- 1990–95 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone seasons
-
The 1990–1995 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone seasons ran year-round from 1 July to 30 June during each year between 1990 and 1995. Tropical cyclone activity in the Southern Hemisphere reaches its peak from mid-February to early March.
1990–91 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season
Main article: 1990–91 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone seasonMain article: 1990–91 Australian region cyclone seasonMain article: 1990–91 South Pacific cyclone season1991–92 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season
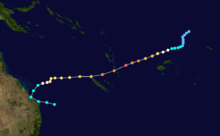
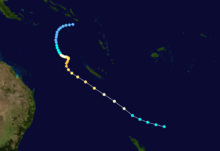
Main article: 1991–92 South Pacific cyclone seasonTropical Cyclone Fran
While out at sea, Fran reached the powerful Category 5 equivalent on the Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale. Eventually, as a Category 2 system, Fran crossed the coast near 1770, Queensland on 16 March 1992. Having crossed the coast a first time, Fran turned to the south-east and crossed the coast again, at Fraser Island, before heading back out to sea. The cyclone damaged houses in Bundaberg and extensively damaged a marina complex at Burnett Heads. The Kolan and Burnett rivers suffered major flooding. No deaths were attributed to this cyclone.
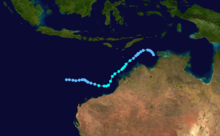
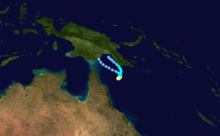
Severe Tropical Cyclone Ian
Category 5 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Category 4 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 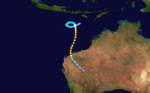
Duration 27 February – 4 March Intensity 210 km/h (130 mph) (10-min), 930 mbar (hPa) A Category 4 stuck Western Australia in March 1992 causing minimal damage. [2]
Tropical Cyclone Neville
Struck Tiwi Islands in April 1992 leaving only minor damage. [3]
Other tropical cyclones
The following tropical cyclones also occurred within the 1991–1992 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season: [4]
- Graham, 2 to 10 December 1991, Indian Ocean
- Alexandra, 20 to 25 December 1991, Indian Ocean
- Bryna, 30 December 1991 to 2 January 1992, crossed Madagascar
Tropical Cyclone Mark
Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Category 2 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 
Duration 7 January – 10 January Intensity 100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min), 980 mbar (hPa) - Celesta, 11 to 13 February 1992, Indian Ocean
- Davilia, 23 to 24 February 1992, Indian Ocean
Severe Tropical Cyclone Harriet
Category 5 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Category 4 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 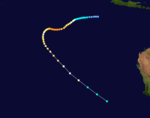
Duration 24 February – 9 March Intensity 210 km/h (130 mph) (10-min), 930 mbar (hPa) Severe Tropical Cyclone Ian
Category 4 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Category 4 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 
Duration 27 February – 7 March Intensity 185 km/h (115 mph) (10-min), 925 mbar (hPa) - Farida, 26 February to 3 March 1992, Indian Ocean
- Gerda, 27 to 28 February, Indian Ocean
- Jane/Irna, 8 to 18 April 1992, Indian Ocean
1992–93 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season
Tropical Cyclone Nina
Nina formed on December 23, 1992, the storm reached Category 1 status before making landfall in northern Queensland, then Nina moved eastward, reaching Category 3 status before becoming extratropical on January 2, 1993. [5]
Tropical Cyclone Kina
Formed on 26 December 1992 over the Pacific Ocean, north of Fiji's main Island, Viti Levu. Tracked towards the capital, Suva, where it caused significant damage and reports of casualties [6]. The main bridge and secondary bridge to the international airport at Nadi collapsed and subsequently delayed the evacuation of tourists from the island, with emergency ferry services forced to ferry passengers from buses waiting on either side of the river bank.
