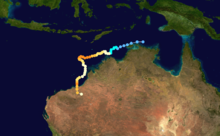
- Cyclone Fay
-
Severe Tropical Cyclone Fay Category 5 cyclone (Australian scale) Category 4 cyclone (SSHS) 
Tropical Cyclone Fay on 22 March 2004 Formed 12 March 2004 Dissipated 28 March 2004 Highest winds 10-minute sustained:
215 km/h (130 mph)
1-minute sustained:
220 km/h (140 mph)
Gusts:
295 km/h (185 mph)Lowest pressure 910 mbar (hPa; 26.87 inHg) Fatalities 0 Areas affected Northern Territory, Northern Western Australia Part of the 2003-04 Australian region cyclone season Cyclone Fay was an intense, late-season tropical cyclone which struck Western Australia during the 2003-04 Australian region cyclone season. Forming as a low-pressure area on March 12, Fay was the only Category 5 cyclone during the season. It had a minimum pressure of 910 mbar (hPa; 26.87 inHg) and maximum wind gusts of 132 mph (213 km/h).[1] Moving in an erratic motion for much of its existence, Fay made landfall on the Pilbara coast on the morning of 27 March as a Category 4 cyclone. While there were no fatalities reported, the cyclone brought record-breaking rainfall to Australia, leading to a sharp decrease in the country's gold output. The cyclone also caused minor damage in the Pilbara region of Western Australia. The Australian Bureau of Meteorology retired the name Fay from use after 2003-04 season.
Contents
Meteorological history
The low pressure system that later developed into Fay formed in the Gulf of Carpentaria on 12 March 2004.[2] The system was designated Tropical Cyclone 18S by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center, with winds of 25 knots (29 mph; 46 km/h). The system then crossed Melville and Bathurst Islands and moved into the Timor Sea, where it intensified[3] and was given the name Fay by the Australian Bureau of Meteorology.[4] Fay began to turn southward on 17 March; simultaneously, the cyclone strengthened due to a weakening of vertical wind shear and an increase in outflow. A day later, a steering ridge to the south of the system strengthened and pushed the cyclone away from the coast and to the northwest.[5]
By March 19 Fay's track had turned to the west-southwest,[5] and on 21 March, Fay became a Category 5 storm,[6] strengthening as it moved into a shortwave trough, intensifying its poleward outflow. A mid-latitude trough caused the steering ridge to weaken, causing Fay to turn to the south.[7] Over the next two days, the environmental shear around the cyclone decreased, which would normally have led to intensification; however, as the shear decreased, the cyclone also moved over an area of dry air, weakening the storm. By 23 March, Fay had moved in a loop, and the storm weakened to a Category 2. It then encountered moister air as it moved southward, leading it to reintensify from 25-27 March, becoming a Category 4 storm as it made landfall on the Pilbara coast between 8:00 a.m. and 9:00 a.m. on 27 March, with estimated wind gusts of 146 mph (235 km/h). Fay then weakened as it moved further inland, and is estimated to have weakened below cyclone strength somewhere between the towns of Nullagine and Telfer.[8]
Preparations
Evacuation centers were set up in the Kimberley region of Western Australia. Schools and businesses were also closed, and flights in and out of the area were cancelled. Shelters were set up for people who could not take shelter in their own homes. Residents of the Bidyadanga Aboriginal community were warned of particularly dangerous storm tide as the center of the cyclone passed to their west.[9] The communities of Sandfire and Pardoo were also warned of dangerous storm tide. Cyclone warnings were issued for areas threatened by the storm, and communities in the path of the storm were warned of expected high rainfall, as amounts greater than 20 centimetres (7.9 in) were expected.[10]
Impact
Satellite rainfall imagery from the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission
Minor damage to buildings and limited tree damage were reported in the vicinity of Port Hedland.[11]
In the town of Nullagine, 120 residents were evacuated to the town's police station, as heavy rain caused flooding.[12] Flooding of the De Grey and Oakover Rivers led to the town being segmented into 4 sections.[13]
As the system passed near the Yarrie mine 200 workers were forced to go under lockdown for 8 hours. The cyclone overturned accommodation units, "shredded" water tanks, cut power lines,[14] and damaged the rail line connecting the mine to Port Hedland.[15]
Heavy rainfall was reported along the track of the cyclone, with a two-day total of 70.1 centimetres (27.6 in) reported at the Nifty Copper Mine and 359 centimetres (141 in) reported in Telfer.[16] The rain from the hurricane delayed the construction of a gas pipeline at the mine for over 7 months, while the pipeline company waited for the floodwaters to dissipate.[17] According to Newcrest Mining, the rainfall amounts at Telfer exceeded the records going back at least 100 years. The heavy rainfall from both Cyclone Monty in February and Cyclone Fay caused gold output in Australia for the quarter to be the lowest in 10 years.[18]
A survey performed by the Australian Institute of Marine Science discovered that the Scott Reef suffered "severe damage," and many coral colonies were uprooted or damaged.[19]
Aftermath
The Bureau of Meteorology retired the name Fay after its usage.[20]
See also
2003–04 Australian region cyclone season
References
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Fay". Australian Government - Bureau of Meteorology. http://www.bom.gov.au/cyclone/history/pdf/fay.pdf. Retrieved 11 August 2011.
