- 1985–90 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone seasons
-
The 1985-1990 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone seasons ran year-round from July 1 to June 30 during each year between 1985 and 1990. Tropical cyclone activity in the Southern Hemisphere reaches its peak from mid-February to early March.
1985–86 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season
Cyclone Nicholas
Category 4 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Category 4 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 
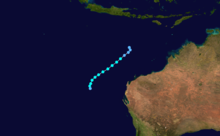
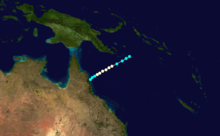
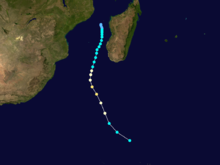
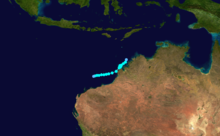
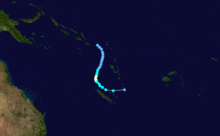
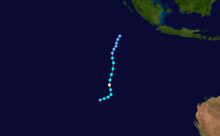
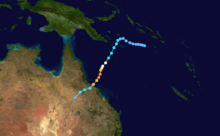
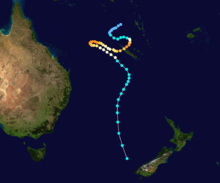
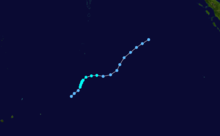
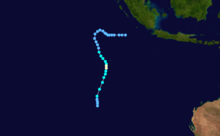
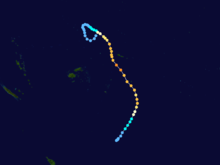
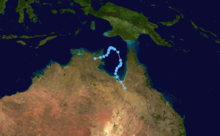
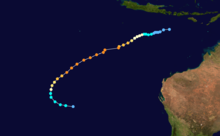
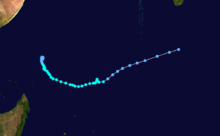
Duration November 25 – December 7 Intensity 165 km/h (100 mph) (10-min), 945 mbar (hPa) Tropical Cyclone Nicholas occurred from 26 November until 7 December 1985 in the Indian Ocean south of Sumatra. Its estimated lowest pressure was 945hPa.[1]
Cyclone Ophelia
Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Tropical storm (SSHS) 

Duration January 7 – January 13 Intensity 80 km/h (50 mph) (10-min), 986 mbar (hPa) Tropical Cyclone Ophelia occurred from 7 January until 12 January 1986 near Cocos Island. Its estimated lowest pressure was 986hPa.[1]
Cyclone Pancho
Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Category 2 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 

Duration January 18 – January 22 Intensity 115 km/h (75 mph) (10-min), 976 mbar (hPa) Tropical Cyclone Pancho occurred from 18 January until 21 January 1986 and remained entirely within the Indian Ocean off Western Australia. Its estimated lowest pressure was 976hPa.[1]
Cyclone Hector
Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 

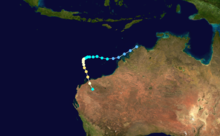
Duration January 17 – January 24 Intensity 85 km/h (55 mph) (10-min), 973 mbar (hPa) Tropical Cyclone Hector occurred from 17 January until 24 January 1986. It crossed the coast near Wyndham, Western Australia and its estimated lowest pressure was 982hPa. Hector caused significant flooding in the Kimberley region of Western Australia.[1]
Cyclone Vernon
Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Tropical storm (SSHS) 
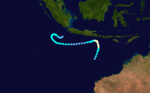
Duration January 21 – January 25 Intensity 70 km/h (45 mph) (10-min), 990 mbar (hPa) Vernon was a weak cyclone that occurred from 21 January until 24 January 1986 and formed in the Gulf of Carpentaria. It crossed Cape York and continued on into the Coral Sea. Its estimated lowest pressure was 990hPa.[1]
Cyclone Winifred
Category 3 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 

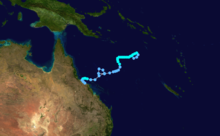
Duration January 27 – February 5 Intensity 130 km/h (80 mph) (10-min), 961 mbar (hPa) Winifred struck Innisfail, Queensland in February,1986 causing extensive damage. There were three deaths attributed to Winifred.[1]
it formed on the Coral Sea on January 29
Cyclone Rhonda
Category 3 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Category 2 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 

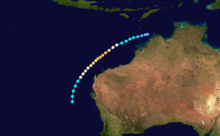
