and then in construction, delayed the completion until November 1878.[4]
The base of the tower, 13 metres (43 ft) in diameter and 4.6 metres (15 ft) high, was constructed of bolted cast iron segments.[5] Both the tower and the dwellings were constructed of timber frame, clad in galvanized iron.[4] The original optical apparatus was a second order lens.[5]
Conditions at the lighthouse were harsh. The location is remote, the quarters were cramped, and the shifting sands sometimes left the lighthouse surrounded by water. The lighthouse keepers chosen were therefore only single, unmarried men.[3][5]
The light source was upgraded twice, in 1923 and in 1929.[4] In 1977 the light was converted to electricity[4] and it was demanned in January 1978.[6] The final upgrade was on 28 September 1987 when the light was converted to solar power[6] and six solar panels were installed on the roof of the quarters, facing north.[4]
Current display
The current light characteristic is two white flashes, separated by five seconds, every 15 seconds (Fl.(2)W. 15s), visible for 17 nautical miles (31 km; 20 mi). A racon on the tower transmits morse code "Q" (– – • –).[7] The apparatus is a VRB-25, rotating at 2 rpm, and the light source is a 12 Volt 35 Watt Halogen lamp with an intensity of 35,050 cd.[6]
Structure
As mentioned above, the lighthouse base is made of bolted cast iron segments, 13 metres (43 ft) in diameter and 4.6 metres (15 ft) high.[5] The tower is 18 metres (59 ft) from the base to the lantern[6], conical in shape, with four intermediate floor levels.[5] It is built of an internal timber frame, clad with galvanised wrought iron plates,[8] painted white.[9] On top of the tower is a Chance Brothers 10 feet 9 inches (3.28 m) diameter lantern, housing the VRB-25 beacon.[6] The dome of the lantern is painted red.[9]
The lighthouse keepers' residence surrounds the base of the tower. They comprise a ring of eight rooms, three bed rooms, two sitting rooms, two kitchens, and a store room. They are constructed of a timber frame with galvanised iron roof. The external walls are covered with corrugated galvanised iron sheets.[5]
Site operation and visiting
The site and the light are operated by the Australian Maritime Safety Authority. The island is accessible by boat, but both the site and the light are closed to the public.[9]
See also
- List of lighthouses and lightvessels in Australia
Wikimedia Commons has media related to: Notes
- ^ List of Lights. Rowlett lists a close "24 m (78 ft)".
- ^ "AIMS Research - Reef Monitoring". data.aims.gov.au. http://data.aims.gov.au/reefpage2/reefpage.jsp?fullReefID=23045A. Retrieved 23 February 2011.
- ^ a b c Lighthouses of Australia Inc.
- ^ a b c d e f g AHD16455.
- ^ a b c d e f g Marquis-Kyle 2009, p. 4.
- ^ a b c d e AN376-01.
- ^ List of Lights
- ^ Marquis-Kyle 2009, pp. 1,4.
- ^ a b c Rowlett.
References
- (PDF) List of Lights, Pub. 111, The West Coasts of North and South America (Excluding Continental U.S.A. and Hawaii), Australia, Tasmania, New Zealand, and the Islands of the North and South Pacific Oceans. List of Lights. United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. 2010. p. 205. http://msi.nga.mil/MSISiteContent/StaticFiles/NAV_PUBS/NIMA_LOL/Pub111/Pub111bk.pdf.
- Rowlett, Russ. "Lighthouses of Australia: Queensland's East Coast". The Lighthouse Directory. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. http://www.unc.edu/~rowlett/lighthouse/qld.htm. Retrieved 2010-11-14.
- "North Reef Light , QLD, AN376-01". Aids to Navigation Schedule Issue 14. Australian Maritime Safety Authority. September 2006. http://www.amsa.gov.au/drawingregister/drawings/ans/AN376-01.pdf.
- "The North Reef Lighthouse". Lighthouses of Queensland. Lighthouses of Australia Inc. http://www.lighthouse.net.au/lights/QLD/North%20Reef/North%20Reef.htm.
- "North Reef Lightstation, North Reef via Curtis Island, QLD, Australia (entry AHD16455)". Australian Heritage Database. Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population and Communities. http://www.environment.gov.au/cgi-bin/ahdb/search.pl?mode=place_detail;place_id=16455.
- Marquis-Kyle, Peter (November 2009). "Queensland’s timber and iron lighthouses: 19th century colonial innovation". 3rd Australasian Engineering Heritage Conference. Dunedin, New Zealand. http://www.ipenz.org.nz/heritage/conference/papers/Marquis-Kyle_P.pdf.
External links
- Searle, Garry. "List of Lighthouses - Queensland". Lighthouses of Australia. SeaSide Lights. http://www.seasidelights.com.au/state.asp?fState=QLD.
Lighthouses of Queensland South East Coast Point Danger • Cleveland Point • Moreton Bay Pile • Bulwer Island • Old Caloundra • New Caloundra • Point Cartwright • Double Island Point
Central Coast Sandy Cape • Lady Elliot Island • Old Burnett Heads • New Burnett Heads • Bustard Head • North Reef • Sea Hill • Cape CapricornNorth Coast Flat Top Island • Pine Islet • Creal Reef • Dent Island • Cape Bowling Green • Cape Cleveland • Bay RockFar North Coast Fitzroy Island • Low Isles • Grassy Hill • Archer Point • Wharton ReefTorres Strait Wyborn Reef • Eborac Island • Goods Island • Booby IslandSee also: List of lighthouses and lightvessels in AustraliaCategories:- Buildings and structures completed in 1878
- Lighthouses in Queensland
- Register of the National Estate
- Commonwealth Heritage List
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.