- Demographic history of Bosnia and Herzegovina
-

This article is part of the series:
Bosnia and Herzegovina- History
- Politics
- President
- Council of Ministers
- Government
- Parliament
- Elections
- Foreign relations
- Subdivisions
- Economy
- Military
- Communications
- Radio
- Television
- Culture
- Demographics
- Demographic history
- Transport
- Geography
This article is about the Demographic history of Bosnia and Herzegovina, and deals with the country's documented demographics over time. For an overview of the various ethnic groups and their historical development, see Nations of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Prehistoric
The oldest traces of mankind in Bosnia and Herzegovina were during the Paleolithic period near Doboj, Prnjavor and in the Valley of the River of Usora. During the Neolithic period there were three cultural zones: the Adriatic in Herzegovina; the Pannonian-Balkan in Bosnia and the transitional zone between the two in the headwaters of the river of Bosnia. Bosnia and Herzegovina is full of archaeological foundings from the Bronze to Iron Age. Throughout the Classical Age cultural and civilization layers of the Illyrians (Daorsi in eastern Herzegovina, Ardiaei, Sardeates, Japodi, etc.), Celts, Teutons, Huns, Ostrogoths and others were formed, though the majority of the populace was Romanized during the conquests at the beginning of the New Era. The Eastern Goths thrust into the area during the early Middle Ages, while Avars and Slavs came in the 6th century.
Kingdom of Bosnia
Due to a variety of factors (such as frequent boundary shifts and a relative isolation from the rest of Europe) there are no detailed statistics dealing with Bosnia's population during the Middle Ages. It is generally estimated that the population of the Kingdom of Bosnia at the height of its power was between 500,000 and 1,000,000 people[1]] There were very few significant urban centers in Bosnia at this time, and even these paled in comparison to the far more urbanized areas along the nearby Dalmatian coast. Among the more notable cities were Jajce, Srebrenica, and Visoko. The overwhelming majority of the population was rural and the social organization of Medieval Bosnia developed into what was called Zadruga. In this system, communities were organized by a few families of common interests usually situated in a cluster housing formation. Leaders of the community were selected according to their age and high ethical standards. Zadruga was primarily an agrarian community greatly dependent on natural resources.
Migrations and other
Throughout the 15th–19th centuries there were many demographic changes. Frequent wars, religious persecutions, rebellions, uprisings, taking of children as tribute, high tributes, high taxes, years of bad crops, epidemics, violence, and oppression have caused a high mortality rate and suffering of the whole population and instigated the migration flows that changed the ethnic structure of the population. So, with arrival of Ottoman empire coincided with the process of Christian population emigration from these regions, which has remained the main feature of the demographic development of the population of Bosnia and Herzegovina until the present day. At the same time, intense internal shifting of the population together with recurrent migrations and also immigrations changed the distribution of some ethnic groups in Bosnia and Herzegovina in the Ottoman period. The later stages saw particularly Muslim migrations from the region.
In the Bosnia proper the population started to move out first from lower regions (Posavina and the river valleys) and then from highlands. The most intensive migration flows originated in the karst Dinaric regions of Herzegovina and western Bosnia. For centuries, the population from these regions, mostly Christian, headed towards sourounding countries):
- The migrations from Western Bosnia (from Glamoč and Unac, Kupres, Grahovo) were heading towards Lika, Croatia proper, and Slovenia, and steady emigration flows from Bosnia and Herzegovina, Dalmatia, and Lika headed towards Slavonia, Syrmia, Banat, Bačka, and Baranja.
- Migrations from the southern Dinaric region of Bosnia and Herzegovina headed towards Dalmatia. Jovan Cvijić states that the first migrations to Dalmatia from the Dinaric hinterland started already at the end of the 12th century, and they became stronger in the Ottoman period from the 15th to the 18th century. Also these migrations shifted the medieval population of Dalmatia that had previously migrated mostly towards Croatia, Slavonija, and Italy. According to Cvijić, almost all of the population of Makarska, Omiš, Split, Šibenik and Bukovica originated from Bosnia and Herzegovina.
- Of the Herzegovina origin were the inhabitants of the city of Dubrovnik and the vicinity, while the population of the Bay of Kotor originated from the Montenegrin and Herzegovina Dinaric regions.