Throughout Fiji, 23 people were killed and damage amounted to $100 million.[1]
Tropical Cyclone Adel
Adel lasted from 13–16 May 1993. During its life, it passed over Bougainville Island and near Goodenough Island, leaving two drowned and a total of at least 15 missing. Leaves were blown from trees, and 345 houses were destroyed, along with a radio tower that was bent over.[7]
Other tropical cyclones
The following tropical cyclones also occurred within the 1992–1993 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season: [8]
- Aviona, 27 September to 1 October 1992, Indian Ocean
- Babie, 18 to 21 October 1992, Indian Ocean
- Joni, 6 to 12 December 1992, Pacific Ocean
- Ken, 19 to 23 December 1992, Indian Ocean
- Colina, 14 to 21 January 1993, Indian Ocean
- Dessilia, 20 to 21 January 1993, crossed Madagascar
- Edwina, 20 to 29 January 1993, Indian Ocean
- Lena, 24 to 29 January 1993, off Western Australia
- Lin, 31 January to 4 February 1993, Pacific Ocean
- Oliver, 4 to 12 February 1993, off Queensland
- Mick, 5 to 9 February 1993, Pacific Ocean
- Nisha, 12 to 16 February 1993, Pacific Ocean
- Finella, 13 to 15 February 1993, near Madagascar
- Oli, 16 to 18 February 1993, Pacific Ocean
- Polly, 25 February to 3 March 1993, Pacific Ocean
- Roger, 12 to 18 March 1993, Pacific Ocean
- Prema, 27 March to 1 April 1993, Pacific Ocean
- Jourdanne, 3 to 9 April 1993, Indian Ocean
- Monty, 10 to 12 April 1993, near Western Australia
- Konita, 2 to 7 May 1993, Indian Ocean
1993–94 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season
Tropical Cyclone Naomi

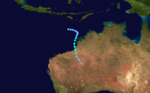
Duration 15 December – 18 December Intensity Winds unknown, Unknown Naomi was the first cyclone of the 1993/94 season. Forming early on 15 December 1993, the storm moved south and strengthened into a Category 3 before making landfall.[2] There was moderate damage and a fishing boat was disabled during the storm. There were no deaths.
Tropical Cyclone Oscar
Cyclone Oscar was a weak system, and only barely reached cyclone strength on 3 January 1994 for about a 12 hour period. It moved on a generally westsouthwest course parallel to the Kimberley and Pilbara coasts. [9]
Tropical Cyclone Pearl
Tropical Cyclone Pearl developed off the northwest Kimberley coast on 11 January 1994 and moved westwards as a very small but severe Category 3 cyclone covering a distance of more than 4000 km, before finally dissipating in the Central Indian Ocean on the 22nd. [10]
Tropical Cyclone Quenton
Tropical Cyclone Quenton began as a tropical low to the east of Christmas Island on 23 January 1994. The low moved slowly west, then on 25 January intensified to cyclone strength and moved southward across the Indian Ocean. By early on the 27th the cyclone had dissipated. [11]
Tropical Cyclone Sharon
Tropical Cyclone Sharon was the most intense cyclone in the Western Australian region during the 1993/94 season. It formed about 1100 km north of Northwest Cape on 13 March 1994, then rapidly intensified during the 14th while moving on a southsouthwest path towards the west Pilbara coast. During the 16th the cyclone rapidly weakened due to movement into a region of strong westerly wind shear. Cyclone warnings were issued for the west Pilbara and upper west coast on the 16th but were cancelled on the morning of the 17th Continued shearing and subsequent movement over cooler waters weakened the storm to below cyclone strength by the morning of the 18th. [12]
Tropical Cyclone Tim
Tropical Cyclone Tim was a very small weak system that moved on a generally westward path from south of Sumatra to the Cocos Islands from 30 March to 1 April 1994. It passed about 100 km to the south of Christmas Island but its effects, other than a wind shift, were barely recognisable on the Island. [13]
Tropical Cyclone Vivienne
Tropical Cyclone Vivienne formed from a tropical low that had moved westward across the Timor Sea. It intensified rapidly during the afternoon and night of 7 April 1994, reaching maximum intensity on 8 April when it was located 550 km to the northnorthwest of Broome. Its development from here on was hampered by vertical wind shear and Vivienne moved on a generally westsouthwest path parallel to, but well offshore from, the Western Australian coastline. It dissipated on 11 April and no watches or warnings were issued. [14]
Tropical Cyclone Willy
Willy was a Category 1 cyclone lasting from 28 to 30 April 1994 that passed about 80 km west of the Cocos Islands. [15]
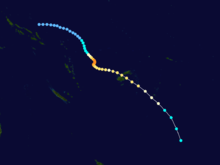
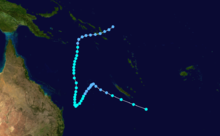
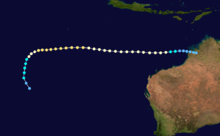
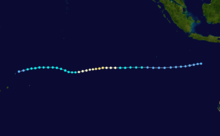
Tropical Cyclone Rewa
Category 5 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Category 4 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 

Duration 26 December – 23 January Intensity 205 km/h (125 mph) (10-min), 905 mbar (hPa) Main article: Cyclone RewaCyclone Rewa formed on 26 December 1993. It looped around the Coral Sea for almost a month, crossed New Caledonia and the Solomon Island, and dissipated on 21 January. Rewa was the longest-lived South Pacific tropical cyclone on record, lasting 25 days, from 26 December to 21 January.
