- Spitz nevus
-
Spitz nevus Classification and external resources 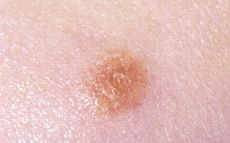
Spitz nevusICD-10 D22 (ILDS D22.L32) ICD-O: M8770/0 DiseasesDB 29807 eMedicine article/1059623 MeSH D018332 A Spitz nevus (also known as an "Epithelioid and spindle-cell nevus,"[1] "Benign juvenile melanoma"[1]:691, and "Spitz's juvenile melanoma"[2]) is a benign melanocytic nevus, a type of skin lesion, affecting the epidermis and dermis.[3]
Spitz nevus is also known as spindle and epithelioid cell nevus and juvenile melanoma. The latter term is generally no longer used as it is misleading: it is not a melanoma, it is a benign lesion; it can also occur in adults, not only in children.[4]
Contents
Epidemiology
Spitz nevi are uncommon. Their annual incidence was estimated in a coastal population of sub-tropical Queensland to be 1.4 cases per 100,000 people. For comparison, the annual incidence of melanoma in the same population, which is high by world standards [5] is 25.4 cases per 100,000 people.[4]
Whilst they are most commonly found on people in their first two decades of life[3], the age range for people with Spitz nevi is from six months to 71 years, with a mean age of twenty-two years and a median age of nineteen years. [4]
Pathology
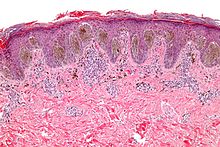 Micrograph of a Spitz nevus showing the characteristic vertically arranged nests of cells ("hanging bananas"). H&E stain.
Micrograph of a Spitz nevus showing the characteristic vertically arranged nests of cells ("hanging bananas"). H&E stain.
The cause of Spitz nevi is not yet known. There is an association with sunburn, but causation is not established. [3] Genetic studies of Spitz nevi have shown that most cells have the normal number of chromosomes, however a minority (25%) of cells have been shown to contain extra copies of parts of some chromosomes, such as the short arm of chromosome 11 (11p). [3]
Spitz nevi characteristically have vertically arranged nests of nevus cells that have both a spindled and an epithelioid morphology. Apoptotic cells may be seen at the dermal-epidermal junction. The main histologic differential diagnoses are pigmented spindle cell nevus and malignant melanoma.
Eponym
The lesion is named after Dr.Sophie Spitz, the pathologist who originally described it in 1948.[6]
See also
References
- ^ a b James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. pp. 1728–30. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
- ^ a b c d LeBoit, PE, Burg G, Weedon D, Sarasin A. (Eds) World Health Organization Classification of Tumours: Pathology and Genetics of Skin Tumours. Lyon: IARCPress. 2006.
- ^ a b c Crotty, K. Spitz Naevus: Histological features and distinction from malignant melanoma. Australasian Journal of Dermatology. 38 (suppl): S49-S53. 1997.
- ^ Ries LAG, et al., eds. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2000. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; 2003: Tables XVI-1-9.
- ^ Spitz S. Melanomas of childhood. Am. J. Pathol.1948;24:591-609.
Gonadal tumors, paraganglioma, and glomus (ICD-O 8590-8719) Gonadal/
sex cord-gonadal stromal (8590-8679)sex cord (Granulosa cell tumour, Sertoli cell tumor)
stroma (Thecoma, Leydig cell tumor)
both (Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour, Luteoma)Paragangliomas And
Glomus tumors (8680-8719)Neuroendocrine tumor: Paraganglioma (Pheochromocytoma)
Vascular tissue neoplasm: Glomus tumor (Glomangiosarcoma)M: NEO
tsoc, mrkr
tumr, epon, para
drug (L1i/1e/V03)
Tumors: Skin neoplasm, Nevi and melanomas (C43/D22, 172/216, ICD-O 8720-8799) Melanoma Mucosal melanoma · Superficial spreading melanoma · Nodular melanoma · lentigo (Lentigo maligna/Lentigo maligna melanoma, Acral lentiginous melanoma)Amelanotic melanoma · Desmoplastic melanoma · Melanoma with features of a Spitz nevus · Melanoma with small nevus-like cells · Polypoid melanoma · Soft-tissue melanomaNevus/
melanocytic nevusNevus of Ito/Nevus of Ota · Compound nevus · Spitz nevus (Pigmented spindle cell nevus) · Halo nevus · Pseudomelanoma
Blue nevus (Blue nevus of Jadassohn–Tièche, Cellular blue nevus, Epithelioid blue nevus, Deep penetrating nevus, Amelanotic blue nevus, Malignant blue nevus)
Congenital melanocytic nevus (Giant pigmented nevus, Medium-sized congenital nevocytic nevus, Small-sized congenital nevocytic nevus)
Balloon cell nevus · Dysplastic nevus/Dysplastic nevus syndrome
This cutaneous condition article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