Throughout the 15th–19th centuries, with coming of the Ottoman empire on the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina the first significant demographic change took place as almost all followers of than Bosnian Church converted to Islam as a method of keeping the ownership of the land they owned before the Ottoman conquest. Their conversions were also of a political nature; while Orthodox and Catholic portions of the Bosnian population had their base in the Serbian Orthodox Church and Catholic Church, Bosnian church followers had no representation on a larger geopolitical scene. Added motivation were also tax reliefs for conversions to Islam. There was also a great influx of Orthodox believers, due to the constant immigrations from Montegro and Serbia, frequent wars (orthodox population participated as soldiers on both sides), and shortage of Catholic preachers.
Preottoman Catholic population had a great share in the emigrations from Bosnia and Herzegovina. The emigration flows were directed towards Dalmatia, Croatia, Slavonia, Baranja and north-west Bačka. The western part of today's region of Bosnia, today known as Bosnian Krajina, was taken by the Ottomans in the 16th century, and was for some time still known as "Turkish Croatia", as its once overwhelming Catholic and Croat majority disappeared and the Ottomans entrenched the new border along the Sava and Una rivers. After more than a century of military losses, the Habsburg Empire waged some victorious wars against Turkey and managed to temporarily shift the border south of the Sava river with the Treaty of Passarowitz (1718), but this was undone as soon as the 1739 Treaty of Belgrade was signed.[2] Austria-Hungary would later take hold of the entire territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina after the Treaty of Berlin (1878), but under different circumstances, leading up to the Bosnian crisis of 1908. Relatively few previous Croatian emigrants came back to Bosnia.
According to the findings of many an author, the Muslim population, in the period of the Ottoman rule, did not emigrate much compared to the migrations of the Orthodox and Catholic population. The Muslim population was characteristic of return migrations as soon as the political and economic situation again became stable or the state borders were shifted. The return movements of the Muslim population from the seaside, Lika, Slavonia, Hungary, and other places are well known. For example, after the Siege of Vienna (1683–1699), territorial losses of the Ottoman Empire and the conquest of Lika and Krbava by the Austrian Imperial Army, mass movements of the Muslim population from those regions took place; the Muslim population headed towards Bihać, Cazin, and Bosanska Krupa where they created an enclave in the vast region of Bosnian Frontier. More intensified immigrations of the Muslim population were noticed in 1690 when they moved from Hungary and Slavonia to the region around the mountain of Majevica.
In the Ottoman period, the Muslim population increased in number in Bosnia and Herzegovina somewhat due to immigrations of Muslims from the Sanjaks of Smederevo and Novi Pazar, and especially from some regions of Montenegro, Sjenica, and Pešter. Immigrations of the Turkish population from Asia Minor also had an impact upon the growth of the Muslim population in Bosnia and Herzegovina from the 15th to 19th century.
However, the increase of the Muslim population was mostly due to their high natality rate given the patriarchic nature of the family structure. In such family structure the duties of the family members were strictly divided where female members of the family almost solely were bearing many children and taking care of the household while male members were engaged in running the land and the politics of the community.
Patriarchal structure was also evident in Orthodox and Catholic families but the statistics do not tend to show as high natality rates. The difference (according to some literary sources of the time) was in the social levels of Muslims relative to their Christian counterparts where the former were landowners and hence upper and upper middle class who could afford to have more offspring and the latter were land workers and hence lower middle to lower class. Such social organization corresponded to a feudal system of the time.
Ottoman Empire
During and shortly after the Ottomans' conquest of Bosnia, between 1463–1557, it is estimated that the Ottoman forces took around 100,000 of Bosnia's inhabitants into captivity and 30,000 young into the Janissaries as a result of the devshirmeh (also known as blood tax).
The Official population census by religion in Bosnia:
Number Type 37,125 Christian houses 332 Muslim houses During the year of 1489 the official population census by religion for Bosnian Sandžak was:
Number Type 25,068 Christian houses 4,485 Muslim houses Contemporary Byzantine historian Michael Critobulus of Imbros described Bosnia and its endings in the first half of the 15th century. According to him next to the mainstream native population of the Kingdom of Bosnia the Serbs, Romans and Hungarians, there were also some Vlachs and Albanians[note 1].