Duration February 17 – February 22 Intensity 120 km/h (75 mph) (10-min), 968 mbar (hPa) Tropical Cyclone Rhonda occurred from 17 February until 22 February 1986. It formed off the Pilbara coast and followed the Western Australian coast before weakening and crossing near Perth. Areas around Perth received heavy rain. Its estimated lowest pressure was 968hPa.[1]
Cyclone Selwyn
Tropical Cyclone Selwyn occurred from 21 February until 26 February 1986 and remained away from land in the Indian Ocean. Its estimated lowest pressure was 980hPa.[1]
Cyclone Tiffany
Tropical Cyclone Tiffany occurred from 25 February until 1 March 1986 and remained away from land in the Indian Ocean. Its estimated lowest pressure was 984hPa.[1]
Cyclone Victor
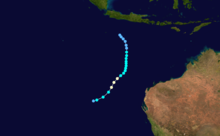
Tropical Cyclone Victor occurred from 1 March until 9 March 1986 and was the most severe cyclone of the Australian region for the season. Fortunately it remained off the Western Australian coast for all its life. Its estimated lowest pressure was 930hPa and highest gusts about 255 km/h.[1]
Cyclone Alfred
Alfred was a weak cyclone that occurred from 2 March until 7 March 1986. Its estimated lowest pressure was 990hPa and it stayed within the Coral Sea.[1]
Cyclone Alison/Krisostoma
Tropical Cyclone Alison occurred from 4 April until 9 April 1986 within the Indian Ocean. It moved westward into the Mauritius area of responsibility and was renamed Krisostoma. Its estimated lowest pressure was 974hPa.[1]
Cyclone Manu
Tropical Cyclone Manu occurred from 21 April until 27 April 1986 off the Queensland coast. Its estimated lowest pressure was 980hPa.[1]
Cyclone Billy/Lily
Tropical Cyclone Billy occurred from 4 May until 15 May 1986. It temporarily moved west into the Mauritius area of responsibility where it was renamed Lily but then moved back again. It crossed the Western Australian coast near Geraldton just after dissipating. Its estimated lowest pressure was 950hPa.[1]
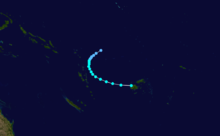
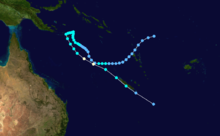
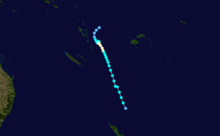
Cyclone Namu
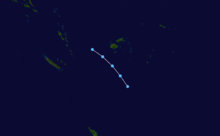
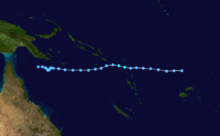
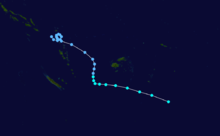
Tropical Cyclone Namu occurred from 16 May until 22 May 1986 near the Solomon Islands. It caused mudslides that killed over 100 people. Its estimated lowest pressure was 960hPa.[1]
Cyclone Delfinina
Tropical Cyclone Delfinina occurred in the southern Indian Ocean around 85°E in January 1986.[1]
Cyclone Costa
Tropical Cyclone Costa occurred in the southern Indian Ocean around 60°E in January 1986.[1]
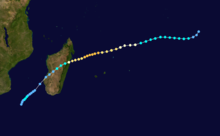
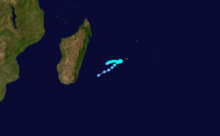
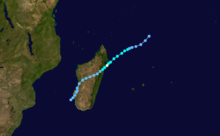
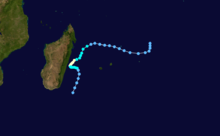
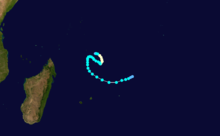
Cyclone Honorinina
Tropical Cyclone Honorinina struck Madagascar in March on 1986. Honorinina struck with winds of 300 km/h killed 32 people. [2]
Other cyclones outside Australia
The following cyclones (with little information) also occurred within the Southern Hemisphere: [3]
- Erinesta, 31 January to 10 February, Indian Ocean
- Filomena, 6 to 10 February, Indian Ocean
- Ima, 6 to 14 February, Pacific Ocean
- June, 7 to 9 February, Pacific Ocean
- Keli, 8 to 10 February, Pacific Ocean
- Gista, 19 to 25 February, Indian Ocean
- Lusi, 3 to 8 March, Pacific Ocean
- Iarima, 13 to 15 March, Indian Ocean
- Jefotra, 26 March to 1 April, Indian Ocean
- Martin, 10 to 14 April, Pacific Ocean
