- 1954 FIFA World Cup Final
-
1954 FIFA World Cup Final Event 1954 FIFA World Cup West Germany Hungary 

3 2 Date 4 July 1954 Venue Wankdorf Stadium, Bern Referee William Ling (England) Attendance 64,000 ← 19501958 →The 1954 FIFA World Cup Final was the final match of the 1954 FIFA World Cup, the fifth FIFA World Cup. The match was played at the Wankdorf Stadium in Bern, Switzerland, on 4 July 1954. The game saw the underdogs West Germany beat the largely favoured Hungary 3–2. In Germany, it is referred to as "Das Wunder von Bern" ("The Miracle of Bern"). The game was the subject of a 2003 German film of the same name.
Contents
Pre-Final Team Status
Hungary
Hungary were favourites to win the 1954 Tournament. In the five years prior to the World Cup 1954 they had remained unbeaten in 32 games, were reigning Olympic Champions and winners of the Central European International Cup in 1953. In 1953 they had defeated England 6–3, becoming the first non-UK team to beat them at Wembley Stadium, and had thrashed England 7-1 in Budapest just before the World Cup.
Hungary and West Germany had already met in the group stage, with Hungary winning 8–3. In the game, Hungarian captain Ferenc Puskás suffered a hairline fracture of the ankle and subsequently missed the next two games; even without him, Hungary beat Brazil (the previous World Cup runners-up) and Uruguay (the World Cup holders) in the quarter final and semi final respectively.
Puskas was still not fully recovered by the final, but manager Gustav Sebes selected him anyway.
The Hungarians' emphatic 8-3 victory over West Germany in the group stages was seen as a firm indication of the likely final scoreline.
West Germany
After the Second World War, the three German states (West and East Germany and the Saar) were not allowed to compete in the 1950 World Cup; as a consequence, the qualification games for the 1954 World Cup were the first return of West Germany national squad to international competitions.
In the 8-3 group game defeat to Hungary, German coach Herberger fielded a reserve team. By not fielding his strongest eleven players, Herberger managed to obscure the real strength of the German team.
The Match
The match was played in heavy rain, weather conditions the German side had christened "Fritz Walter-weather",[1] as the German team captain Fritz Walter was known for playing his best football under those conditions. In addition, the Germans were equipped with footwear supplied by adidas, which had produced a hitherto unheard of design of boot with exchangeable, screw-in studs that could be adapted to any weather. This enabled the German players to wear their regular boots despite the adverse weather.
Although he was not fully fit in time, Ferenc Puskás was back in the Hungarian lineup for the final match, and he put his team ahead after only six minutes. When Zoltán Czibor added the second goal for Hungary a mere two minutes later, the pre-tournament favourites seemed destined to ease to victory over Germany, just as they had in the group stages
However, Germany equalised quickly, with goals from Max Morlock (10') and Helmut Rahn (18'). Having leveled the scores, the Germans now looked a match for the Hungarians and managed to reach half time at 2–2, with both teams several promising chances to take the lead. In the second half, the Hungarians poured forward looking to retake the lead, but their attempts were repeatedly foiled by the German defence, with goalkeeper Toni Turek pulling off several fine saves.[2]
With six minutes left, German striker Helmut Rahn scored West Germany's third goal. Two minutes before the end, Puskás appeared to equalise once more, but he was ruled off-side by the Welsh linesman Benjamin Griffiths. The match and Hungary’s unbeaten run ended in one of the biggest upsets in the history of football.
Controversies
Three controversial calls surround this final game, each favouring the German team. Firstly, Hungarian goalkeeper Grosics was allegedly interfered with in the goal area by Hans Schäfer for the second German goal; secondly, Puskás apparently equalised the match in the 89th minute but from an offside position; the third was an alleged foul on Kocsis in the penalty area in the final minute.
Germans brutally beat Ferenc Puskás resulting in a ankle fracture.
A study conducted by the University of Leipzig has revealed that the victorious German national squad may have been injected with methamphetamine prior to the match. The players believed they were being injected with Vitamin C. The study, entitled, "Doping in Germany" was sponsored by the German Olympic Committee. [3]
Impact on German history
The unexpected win evoked a wave of euphoria throughout Germany, which was still suffering in the aftermath of World War II. This was also the first time since the Second World War that the German national anthem was played in public.[4] The 1954 victory is regarded as a turning point in post-war German history by German historians Arthur Heinrich and Joachim Fest.[citation needed]
As television was only available to few homes or public places in Germany, a German radio commentator Herbert Zimmermann became a popular German personality due to his reports. His emotional reporting style ("Halten Sie mich für verrückt, halten Sie mich für übergeschnappt" - "call me crazy, call me nuts") and especially his comments when Germany scored the winning goal ("Aus dem Hintergrund müsste Rahn schießen, Rahn schießt - TOR, TOR, TOR!" - "Rahn has to shoot from the background, Rahn shoots - goal, goal, goal!"),[4] and after the final whistle ("AUS! AUS! AUS! Das Spiel ist aus. Deutschland ist Weltmeister, schlägt Ungarn 3 zu 2!" - "Over! Over! Over! The game is over! Germany are World Champions, beat Hungary 3–2!") are well known in Germany.