Turkish historian Ömer Lütfü Barkan conducted a population census based on religion in the Bosnian Sandžak during 1520 - 1530. At which time there were over 334,325 inhabitants of whom 38,7% were followers of Islam.
During the late 16th century and early 17th century, according to various Austrian and Ottoman sources, Bosnia's entire nobility, the greater part of her citizenry and a part of the serfdom were Muslims, around 75% of the population of the Bosnian pashadom.[citation needed]
The Islamic population of Bosnia and Herzegovina, during Late 18th century to the Early 19th century, started to gradually drop due to frequent wars fought by the Ottoman Empire. Muslims were required by Ottoman law to serve in the military, whereas Christians were not part of the army. With the created of independent states of Serbia and Montenegro, migrations of Serbs to the two states were in massive waves in the 1810s, 1820s and 1870s.
Both Muslim and Christian populations were considerably thinned in the 18th century due to frequent plagues. In particular, a huge plague epidemic reportedly halved the entire population of Bosnia and Herzegovina between 1813 and 1815.
Johann Roskiewicz estimated the ethnic composition of the population in 1867 as:
- In Bosnia:
- 782,000 Slavs (which he called "Croatians and Serbs")
- 9,000 Roma (which he called "Gipsies")
- 5,000 Jews
- In Herzegovina:
- 227,000 Slavs
- 2,500 Roma
- 500 Jews
During the period of 1875/1876 an Ottoman population census by religion was conducted, but with vague, imprecise and varying figures, often favoring Muslims over Christians :
Type Percentage Range Greek Orthodox Christians 32.63% - 46.6% Sunni Muslims 32.6% - 51.9% Catholic Christians 14.97% - 20.17% Final results of Ottoman administration in Bosnia and Herzegovina was rearranging most of its religious and ethnical map. New empire created mostly Muslim elites which made up the majority in most of the cities, as in the westernmost and easternmost borderparts of Bosnia (Cazin area, parts of Drina valley and larger area around Tuzla). Prewar catholic majority west of Vrbas (area was part of Croatian Kingdom before the ottomans) had disappeared and was exchanged by orthodox majority , due to constant immigration of Orthodox, sortage of Catholic priesthood and emigrations of Catholics from that area. Catholics also mostly disappeared from Eastern Bosnia (Srebrenica region was one of Hungarian banates) and dropped to a minority in northern Bosnia (except for large parts of Bosnian Posavina). In central Bosnia Catholics dropped roughly to about one half of the population, and Herzegovina was basically divided into Catholic and Orthodox parts with a Muslim majority in most of the cities.
Territorial distribution
The Muslim population was mostly urban and comprised the majority in most of Bosnia and Herzegovina towns (Sarajevo, Tuzla, Banja Luka) as in western (Cazin) and estern borderparts (parts of Drina valley) of the country due to religious wars with neighbouring countries. In general, Muslims were the dominant group in most developed urban centers of the country.
Most of western parts of Bosnia, eastern parts of Herzegovina and parts of Drina valley had Orthodox majority. Those were large, but mostly mountainous regions. The re-establishment of the Pec Patriarchate in 1557 and sortage of catholic priesthood contributed greatly to preservation of Serbian presence in these areas.
The Catholic population comprised majority in the most of the Herzegovina, Posavina and Central Bosnia . The preservation of a Catholic presence in these areas was greatly contributed by the establishment of the Franciscian Order, which acted against Catholic emigration.
Due to the frequent migrations and religious wars, a lot of those areas contained few (or more) of small enclaves of peoples of other religions.
Bosnia accepted a wave of immigrants of Jews that were expelled from Spain since the 15th century. They settled in Sarajevo, Travnik, Banja Luka and Bihac. The immigration of the Roma, Cincars, Cerkez, in small numbers, coincided with the Ottoman conquest of Bosnia and Herzegovina. None of these groups considerably influenced the overall population structure of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
During the liberation wars fought by the Serbs between 1875 and 1878, Bosnia and Herzegovina lost 13,64% of its population (150,000 out of total 1,100,000) of whom most were Serbs.
