- Cacodylic acid
-
Cacodylic acid 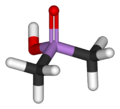
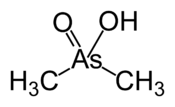 Dimethylarsinic acidOther namesDimethylarsenic acid, Cacodylic acid, Hydroxydimethylarsine oxide, Arsecodile, Ansar, Silvisar, Phytar 560, DMAA, UN 1572
Dimethylarsinic acidOther namesDimethylarsenic acid, Cacodylic acid, Hydroxydimethylarsine oxide, Arsecodile, Ansar, Silvisar, Phytar 560, DMAA, UN 1572Identifiers CAS number 75-60-5 
PubChem 2513 ChemSpider 2418 
UNII AJ2HL7EU8K 
EC number 200-883-4 DrugBank DB02994 KEGG C07308 
ChEBI CHEBI:29839 
RTECS number CH7525000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=[As](O)(C)C
Properties Molecular formula C2H7AsO2 Molar mass 137.9977 g/mol Appearance White crystals or powder Density > 1.1 g/cm3 Melting point 192 - 198 °C
Boiling point > 200 °C
Solubility in water 667 g/l Acidity (pKa) 6.3 Hazards MSDS External MSDS EU classification  T+
T+R-phrases R26/27/28, R40  acid (verify) (what is:
acid (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Cacodylic acid is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3)2AsO2H. Derivatives of cacodylic acid, cacodylates, were frequently used as herbicides. For example, "Agent Blue," one of the chemicals used during the Vietnam War, is a mixture of cacodylic acid and sodium cacodylate. Sodium cacodylate is frequently used as a buffering agent in the preparation and fixation of biological samples for electron microscopy.
Contents
History
Significant early research into cacodyls was done by Robert Bunsen at the University of Marburg. Bunsen said of the compounds, "the smell of this body produces instantaneous tingling of the hands and feet, and even giddiness and insensibility...It is remarkable that when one is exposed to the smell of these compounds the tongue becomes covered with a black coating, even when no further evil effects are noticeable". His work in this field led to an increased understanding of the methyl radical.
Cacodyloxide, ((CH3)2As)2O, is often considered the first organometallic compound to be prepared synthetically.
Synthesis and reactions
In the 18th century it was known that combining As2O3 and four equivalents of potassium acetate (CH3CO2K) gives a product called "Cadet's fuming liquid" which contains cacodyl oxide, ((CH3)2As)2O and cacodyl, ((CH3)2As).
Cacodylic acid can be reduced to dimethylarsine (III) derivatives, which are versatile intermediates for the synthesis of other organoarsenic compounds:[1][2]
- (CH3)2AsO2H + 2 Zn + 4 HCl → (CH3)2AsH + 2 ZnCl2 + 2 H2O
- (CH3)2AsO2H + SO2 + HI → (CH3)2AsI + SO3 + H2O
Health effects
Cacodylic acid is highly toxic by ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact. Once thought to be a byproduct of inorganic arsenic detoxification, it is now believed to have serious health consequences of its own. It has been shown to be teratogenic in rodents, most often causing cleft palate but also fetal fatality at high doses. It has been shown to be genotoxic in human cells, causing apoptosis and also decreased DNA production and shorter DNA strands. While not itself a strong carcinogen, cacodylic acid does promote tumors in the presence of carcinogens in organs such as the kidneys and liver.
See also
References
- ^ Feltham, R. D.; Kasenally, A. and Nyholm, R. S., "A New Synthesis of Di- and Tri-Tertiary Arsines", Journal of Organometallic Chemistry, 1967, volume 7, 285-288.
- ^ Burrows, G. J. and Turner, E. E., "A New Type of Compound containing Arsenic", Journal of the Chemical Society Transactions, 1920, 1374-1383
- Kenyon, E. M.; Hughes, M. F. (2001). "A Concise Review of the Toxicity and Carcinogenicity of Dimethylarsenic Acid". Toxicology 160 (1-3): 227–236. doi:10.1016/S0300-483X(00)00458-3.
- Elschenbroich, C; Salzer, A. (1992) Organometallics, 2nd Edition
- Bunsen Biography
External links
Categories:- Arsenical herbicides
- Arsinic acids
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