Match summary
4 July 1954
17:00 (CET)West Germany 
3 – 2  Hungary
HungaryWankdorf Stadium, Bern
Attendance: 64,000
Referee: William Ling (England)Morlock  10'
10'
Rahn 18', 84'
18', 84'Report Puskás  6'
6'
Czibor 8'
8'
WEST GERMANY:GK 1 Toni Turek RB 7 Josef Posipal LB 3 Werner Kohlmeyer RH 6 Horst Eckel CH 10 Werner Liebrich LH 8 Karl Mai IR 13 Max Morlock IL 16 Fritz Walter (c) RW 12 Helmut Rahn CF 15 Ottmar Walter LW 20 Hans Schäfer Manager: Sepp Herberger 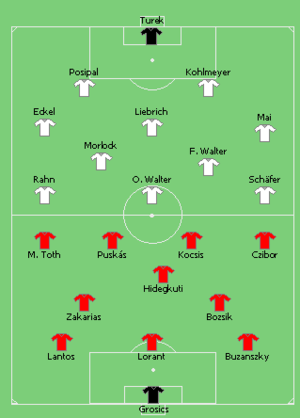

HUNGARY:GK 1 Gyula Grosics RB 2 Jenő Buzánszky CB 3 Gyula Lóránt LB 4 Mihály Lantos HB 5 József Bozsik HB 6 József Zakariás SS 9 Nándor Hidegkuti RW 11 Zoltán Czibor CF 8 Sándor Kocsis CF 10 Ferenc Puskás (c) LW 20 Mihály Tóth Manager: Gusztáv Sebes Assistant referees:
 Vincenzo Orlandini
Vincenzo Orlandini
 Sandy Griffiths
Sandy GriffithsReferences
- ^ Wessel, Markus. "Hoch gepokert und gewonnen" (in German). ARD. Archived from the original on 2009-09-03. http://web.ard.de/special/helden1954/pages/2437.php?ch=1/. Retrieved 23 August 2009.
- ^ Video clip on YouTube
- ^ "Researcher raises doping spectre over 1954 WCup". USA Today. 26 October 2010. http://www.usatoday.com/sports/soccer/2010-10-26-3288531362_x.htm.
- ^ a b "Das Trauma von Bern: Die unbekannte Seite des legendären Endspiels" (in German). Norddeutscher Rundfunk. 22 February 2004. Archived from the original on 2009-09-03. http://www.ndrtv.de/kulturreport/traumavonbern.html. Retrieved 24 August 2009.
External links
- Official FIFA match report - fifa.com, FIFA, 2002.
- "Mourning the Miracle of Bern"
1954 FIFA World Cup Stages General information 1954 FIFA World Cup finalists Champions Runners-up Third place Fourth place Eliminated in the quarter-finals Eliminated in the group stage FIFA World Cup Tournaments - Uruguay 1930
- Italy 1934
- France 1938
- Brazil 1950
- Switzerland 1954
- Sweden 1958
- Chile 1962
- England 1966
- Mexico 1970
- West Germany 1974
- Argentina 1978
- Spain 1982
- Mexico 1986
- Italy 1990
- United States 1994
- France 1998
- South Korea & Japan 2002
- Germany 2006
- South Africa 2010
- Brazil 2014
- Russia 2018
- Qatar 2022
Finals Squads Qualification Other articles - Awards
- Balls
- Broadcasters
- Droughts
- Finals
- Goalscorers
- Hat-tricks
- History
- Hosts
- Mascots
- Milestone goals
- Official songs
- Penalty shoot-outs
- Qualification
- Records
- Red cards
- Referees
- Team appearances
- Trophy
- Video games
1Decisive match of a final group stage. 2No qualification took place as places were given by invitation only.Germany team (background) Results by years 1920–1929 · 1930–1939 · 1940–1949 · 1950–1959 · 1960–1969 · 1970–1979 · 1980–1989 · 1990–1999 · 2000–2009 · 2010–2019Famous Matches 1954 World Cup Final (West Germany vs Hungary) · 1966 World Cup Final (England vs West Germany) · 1970 World Cup Game of the Century (Italy vs West Germany) · 1972 EURO Final (USSR vs West Germany) · 1974 World Cup Final (Netherlands vs West Germany) · 1976 EURO Final (Czechoslovakia vs West Germany) · 1978 FIFA World Cup (Austria vs West Germany) · 1980 EURO Final (West Germany vs Belgium) · 1982 FIFA World Cup Shame of Gijón (West Germany vs Austria) · 1982 World Cup Semi Final (West Germany vs France) · 1982 World Cup Final (Italy vs West Germany) · 1986 World Cup Final (Argentina vs West Germany) · 1990 World Cup Final (West Germany vs Argentina) · 1992 EURO Final (Denmark vs Germany) · 1996 EURO Final (Czech Republic vs Germany) · FIFA World Cup 2002 Qualifying (England vs Germany) · FIFA World Cup 2002 Qualifying (Germany vs England) · 2002 World Cup Final (Germany vs Brazil) · 2008 EURO Final (Germany vs Spain)Related articles Obtained titles Categories:- 1954 FIFA World Cup
- FIFA World Cup Finals
- Germany national football team matches
- Hungary national football team matches
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