Austro-Hungarian Empire
1879
During 1879 the first thorough population census stated that there were 1,158,164 citizens of Bosnia and Herzegovina in 1879, by religion:
Type Percentage Range Greek Orthodox Christians 496,485 (42,88%) Sunni Muslims 448,613 (38.75%) Catholics 209,391 (18.08%) others 3,675 (0.31%) 1885
According to the 1885 population census there were 1,336,091 citizens of Bosnia and Herzegovina:
Type Percentage Range Serb Orthodox Christians 571,250 (42.76%) Sunni Muslims 492,710 (38.88%) Catholics 265,788 (19.88%) others 6,343 (0.47%) 1895
The year of 1895 was a busy year. An Austro-Hungarian population census conducted in Bosnia and Herzegovina on 22 April 1895 which reported that the area of Bosnia had approximately 1,361,868 inhabitants while Herzegovina had 229,168 inhabitants
The number of persons per square mile was the second lowest in Austro-Hungary: 80 inhabitants per square mile. The number of persons per square mile across districts:
Type Number Doljna Tuzla 106 Banjaluka 96 Bihać 91 Sarajevo 73 Mostar (Hercegovina) 65 Travnik 62 There were 5,388 settlements, 11 of which had more than 5,000 inhabitants. Over 4,689 of those settlements contained less than 500 inhabitants.
The Ethnic structure was:
Name Description Slavic nation 98% Serb Orthodox Christians 673,246 (42.94%) Sunni Muslims 548,632 (34.99%) Catholics 334,142 (21.31%) Albanians 30,000 Jews none Ottoman Turkish merchants none Austrian troops none others 12,072 (0.76%) The population census by religion:
Type Description Serb Orthodox Christians 674,000 (43%) Muslims 550,000 (35%) Catholics 334,000 (21.3%) Jews 8,000 Protestants 4,000 The territorial distribution among the area didn't change much. The towns became more multiethnic.
Some of the other minor minorities include the Albanians which lived in the southeast. Turkish merchants could be found in trading centres. The Austrian troops could be found in military garrisons, while the Jews that migrated from Spain earlier could be found in the cities. They were all divided according to occupation, 1,385,291 inhabitants (85%) were farmers or wine-cultivators. There were a total of 5,833 large estates, chiefly held by the Muslims. 88,970 cultivators serve as kmets. 88,867 free peasants own the land they till. 22,625 peasants own farming-land and also cultivate the land of others
1910
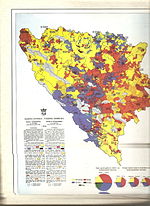
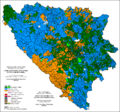
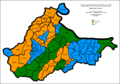
 Ethnic composition, 1910 According to the 1910 population census by districts Bosnia and Herzegovina
Ethnic composition, 1910 According to the 1910 population census by districts Bosnia and Herzegovina
According to the 1910 population census there were 1,898,044 citizens of Bosnia and Herzegovina:
Type Description Serb Orthodox Christians 825,918 (43.49%) Sunni Muslims 612,137 (32.25%) Catholics 434,061 (22.87%) others 26,428 (1.39%) Territorial distribution
The Urban population was:
- Sunni Muslims 50.76%
- Catholics 24.49%
- Greek Orthodox Christians 19.92%
Conducted in 1910 by Austro-Hungary. Percentages land ownership:
- Muslims owning 91.1%
- Orthodox Serbs owning 6%
- Catholic Croats owning 2.6%
- others owned 0.3%
World War I
The First World War left Bosnia and Herzegovina without a total figure of 360,000 citizens or 19% of its population.
Migrations
As soon as the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs was formed, a number of earlier colonized families started to emigrate and return to their homelands, among them Germans, Czechs, Poles, Slovaks, Hungarians and Ruthenians.
The new planned resettlement plans hit most the Orthodox Serb population, as large masses were moved from passive regions of Herzegovina and Bosnia to Vojvodina, eastern Banat in presice; while some left to Kosovo: inhabiting the region from Kačanik to Vučitrn, around Pristina, Lipljan, Peć, Istok, Đakovica, and in Drenica. Somealso left to Macedonia.