1986–87 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season
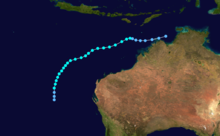
Cyclone Jason
Jason stuck Baniyalla, Northern Territory in February, 1987 damaging 20 buildings.[4]
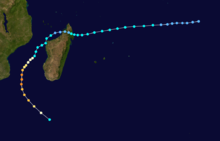
Cyclone Clotilda
Cyclone Clotilda form between Madagascar and Reunion Island. Clotilda moved southeastward and spent three days traversing Reunion Island from northeast to southwest. Clotilda brought the highest rainfall totals since Cyclone Hyacinthe in 1980. Seven people were killed and 2 others were missing.[5]
Other cyclones
The following cyclones also occurred within the 1986/1987 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season: [6]
- Osea, 22 to 25 November 1986, Pacific Ocean
- Patsy, 14 to 18 December 1986, Pacific Ocean
- Raja, 23 December 1986 to 1 January 1987, Pacific Ocean
- Sally, 28 December 1986 to 4 January 1987, Pacific Ocean
- Tusi, 16 to 20 January 1987, Pacific Ocean
- Alinina, 16 to 23 January 1987, Indian Ocean
- Connie, 17 to 20 January 1987, near Western Australia
- Irma, 19 to 20 January 1987, Gulf of Carpentaria
- Damien, 1 to 5 February 1987, near Western Australia
- Uma, 5 to 9 February 1987, Pacific Ocean
- Veli, 8 to 9 February 1987, Pacific Ocean
- Clotilda, 11 to 16 February 1987, Indian Ocean
- Elsie, 22 to 25 February 1987, near Western Australia
- Wini, 1 to 6 March 1987, Pacific Ocean
- Daodo, 3 to 15 March 1987, Indian Ocean
- Yali, 8 to 12 March 1987, Pacific Ocean
- Kay, 8 to 16 April 1987, Pacific Ocean
- Zuman, 23 to 26 April 1987, Pacific Ocean
- Blanche, 22 to 25 May 1987, Timor Sea
1987–88 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season
Cyclone Charlie
Charlie struck Ayr, Queensland in March,1988 killing one person and leaving $2,300,000 dollars (1988 USD) in damage. [7]
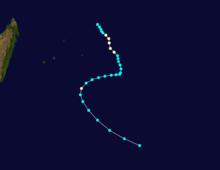
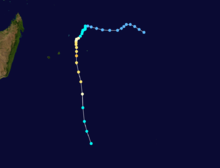
Cyclone Bola
Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 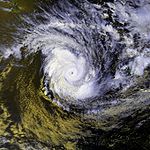
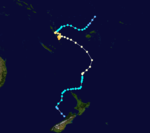
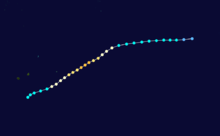
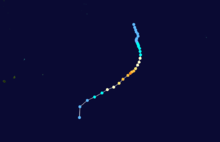
Duration February 24 – March 4 Intensity 195 km/h (120 mph) (1-min), 935 mbar (hPa) Main article: Cyclone BolaCyclone Bola struck New Zealand between February and March, 1988 killing 3 people.
Cyclone Filao
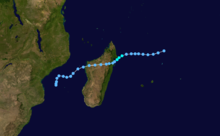
Cyclone Filao struck eastern Mozambique. Resulting floods killed 100 people. [8]
Other cyclones
The following cyclones also occurred within the 1987/1988 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season: [9]
- Ariny, 9 to 14 December 1987, Indian Ocean
- Bernandro, 27 December 1987 to 1 January 1988, Indian Ocean
- Agi, 6 to 14 January 1988, Pacific Ocean
- Anne, 7 to 14 January 1988, Pacific Ocean
- Calidero, 13 to 15 January 1988, Madagascar
- Doaza, 23 January to 2 February 1988, Indian Ocean
- Frederic, 31 January to 2 February 1988, Indian Ocean
- Gwenda/Ezenina, 8 to 16 February 1988, Indian Ocean
- Cilla, 28 February to 3 March 1988, Pacific Ocean
- Gasitao, 16 to 23 March 1988, Indian Ocean
- Hely, 27 to 28 March 1988, Indian Ocean
- Dovi, 9 to 15 April 1988, Pacific Ocean
- Iarisena, 9 to 10 May 1988, Indian Ocean
1988–89 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season
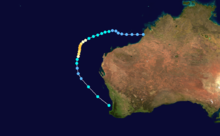
Cyclone Ilona
Ilona developed off the Western Australian coast on 12 December 1988 and made landfall northeast of Onslow, Western Australia on 17 December 1988. Ilona attained a minimum central pressure of 960 mb and maximum wind speed of 85 knots.
