- Deuterated benzene
-
Deuterated benzene 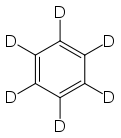
Identifiers CAS number 1076-43-3 PubChem 71601 ChemSpider 64671 
EC number 214-061-8 UN number 1114 Beilstein Reference 1905426 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [2H]c1c([2H])c([2H])c([2H])c([2H])c1[2H]
Properties Molecular formula C62H6 Molar mass 84.1488 g mol−1 Exact mass 84.084610668 g mol−1 Density 0.950 g cm−3 Melting point 7 °C, 280 K, 44 °F
Boiling point 72 °C, 345 K, 161 °F
Thermochemistry Specific heat capacity, C 152.46 J K−1 mol−1 Hazards EU classification  F
F  T
TR-phrases R45, R46, R11, R36/38, R48/23/24/25, R65 S-phrases S53, S45 NFPA 704 Flash point −11 °C Related compounds Related compounds Benzene  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Deuterated benzene (C6D6), is a form (called an isotopologue) of benzene (C6H6)in which the hydrogen atom ("H") is replaced with deuterium (heavy hydrogen) isotope ("D"). Deuterated benzene is a common solvent used in NMR spectroscopy.
Deuterated NMR Solvents Deuterated Deuterated acetone - (CD3)2C=O • Deuterated benzene - C6D6 • Deuterated chloroform - CDCl3 • Deuterated dichloromethane - CD2Cl2 • Deuterated DMF - (CD3)2NCOD • Deuterated DMSO - (CD3)2S=O • Deuterated ethanol - C2D5OD • Deuterated methanol - CD3OD • Deuterated THF - (C4D8)O • Deuterated water - D2O
Reference: 1H and 13C chemical shifts
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.

