- DSS (NMR standard)
-
DSS (NMR standard) 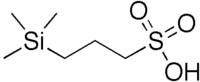 2,2-Dimethyl-2-silapentane-5-sulfonic acidSystematic name3-(Trimethylsilyl)propane-1-sulfonic acid
2,2-Dimethyl-2-silapentane-5-sulfonic acidSystematic name3-(Trimethylsilyl)propane-1-sulfonic acidIdentifiers Abbreviations DSS CAS number 18173-90-5 
PubChem 74873, 16217602 (2H6)propane ChemSpider 17345119 (2H6)propane 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- C[Si](C)(C)CCCS(O)(=O)=O
C[Si](C)(C)CCCS(=O)(=O)O
- InChI=1S/C6H16O3SSi/c1-11(2,3)6-4-5-10(7,8)9/h4-6H2,1-3H3,(H,7,8,9)
Key: TVZRAEYQIKYCPH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Properties Molecular formula C6H16O3SSi Molar mass 196.34 g mol−1 Exact mass 196.058941601 g mol-1 Appearance White solid Boiling point 120 °C, 393 K, 248 °F
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox references DSS (4,4-dimethyl-4-silapentane-1-sulfonic acid) is a chemical compound used in proton- and carbon-related NMR spectroscopy as a calibration standard, similar to tetramethylsilane (TMS), but with much higher water solubility. Whereas TMS is the most common NMR standard used in organic solvents such as chloroform or benzene, DSS or its sodium salt is more often used for protein experiments in water.
The low electronegativity of the silicon shields the nine identical methyl protons. The result is a high intensity proton signal further upfield (at lower chemical shift) than almost all peaks found in naturally occurring organic molecules. The resulting standard peak is easily identified as such and set to chemical shift 0.0.
The proton spectrum of DSS also exhibits minor peaks at 3.1 ppm (triplet), 1.9 ppm (pentet), and 0.8 ppm (triplet) at an intensity of 22% of the reference peak at 0 ppm. However, these peaks appear much smaller than 22% of the height of the reference singlet because of their width (i.e. multiplicity). If these peaks pose a problem, a deuterated version of DSS is available at much higher cost.
Alternatives
Trimethylsilyl propionate (TSP) is a related compound used as an NMR standard. It uses a carboxylic acid instead of the sulfonic acid found in DSS to confer water solubility. As a weaker acid, TSP is more prone to be affected by sample pH.
4,4-Dimethyl-4-silapentane-1-ammonium trifluoroacetate (DSA) has also been proposed as an alternative, to overcome certain drawbacks of DSS.[1]
References
- ^ James S. Nowick, Omid Khakshoor, Mehrnoosh Hashemzadeh, and Justin O. Brower (2003). "DSA: A New Internal Standard for NMR Studies in Aqueous Solution". Org. Lett. 5 (19): 3511–3513. doi:10.1021/ol035347w. PMID 12967312.
Categories:- Sulfonic acids
- Silanes
- C[Si](C)(C)CCCS(O)(=O)=O
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