Cyclone Delilah
This was a strong tropical storm that formed off the Queensland coast on 28 December 1988 and tracked virtually eastward before dissipating on 1 January 1989.
Cyclone John
John was a moderate tropical storm that developed in the central Indian Ocean on 23 January 1989. The storm followed a generally southward trajectory and attained a minimum central pressure of 990 mb before dissipating on 2 February 1989.
Cyclone Ned
Occurring between 26 March to 31 March 1989, Ned crossed the Western Australian coast near Rockingham on 1 April 1989. Rottnest and Fremantle reported wind gusts of more than 100 km/h between 6 and 7 am. Only minor damage was reported on land. [10]
Cyclone Aivu
Aivu made landfall near Ayr, Queensland on April 4, 1989 causing serious damage and killing one person.[11]
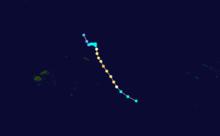
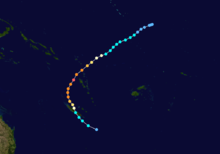
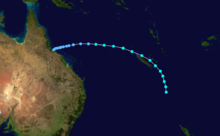
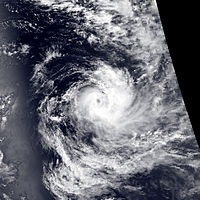
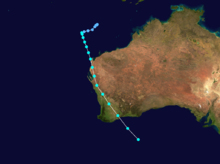
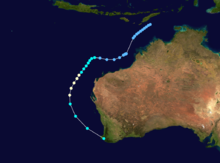
Severe Tropical Cyclone Orson
Category 5 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Category 5 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 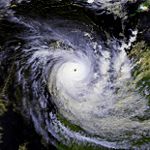
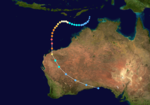
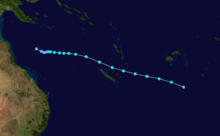
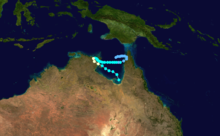
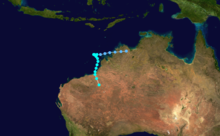
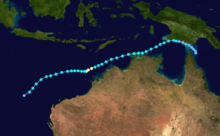
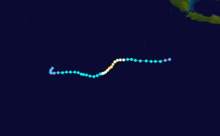
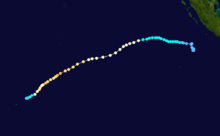
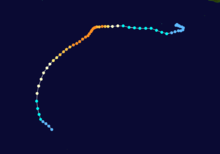
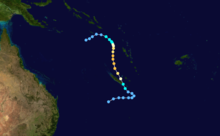
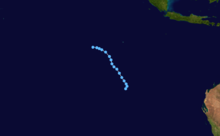
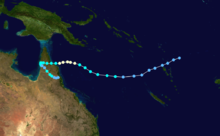
Duration April 16 – April 23 Intensity 260 km/h (160 mph) (10-min), 905 mbar (hPa) Main article: Cyclone OrsonCyclone Orson was one of the most powerful tropical cyclones to affect the Western Australian coast, and damaged offshore oil rigs before making landfall. Several Indonesian fishing vessels were reportedly sunk by the cyclone in the vicinity of Ashmore Island, with at least four lives being lost.
A pressure of 905 hPa was recorded as the eye of the cyclone passed over North Rankin gas platform, the second lowest ever pressure recorded in an Australian cyclone.