- ^ "Severe Tropical Cyclone Fay". Previous Cyclones. Australian Government - Bureau of Meteorology. http://www.bom.gov.au/cyclone/history/fay.shtml. Retrieved 11 August 2011.
- ^ Atangan, J.F.; Amanda Preble. "2004 Annual Tropical Cyclone Report". U.S. Naval Pacific Meteorology and Oceanography Center / Joint Typhoon Warning Center. p. 264. http://www.usno.navy.mil/NOOC/nmfc-ph/RSS/jtwc/atcr/2004atcr.pdf. Retrieved 25 October 2011.
- ^ "Severe Tropical Cyclone Fay". Previous Cyclones. Australian Government - Bureau of Meteorology. http://www.bom.gov.au/cyclone/history/fay.shtml. Retrieved 11 August 2011.
- ^ a b Atangan, J.F.; Amanda Preble. "2004 Annual Tropical Cyclone Report". U.S. Naval Pacific Meteorology and Oceanography Center / Joint Typhoon Warning Center. p. 264. http://www.usno.navy.mil/NOOC/nmfc-ph/RSS/jtwc/atcr/2004atcr.pdf. Retrieved 25 October 2011.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Fay". Australian Government - Bureau of Meteorology. http://www.bom.gov.au/cyclone/history/pdf/fay.pdf. Retrieved 11 August 2011.
- ^ Atangan, J.F.; Amanda Preble. "2004 Annual Tropical Cyclone Report". U.S. Naval Pacific Meteorology and Oceanography Center / Joint Typhoon Warning Center. p. 264. http://www.usno.navy.mil/NOOC/nmfc-ph/RSS/jtwc/atcr/2004atcr.pdf. Retrieved 25 October 2011.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Fay". Australian Government - Bureau of Meteorology. http://www.bom.gov.au/cyclone/history/pdf/fay.pdf. Retrieved 11 August 2011.
- ^ "Western Australia battens down for Cyclone Fay". The Sydney Morning Herald. 25 March 2004. http://www.smh.com.au/articles/2004/03/25/1079939765555.html. Retrieved 11 August 2011.
- ^ "WA coastline may escape Fay's fury". The Age (Melbourne). 27 March 2004. http://www.theage.com.au/articles/2004/03/27/1080330979160.html. Retrieved 11 August 2011.
- ^ "Flood warning as Cyclone Fay fades". ABC News. http://www.abc.net.au/news/2004-03-27/flood-warning-as-cyclone-fay-fades/159394. Retrieved 25 October 2011.
- ^ "Cyclone Fay floods force evacuation". The Age (Melbourne). 28 March 2004. http://www.theage.com.au/articles/2004/03/28/1080412223804.html. Retrieved 11 August 2011.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Fay". Australian Government - Bureau of Meteorology. http://www.bom.gov.au/cyclone/history/pdf/fay.pdf. Retrieved 11 August 2011.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Fay". Australian Government - Bureau of Meteorology. http://www.bom.gov.au/cyclone/history/pdf/fay.pdf. Retrieved 11 August 2011.
- ^ "Cyclone Fay Floods Pilbara Township". llawarra Mercury. 29 March 2004. http://www.accommodationporthedland.com.au/accommodation-port-hedland-articles/2004/3/29/cyclone-fay-floods-pilbara-township/. Retrieved 25 October 2011.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Fay". Australian Government - Bureau of Meteorology. http://www.bom.gov.au/cyclone/history/pdf/fay.pdf. Retrieved 11 August 2011.
- ^ "GasNet’s Telfer Pipeline sets benchmark in tackling Australian extremes". The Australian Pipeliner. October 2004. http://pipeliner.com.au/news/gasnets_telfer_pipeline_sets_benchmark_in_tackling_australian_extremes/043537/. Retrieved 25 October 2011.
- ^ "Aussie gold output hits record low". The Sydney Morning Herald. 24 May 2004. http://www.smh.com.au/articles/2004/05/24/1085344029026.html. Retrieved 11 August 2011.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Fay". Australian Government - Bureau of Meteorology. http://www.bom.gov.au/cyclone/history/pdf/fay.pdf. Retrieved 11 August 2011.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Names". Australian Government - Bureau of Meteorology. http://www.bom.gov.au/cyclone/about/names.shtml. Retrieved 11 August 2011.
List of retired Australian cyclone names 1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s 2010s Categories:- Retired Australian region cyclones
- 2003–04 Australian region cyclone season
- 2004 in Australia
- Category 5 Australian region cyclones
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.