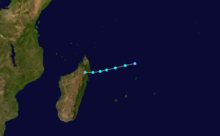
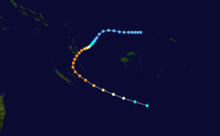
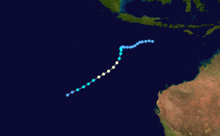
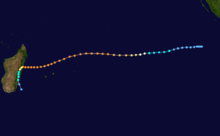
Intense Tropical Cyclone Geralda
Intense tropical cyclone (MFR) Category 5 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 
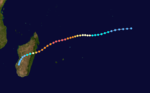
Duration 26 January – 5 February Intensity 205 km/h (125 mph) (10-min), 905 mbar (hPa) Part of a spree of four powerful cyclones to impact Madagascar this year, Geralda killed 200 people and left half a million homeless as it made landfall on the island in early February.
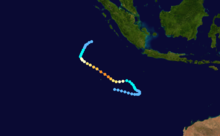
Tropical Cyclone Hollanda
Main article: Cyclone HollandaNamed shortly after Geralda was dissipating, Hollanda, a category 4 cyclone was the most devastating tropical cyclone to have hit the island of Mauritius in the Indian Ocean since tropical cyclone Gervaise in 1975. The cyclone passed 10 km to the west of Mauritius on February 10, 1994. The island was seriously affected, with winds of over 160 km/h (100 mph) and torrential rains (an average of 400mm for the island). The maximum gusts speed recorded was 218 km/h when Hollanda was at its closest to the country, earning a warning cyclone class 4 (the maximum). A warning cyclone class 4 is issued by the Mauritian Meteorological Services when gusts speeds of the order of 120 km/h is being recorded on the island and is expected to continue. On the Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale, Hollanda reached category 4 (winds speeds of 210–249 km/h). Some sources issued that tropical cyclone Hollanda could have exceeded the gusts speed of 216 km/h and reached about 300 km/h in Port Louis due to the considerable damage caused in the northern part of the island. In the capital city, some concrete buildings were severely damaged and a construction tower crane collapsed. The Mauritius Meteorological Services rejected that Hollanda could have peak to a category 5 or a very intense tropical cyclone with gusts of 280–300 km/h. During the cyclone, three people died by a falling tree, 50% of the telephone system was down, electrical power was nearly completely out, 50% of sugar plantation was destroyed, many vegetables fields were devastated, 1500 people became homeless and concrete buildings were moderately damaged. Major roads were blocked by trees and landslides. The estimated damaged caused by the cyclone was USD 135.4 million.[16][17][18]
Tropical Cyclone Nadia
The last of the spree of devastating Madagascar cyclones, Nadia made landfall in Madagascar in late March. After crossing the northern tip of the island, Nadia impacted Mozambique before returning to the Mozambique channel and finally dissipating. Nadia killed dozens in Madagascar. It claimed around 200 more lives in Mozambique and left over one million people homeless.