Orson formed on 18 April 1989 and crossed the coast on Sunday 23 April 1989 at Cape Preston, about 70 km west of Karratha. The maximum wind gust recorded at Dampier was 183 km/h, however Mardie station, about 30 km west of the cyclone path, registered a gust of 211 km/h. Orson caused widespread roof and structural damage at Pannawonica as it passed over the townsite. The total damage cost was estimated to be in excess of $20M (1989 value). [12] [13]
Other cyclones
The following cyclones also occurred within the 1988/1989 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season: [14]
- Adelinina, 1 to 4 November 1988, Indian Ocean
- Barisaona, 8 to 20 November 1988, Indian Ocean
- Gina, 7 to 9 January 1989, Pacific Ocean
- Edme, 20 to 25 January 1989, Indian Ocean
- Firinga, 26 January to 1 February 1989, Indian Ocean
- Kirrily, 6 to 10 February 1989, Indian Ocean
- Harry, 8 to 19 February 1989, reached Category 5 in Pacific Ocean
- Leon-Hanitra, 17 to 28 February 1989, Indian Ocean
- Gizela, 18 to 22 February 1989, Indian Ocean
- Ivy, 23 February to 1 March 1989, Pacific Ocean
- Judy, 24 to 28 February 1989, Pacific Ocean
- Marcia, 3 to 4 March 1989, Indian Ocean
- Jinabo, 25 to 30 March 1989, Indian Ocean
- Krissy, 30 March to 7 April 1989, Indian Ocean
- Kerry, 31 March to 2 April 1989, Pacific Ocean
- Lezissy, 6 to 9 April 1989, Indian Ocean
- Lili, 7 to 11 April 1989, Pacific Ocean
- Meena, 3 to 10 May 1989, crossed Cape York Peninsula
- Ernie, 7 to 12 May 1989, Pacific Ocean
1989–90 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season
Main article: Timeline of the 1989–90 South Pacific cyclone seasonCyclone Nancy
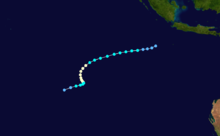
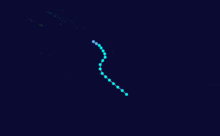
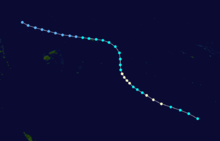
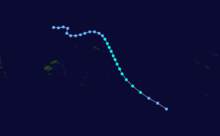
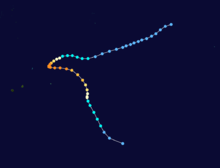
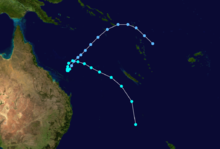
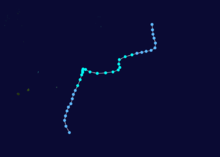
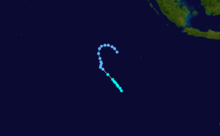
On February 3, 1990, Cyclone Nancy made landfall near Byron Bay, bringing flashfloods that killed five people.[15]
Cyclone Hilda
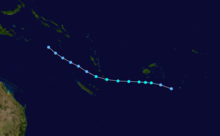
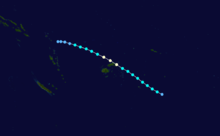
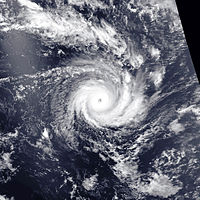
March 4–7, 1990, Pacific Ocean. Cyclone Hilda had cloud tops estimated at 62,000 feet tall. The measured cloud top temperature was -152°F, which is the coldest cloud-top temperature ever measured.
Other cyclones
The following cyclones also occurred within the 1989-1990 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season: [16]
- Pedro, 8 to 12 November 1989, Indian Ocean
- Felicity, 15 to 18 December 1989, crossed Cape York, Queensland
- Alibera, 19 December 1989 to 2 January 1990, crossed Madagascar
- Bavomavo, 2 to 7 January 1990, Indian Ocean
- Sam, 13 to 18 January 1990, near Western Australia
- Tina, 25 to 28 January 1990, crossed Western Australia
- Ofa, 31 January to 8 February 1990, Pacific Ocean
- Cezera, 1 to 9 February 1990, Indian Ocean
- Dety, 2 to 8 February 1990, Indian Ocean
- Peni, 13 to 17 February 1990, Pacific Ocean
- Vincent, 1 to 6 March 1990, near Western Australia
- Edisaona, 1 to 7 March 1990, Indian Ocean
- Greg, 3 to 5 March 1990, Gulf of Carpentaria
- Walter, 4 to 6 March 1990, Indian Ocean
- Felana, 8 to 15 March 1990, Indian Ocean
- Gregoara, 13 to 22 March 1990, Indian ocean
- Alex, 16 to 24 March 1990, Indian Ocean
- Ivor, 16 to 22 March 1990, crossed Cape York, Queensland
- Rae, 22 to 23 March 1990, Pacific Ocean
- Bessi, 16 to 17 April 1990, Indian Ocean
- Ikonjo, 12 to 20 May 1990, Indian Ocean
See also
References
Categories:- Hurricane articles without infoboxes
- 1985–90 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone seasons
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.