- Dhanyasi
-
Carnatic Music Concepts Sruti • Swara • Raga • Tala • Melakarta • Asampurna Melakarta
Compositions Varnam • Kriti • Geetham • Swarajati • Ragam Thanam Pallavi • Thillana
Instruments melody: Vocals • Saraswati veena • Venu • Violin • Chitra veena • Nadaswaram • Mandolin
rhythm: Mridangam • Ghatam • Morsing • Kanjira • Thavil
drone: Tambura • Shruti box
Composers Dhanyasi (pronounced dhanyāshi, Sanskrit: धन्याशि, Tamil: தன்யாசி) is a rāgam in Carnatic music (musical scale of South Indian classical music). It is a janya rāgam (derived scale) from the 8th melakarta scale Hanumatodi. It is a janya scale, as it does not have all the seven swaras (musical notes) in the ascending scale. It is a combination of the pentatonic scale Shuddha Dhanyasi and the sampurna raga scale Hanumatodi.[1]
This is the common and popular scale and is used for portraying the bhakthi rasa.[1] According to the Muthuswami Dikshitar school, there exists a scale with same name, Dhanyasi, which is derived from Natabhairavi melakarta scale, instead of Hanumatodi scale.[2] This scale is less popular and has far less compositions set to it.
Contents
Structure and Lakshana
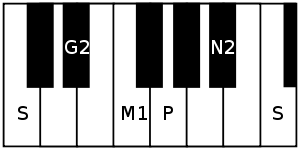
Dhanyasi is an asymmetric rāgam that does not contain rishabham or dhaivatam in the ascending scale. It is an audava-sampurna rāgam (or owdava rāgam, meaning pentatonic ascending scale).[1][2] Its ārohaṇa-avarohaṇa structure (ascending and descending scale) is as follows:
The notes used in this scale are shadjam, sadharana gandharam, shuddha madhyamam, panchamam and kaishiki nishadham in ascending scale, with shuddha dhaivatam and shuddha rishabham included in descending scale. For the details of the notations and terms, see swaras in Carnatic music.
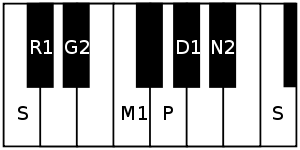
The rāgam used by Dikshitar school of music uses chathusruti dhaivatam (D2) in the descending scale, in place of shuddha dhaivatam (D1), bringing it under the 20th melakarta Natabhairavi.[2]
Popular compositions
There are many compositions set to Dhanyasi rāgam.
- Sangeeta gnanamu and Nee chitthamu composed by Tyagaraja
- Kalayami sriramam by Swati Tirunal
- Chudamanikanda by Arunachala Kavi
- Nammina varini by Bhadrachala Ramadas
- Dasara nindisabeda by Purandara Dasa
- Vani arul purivai by Papanasam Sivan
- Sri Ranganathaya namasthe and Mayuranatham anisham by Muthuswamy Dikshitar
- Meenalochana brova by Shyama Shastri
Related rāgams
This section covers the theoretical and scientific aspect of this rāgam.
Scale similarities
- Udayaravichandrika, also known as Shuddha Dhanyasi has a symmetric pentatonic scale, with the notes same as the ascending scale of Dhanyasi. Its ārohaṇa-avarohaṇa structure is S G2 M1 P N2 S : S N2 P M1 G2 S
- Dhanyasi scale as per Dikshitar school uses chatusruti dhaivatam in descending scale in place of the shuddha dhaivatam. Its ārohaṇa-avarohaṇa structure is S G2 M1 P N2 S : S N2 D2 P M1 G2 R1 S
References
- ^ a b c Ragas in Carnatic music by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications
- ^ a b c Raganidhi by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras
Melakarta Ragas Shuddha
Madhyama
RagasIndu chakraNetra chakraAgni chakra13. Gayakapriya · 14. Vakulabharanam · 15. Mayamalavagowla · 16. Chakravakam · 17. Suryakantam · 18. HatakambariVeda chakra19. Jhankaradhvani · 20. Natabhairavi · 21. Keeravani · 22. Kharaharapriya · 23. Gourimanohari · 24. VarunapriyaBana chakra25. Mararanjani · 26. Charukesi · 27. Sarasangi · 28. Harikambhoji · 29. Dheerasankarabharanam · 30. NaganandiniRitu chakra31. Yagapriya · 32. Ragavardhini · 33. Gangeyabhushani · 34. Vagadheeswari · 35. Shulini · 36. ChalanataPrati
Madhyama
RagasRishi chakraVasu chakra43. Gavambhodi · 44. Bhavapriya · 45. Shubhapantuvarali · 46. Shadvidamargini · 47. Suvarnangi · 48. DivyamaniBrahma chakra49. Dhavalambari · 50. Namanarayani · 51. Kamavardani · 52. Ramapriya · 53. Gamanashrama · 54. VishwambariDisi chakra55. Shamalangi · 56. Shanmukhapriya · 57. Simhendramadhyamam · 58. Hemavati · 59. Dharmavati · 60. NeetimatiRudra chakra61. Kantamani · 62. Rishabhapriya · 63. Latangi · 64. Vachaspati · 65. Mechakalyani · 66. ChitrambariAditya chakra67. Sucharitra · 68. Jyoti swarupini · 69. Dhatuvardani · 70. Nasikabhushani · 71. Kosalam · 72. RasikapriyaJanya Ragas A-D Abheri · Abhogi · Andolika · Amritavarshini · Anandabhairavi · Arabhi · Atana · Bhairavi · Bhupalam · Bilahari · Devagandhari · DhanyasiG-K M-N Madhuvanti · Madhyamavati · Malahari · Malayamarutam · Mohanakalyani · Mohanam · Nagasvaravali · NiroshtaR-S Ranjani · Revati · Sahana · Saramati · Saveri · Shivaranjani · Shuddha Saveri · Shree ranjani · SunadavinodiniU-V Udayaravichandrika (Shuddha Dhanyasi) · ValajiCategories:- Carnatic Ragas
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.