The earlier emigrational tendency of the Muslim population towards Ottoman-held territories continued.
A great number of the population, among whom the Serbs and Croats from the karst regions of Herzegovina and Western Bosnia were most numerous, moved to the northern regions of Yugoslavia and abroad (North and South America, Canada, France, Belgium, etc.)
Kingdom of Yugoslavia
1921
The Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes conducted a population census in the territorial entity of Bosnia and Herzegovina on 31 January 1921. There were 1,890,440 persons in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The people were split among two nationalities:
- Serbs and Croats
- undecided and others (mostly Muslims)
By religion:
- Serbian Orthodox Christians 829,290 (43.87%)
- Sunni Muslims 588,244 (31.07%)
- Catholic Christians 444,308 (23.58%)
- others 28,595 (1.58%)
Territorial distribution
Following the Agrarian reforms of 1918 and 1919 [3], the government confiscated numerous lands owned by Muslim Bosnians. The entire land was split among the people based on territorial distribution. Serbs got the most, while Croats the least.
1931
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia has conducted a population census on the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina on 31 March 1931 which stated that there were 2,323,555 persons. The population was given several nationalities:
- Yugoslavs (Slavs, the majority)
- Germans
- Ukrainians
- Poles
- Hungarians
- Roma
- Turks
By religion:
Name Number Percentage Serbian Orthodox Christians 1,028,139 44.25% Sunni Muslims 718,079 30.9% Catholics 547,949 23.58% others 29,388 1.27% Sarajevo
The population of the district of Sarajevo according to the 1921 Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes religious population census:
- Serbian Orthodox Christians 55,477 (38.6%%)
- Sunni Muslims 50,270 (34.9%)
- Catholics 29,395 (20.4%)
- others 8,768 (6.1%)
There were 8 municipalities and their populations were:
- Serbs comprised the majority in 5 municipalities: Ilidža, Koševo, Pale, Rajlovac, and Trnovo
- Muslims comprised the majority in the City of Sarajevo and in 2 municipalities: Bjelašnica and Ozren
The same year the City of Sarajevo had 78,173 inhabitants:
- Sunni Muslims 29,649 (37.9%)
- Catholics 21,373 (27.3%)
- Serbian Orthodox Christians 18,630 (23.8%)
- others 8,522 (11.0%)
World War II
Losses
The Federal Bureau of Statistics in Belgrade composed a figure of 179,173 persons killed in the war in Bosnia and Herzegovina during the Second World War:
- 129,114 Serbs (72.1%)
- 29,539 Muslims (16.5%)
- 7,850 Croats (4.4%)
- others (7%)
Expulsions and relocations
By the plans of Nazi Germany and the Independent State of Croatia 110,000 Serbs were relocated and transported to German-occupied Serbia. Just in the period of May to August 1941 over 100,000 Serbs were expelled to Serbia. In the heat of war Serbia had 200,000-400,000 Serbian refugees from Ustaša-held Bosnia and Herzegovina. By the end of war 137,000 Serbs have permanently left the territories of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
The Muslim population of Bosnia and Herzegovina was also exposed to suffering and intense relocation, mainly to cities and mostly to Sarajevo, to where a portion of the Muslim population from Serbia, Montenegro, Kosovo and Metohia, and Macedonia was relocated thus enlarging the overall Muslim percentage in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
1945-1948 colonization of Vojvodina
Prior to the expulsions of Germans from Vojvodina in 1945-1948, a number of inhabitants of Bosnia and Herzegovina moved to the new living spaces in Vojvodina:
- Serbs around 70,000 (98%)
- Croats and Muslims (around 2%)
1948
According to the 1948 People's Federal Republic of Yugoslavia population census, the People's Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina had 2,565,277 inhabitants:
- Serbs 1,136,116 (44.3%)
- undecided 788,403 (30.7%)
- Croats 614,123 (23.9%)
- Slovenes 4,338 (0.2%)
- Montenegrins 3,094 (0.1%)
- Macedonians 675
- others 18,528 (0.8%)
NOTE: There was no formal definition for Bosniaks / Bosnian muslims at the time, så a great majority defined them selfs as undecided. Or in certain cases as Serbs or croats
1953
According to the 1953 Yugoslav population census, Bosnia and Herzegovina had 2,847,790 inhabitants:
- Serbs 1,264,372 (44.4%)
- undecided 891,800 (31.3%)
- Croats 654,229 (23%)
- Montenegrins 7,336 (0.3%)
- Slovenes 6,300 (0.2%)
- Macedonians 1,884 (0.1%)
- others 21,869 (0.7%)
NOTE: There was no formal definition for Bosniaks / Bosnian muslims at the time, så a great majority defined them selfs as undecided. Or in certain cases as Serbs or croats
1961
According to the 1961 Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia population census, the Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina had 3,277,948 inhabitants:
- Serbs 1,406,057 (42.9%)
- Muslims by nationality[note 2] 842,248 (25.7%)
- Croats 711,665 (21.7%)
- Yugoslavs 275,883 (8.4%)
- Montenegrins 12,828 (0.4%)
- Rusyns 6,136 (0.2%)
- Slovenes 5,939 (0.2%)
- Albanians 3,642 (0.1%)
- Macedonians 2,391 (0.1%)
- Turks 1,812 (0.1%)
- Hungarians 1,415 (0.1%)
- others 6,849 (0.2%)
1971
According to the 1971 Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia population census, the Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina had 3,746,111 inhabitants:
- Muslims[note 3] 1,482,430 (39.6%)
- Serbs 1,393,148 (37.2%)
- Croats 772,491 (20.6%)
- Yugoslavs 43,796 (1.2%)
- Montenegrins 13,021 (0.3%)
- Ukrainians 5,332 (0.2%)
- Slovenes 4,053 (0.2%)
- Albanians 3,764 (0.1%)
- Macedonians 1,773 (0.0%)
- Roma 1,456 (0.0%)
- Hungarians 1,262 (0.0%)
- others 23,584 (0,8%)
1981
According to the 1981 Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia population census, the Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina had 4,124.008 inhabitants:
- Muslims 1,629,924 (39.5%)
- Serbs 1,320,644 (32%)
- Croats 758,136 (18.4%)
- Yugoslavs[note 4] 326,280 (7.9%)
- Montenegrins 14,114 (0.3%)
- Roma 7,251 (0.2%)
- Ukrainians 4,502 (0.1%)
- Albanians 4,396 (0.1%)
- Slovenes 2,755 (0.1%)
- Macedonians 1,892 (0.1%)
- others 54,119 (1.4%)
During the time of Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, percentage of Croats in Bosnia and Herzegovina fell by more than a quarter.
Territorial distribution
The 1981 territorial population distribution in the Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina:
- Serbs:
- majority in 2,439 settlements or 41.4% of the total settlements
- lived in 34.3% of the total housing
- Muslims
- majority in 2,179 settlements or 37%of the total settlements
- lived in 37.6% of the total housing
- Croats
- majority in 1,016 settlements or 17.3% of the total settlements
- lived in 17.3% of the total housing
- mixed and rest
- 223 settlements
Fall of Croat settlements was due to immigration in foreign countries of western Europe (and hostile approach from SFRY government). During SFRY Bosnian Serb and Bosniak nations had most privileges to grow, and while Serbs colonized Vojvodina, Bosniaks stayed in Bosnia. Also as the data shows, Serbian people were less urbanized than Bosniaks or Croats and preferred smaller settlements (31% percent of populations lived in 41% of settlements).