Tropical Cyclone Alexina
Tropical Cyclone Bettina
Tropical Cyclone Cecilia
Tropical Cyclone Daisy
Tropical Cyclone Edmea
Tropical Cyclone Farah
Tropical Cyclone Ivy
Tropical Cyclone Julita
Tropical Cyclone Kelvina
Tropical Cyclone Litanne
Tropical Cyclone Mariola
Tropical Cyclone Odille
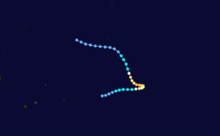
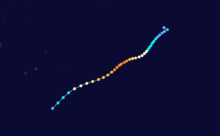
Tropical Depression 29P
Tropical depression (SSHS) 
Duration April 24 – April 25 Intensity 55 km/h (35 mph) (1-min), 1000 mbar (hPa) On April 20, the JTWC started to monitor an area of low pressure that located over the Solomon Islands about 155 km (95 mi) to the north of Honiara.[3] During that day the disturbance moved towards the southeast and passed over several of the Solomon Islands, before emerging into the Australian basin.[3] Over the next couple of days the disturbance gradually developed further while moving towards the southwest before re-curving and moving southeastwards.[3] On April 24, as it moved back into the South Pacific basin, the JTWC initiated advisories on the disturbance, designating it as Tropical Cyclone 29P, with peak windspeeds equivalent to a tropical depression.[3][4] As the system was classified, it recurved again and started to move slowly towards the northwest, and started to feel the effects of a hgih amount of vertical windshear.[3][4] As a result of the windshear, the center became exposed and displaced from the deep convection before the JTWC issued their final advisory on April 25 as 29P weakened into an area of low pressure, before dissipating later that day about 600 km (370 mi) to the southwest of Honiara.[3][4]
1994–95 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season
Main article: 1994–95 South Pacific cyclone seasonAustralian region
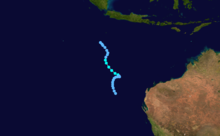
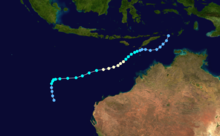
Tropical Cyclone Annette
Category 4 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Category 5 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 
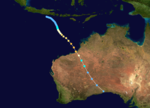
Duration 10 December – 20 December Intensity 185 km/h (115 mph) (10-min), 925 mbar (hPa) Annette formed on 15 December 1994. The storm moved southeastward while intensifying to a Category 4 cyclone. Annette made landfall at Mandora Station on 18 December. There was considerable damage to homes and crops and about a 1,000 cattle were lost in the storm.[19]
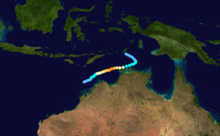
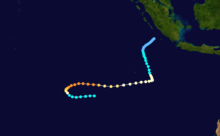
Tropical Cyclone Bobby
Category 4 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Category 5 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 
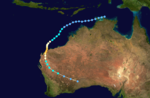
Duration 18 February – 27 February Intensity 180 km/h (115 mph) (10-min), 930 mbar (hPa) Severe Tropical Cyclone Bobby, a Category 4 cyclone with estimated winds up to 270 km/hour near the centre, crossed the Western Australian Pilbara coast to the east of Onslow between midnight and 0100 on the 25 February 1995. Seven lives were lost when two fishing trawlers were sunk off the coast from Onslow. A bulk ore carrier also ran aground in the cyclone. There was very minor property damage reported from the Karratha area and approximately 20 houses in Onslow suffered superficial roofing damage. Cyclone Bobby also brought heavy rains and extensive flooding to the south of the Pilbara area, which damaged roads, bridges and crops and seriously affected mining production. A motorist was drowned inland from Carnarvon while attempting to cross a flooded creek.[5][6][7]
Tropical Cyclone Chloe
Category 5 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Category 5 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 
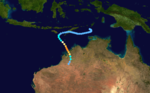
Duration 29 March – 9 April Intensity 200 km/h (125 mph) (10-min), 925 mbar (hPa) The third major cyclone to strike Australia. Cyclone Chloe reached Category 5 status before making landfall in the uninhabited section of the coast of the Kimberley region of Western Australia on 7 April 1995. The storm dissipated well inland.[20]
