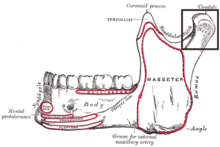
- Condylar resorption
-
Condylar resorption, also called idiopathic condylar resorption, ICR, and condylysis, is a Temporomandibular joint disorder in which one or both of the mandibular condyles are broken down in a bone resorption process. This disorder is nine times more likely to be present in females than males, and is more common among teenagers.[1]
Contents
Symptoms
Symptoms that may be associated with condylar resorption include:
- Occlusion
- Anterior open bite
- Receding chin
- Clicking or popping when opening or closing the jaw
- Pain when opening or closing the jaw
- Limited jaw mobility
Causes
Condylar resorption is an idiopathic condition, though there are some theories relating to its possible cause. Because condylar resorption is more likely to be in young females, hormonal mediation may be involved. Strain on the temporomandibular joint from orthodontics or orthognathic surgery may be related to the condition. Reactive arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis are other possible causes.[2]
Treatments
Treatment of condylar resorption is controversial. Orthognathic surgery may be done to reconstruct and stabilize the condyles and disc of the temporomandibular joint. Anti-infammatory medication is also used to slow the resorption process. Orthodontics may be used to treat the occlusion. Arthrocentesis, and arthroscopic surgery are also sometimes used to treat disc displacement and other symptoms.[2]
See also
- TMJ disorder
- Orthognathic surgery
References
- ^ Larry M. Wolford, DMD1, Idiopathic condylar resorption of the temporomandibular joint in teenage girls (cheerleaders syndrome), Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2001 July; 14(3): 246–252. PMCID: PMC1305829
- ^ a b Fonseca, Raymond J. , Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: Temporomandibular disorders, Elsevier Health Sciences, 2000, ISBN 072169635X, 9780721696355
Dentistry Recognized specialties
(in the United States)Endodontics - oral and maxillofacial pathology - Oral and maxillofacial radiology - Oral and maxillofacial surgery - Orthodontics and dentofacial orthopedics - Pediatric dentistry - Periodontics - Prosthodontics - Dental public healthFields that are not recognized specialties
(in the United States)Dental surgery Dental extraction - Tooth filling - Root canal therapy - Root end surgery - Scaling and root planing - Teeth cleaning -Dental bonding - Tooth polishing - Tooth bleaching - Dental implantSee also Index of oral health and dental articles - Outline of dentistry and oral health - Oral hygiene - Dental instruments - Restorative materials - Infant oral mutilationDentofacial anomalies and jaw disease (K07–K10, 524–526) Jaw Maxillomandibular anomaliesCategories:- Pain
- Dental disorders
- Musculoskeletal disorders
- Medical terms
- Idiopathic diseases
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.