1991
Yugoslav population census, Bosnia and Herzegovina had 4,377,053 inhabitants:
- Muslims 1,902,956 (43.47%)
- Serbs 1,366,104 (31.21%)
- Croats 760,872 (17.38%)
- Yugoslavs 242,682 (5.54%)
- others 104,439 (2.40%):
- Montenegrins - 10,071
- Roma - 8,864
- Albanians - 4,922
- Ukrainians - 3,929
- Slovenes - 2,190
- Macedonians - 1,596
- Hungarians - 893
- Italians - 732
- Czechs - 590
- Poles - 526
- Germans - 470
- Jews - 426
- Russians - 297
- Slovaks - 297
- Turks - 267
- Romanians - 162
- Ruthenians - 133
- Other nationalities - 17,592
- Undefined nationality - 14,585
- Regional defined - 224
- Unknown - 35,670
Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina
1992 estimate
4.4 million people of which:
Bosnian War
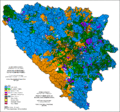
During the Bosnian War (1992–1995) ethnic cleansing drastically changed the ethnic composition and population distribution in Bosnia and Herzegovina. (See: Casualties of the Bosnian War)
1996 UNHCR census
In 1996 the UNHCR conducted a detailed population census in the whole country. This census was not only officially considered "official" because the Government of BH refused to recognize it, claiming that its recognition would be the same as the recognition of the ethnic cleansing conducted in the war. It was concluded that Bosnia and Herzegovina had 3,919,953 inhabitants:
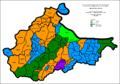
Type Number Percentage Bosniaks 1,805,910 46.07% Serbs 1,484,530 37.88% Croats 571,317 14.58% others 58,196 1.47% Federation
Totally 2,444,665
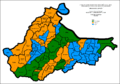
Type Number Percentage Bosniaks 1,773,566 72.5% Croats 556,289 22.8% Serbs 56,618 2.3% others 58,192 2.4% Republika Srpska
Totally 1,475,288
Type Percentage Range Serbs 1,427,912 (96.8%) Bosniaks 32,344 (2.2%) Croats 15,028 (1%) others 4 Modern
3,922,205 (2002)
4,025,476 (July 2005 estimate)
Ethnic (2000 estimate)
Type Percentage Range Bosniaks 48% (of whom around 97% are followers of Islam) Serbs 37.1% (of whom around 99% are followers of the Serb Orthodox Church) Croats 14.3% (of whom around 88% are followers of the Catholic Church) others 0.6% Religious (2008 estimate)
Type Percentage Range[4] Muslims 45% Serb Orthodox 36% Roman Catholics 15% other 4% See also
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Republika Srpska
- Brčko District
- Herzeg-Bosnia
- Western Bosnia
- History of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bosniaks
- Bosnians
- Croats
- Serbs
- Muslims by nationality
- 1991 Bosnia and Herzegovina Population Census
Notes
- ^ Michael Critobulus of Imbros
- ^ In 1961 Muslim Bosnians were still not recognized as a nationality but on the 1961 census about 600,000 people declared themselves as "undecideds" as their other options were to declare themselves as Serbs, Croats or Yugoslavs. Because of large Muslim community in Bosnia, the census commission logically concluded to group them as "Muslims in a national sense".
- ^ In 1971 with constitutional amendments Muslims became a nationality which explained the drop in numbers in Serb, Croat and Yugoslav columns as many chose this over their previous option. Although a preferred option of Bosnian leadership was to use the term "Bosnians" in the constitutional amendment, Muslims was the officially accepted term (see Hamdija Pozderac)
- ^ Following the death of Josip Broz Tito in 1980 there was a surge in Yugoslavian patriotism that was evident in 1981 census as much of the population decided to declare themselves as Yugoslavs.
- ^ Following the 1991 census Bosnian-Herzegovinian government in constitutional amendment in 1993 introduced the name Bosniaks to replace the name Muslim, since the Yugoslav policy was considered to be neglecting the Bosniak's Bosnian identity.(see Hamdija Pozderac)
References
- ^ .[1]
- ^ Drago Roksandić, Faculty of Philosophy (2007-10-02). "Posavska krajina/granica od 1718. do 1739. godine - The Sava military borderland, 1718 - 1739" (in Croatian). University of Zagreb. http://hrcak.srce.hr/file/77458. Retrieved 2010-06-29.
- ^ [2]
- ^ International Religious Freedom Report 2008 - Bosnia and Herzegovina
External links
- 1991 Census in BIH - census data for all municipalities
- 1991 Census in BIH - census data for settlements
- Census data
- Serbs of SFRJ
- The Serbs of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bosnia and Herzegovina in the Catholic Encyclopedia
- The historical aspect of the Serbian question in the Yugoslav crisis
- Agrarian reform of 1918
- Population of Bosnia and Herzegovina (in Croatian and Bosnian)
- CIA World Fact book - Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Short documentary on Displaced people and refugees in Bosnia and Herzegovina
Demographic history of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.