Other tropical cyclones
The following tropical cyclones also occurred within the 1994–1995 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season: [21]
Category 3 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 

Duration 28 February – 9 March Intensity 135 km/h (85 mph) (10-min), 960 mbar (hPa) - Violet, 3 to 7 March 1995, Category 3 in Pacific Ocean
- Warren, 5 to 6 March 1995, Gulf of Carpentaria
- Agnes, 17 to 22 April 1995, Category 3 near Cape York, Queensland
South-West Indian Ocean
Intense Tropical Cyclone Albertine
Intense tropical cyclone (MFR) Category 4 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 
Duration 21 November – 3 December Intensity 175 km/h (110 mph) (10-min), 925 mbar (hPa) Moderate Tropical Storm Bentha
Moderate tropical storm (MFR) Tropical storm (SSHS) 
Duration 3 January – 6 January Intensity 85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min), 984 mbar (hPa) Moderate Tropical Storm Christelle
Moderate tropical storm (MFR) Tropical storm (SSHS) 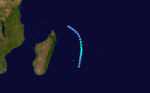
Duration 6 January – 9 January Intensity 85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min), 980 mbar (hPa) Intense Tropical Cyclone Dorina
Intense tropical cyclone (MFR) Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 
Duration 20 January – 29 January Intensity 175 km/h (110 mph) (10-min), 925 mbar (hPa) Severe Tropical Storm Fodah
Severe tropical storm (MFR) Tropical storm (SSHS) 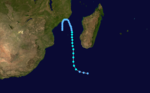
Duration 24 January – 26 January Intensity 100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min), 970 mbar (hPa) Tropical Cyclone Gail
Tropical cyclone (MFR) Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 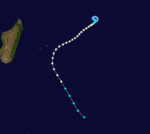
Duration 5 February – 11 February Intensity 140 km/h (85 mph) (10-min), 975 mbar (hPa) Moderate Tropical Storm Heida
Moderate tropical storm (MFR) Tropical storm (SSHS) 
Duration 5 February – 7 February Intensity 75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min), 990 mbar (hPa) Tropical Cyclone Ingrid
Tropical cyclone (MFR) Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 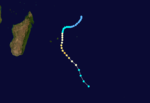
Duration 24 February – 1 March Intensity 150 km/h (90 mph) (10-min), 945 mbar (hPa) Severe Tropical Storm Josta
Severe tropical storm (MFR) Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 
Duration 7 March – 12 March Intensity 105 km/h (65 mph) (10-min), 972 mbar (hPa) Moderate Tropical Storm Kylie
Moderate tropical storm (MFR) Category 2 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 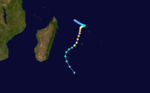
Duration 7 March – 12 March Intensity 85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min), 984 mbar (hPa) Tropical Depression Lidy
Tropical depression (MFR) 
Duration 14 March – 20 March Intensity 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min), 996 mbar (hPa) Intense Tropical Cyclone Marlene
Intense tropical cyclone (MFR) Category 4 tropical cyclone (SSHS) 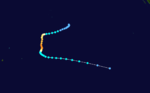
Duration 30 March – 10 April Intensity 185 km/h (115 mph) (10-min), 920 mbar (hPa) See also
References
- ^ http://www.apfm.info/pdf/case_studies/cs_fiji.pdf
- ^ [1]
- ^ a b c d e f Unattributed (2001-05-21). "Tropical Cyclone 29P Best Track Analysis". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. United States Navy. http://www.usno.navy.mil/NOOC/nmfc-ph/RSS/jtwc/best_tracks/1994/1994s-bsh/bsh291994.txt. Retrieved 2011-08-12.
- ^ a b c Roth, David (1994-04-12). "Weekly Tropical Cyclone Summary #140 (April 3 – 10, 1994)". http://groups.google.com/group/sci.geo.meteorology/browse_thread/thread/79eacfdbf3852891/036cb3fa4e7553fb?. Retrieved 2011-08-12.
- ^ Bureau of Meterology
- ^ Tropical Cyclones
- ^ Bobby and the Banded Stilts
External links
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.