- Asia-Pacific Partnership on Clean Development and Climate
-
"Asia Pacific Partnership" redirects here. For the US-led humanitarian deployment, see Pacific Partnership.
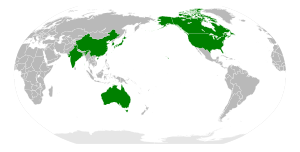
APP countries:
The Asia-Pacific Partnership on Clean Development and Climate, also known as APP, was an international, voluntary, public-private partnership among Australia, Canada, India, Japan, the People's Republic of China, South Korea, and the United States announced July 28, 2005 at an Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN) Regional Forum meeting and launched on January 12, 2006 at the Partnership's inaugural Ministerial meeting in Sydney. As of 5 April 2011, the Partnership formally concluded although a number of individual projects continue. The conclusion of the APP and cancellation of many of its projects attracted almost no media comment.
Foreign, Environment and Energy Ministers from partner countries agreed to co-operate on the development and transfer of technology which enables reduction of greenhouse gas emissions that is consistent with and complementary to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change and other relevant international instruments, and is intended to complement but not replace the Kyoto Protocol.,[1] Ministers agreed to a Charter, Communique and Work Plan that "outline a ground-breaking new model of private-public task forces to address climate change, energy security and air pollution."
Member countries account for over 50% of the world's greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, GDP and population. Unlike the Kyoto Protocol (currently unratified by the United States), which imposes mandatory limits on greenhouse gas emissions, the Partnership engages member countries to accelerate the development and deployment of clean energy technologies, with no mandatory enforcement mechanism. This has led to criticism that the Partnership is worthless, by other governments, climate scientists and environmental groups. Proponents, on the other hand, argue that unrestricted economic growth and emission reductions can only be brought about through active engagement by all major polluters, which includes India and China, within the Kyoto Protocol framework neither India nor China are yet required to reduce emissions.
Canada became the 7th member of the APP at the Second Ministerial Meeting in New Delhi on October 15, 2007. Canada's Prime Minister Stephen Harper earlier expressed his intention to join the Partnership in August 2007, despite some domestic opposition.[2]
Contents
Aims
U.S. President George W. Bush called it a "new results-oriented partnership" that he said "will allow our nations to develop and accelerate deployment of cleaner, more efficient energy technologies to meet national pollution reduction, energy security and climate change concerns in ways that reduce poverty and promote economic development."[3] John Howard, the former Australian Prime Minister, described the pact as "fair and effective"[citation needed]
However, the Worldwide Fund for Nature stated that "a deal on climate change that doesn't limit pollution is the same as a peace plan that allows guns to be fired" whilst the British Governments' chief scientific adviser, Sir David King, in a BBC interview said he doubted the new deal could work without setting caps on emissions, but added it should be seen as a sign of progress on climate change.[4] Compared to the Kyoto Protocol, which so far requires no emission reductions from India and China, the APP actively engages both countries through building market incentives to reduce greenhouse emissions along with building capacity and providing clean technology transfers. Proponents argue that this approach creates a greater likelihood that both India and China will, sooner rather than later, effectively cut their greenhouse emissions even though they are not required to do so under the Kyoto Protocol.
Areas for collaboration
The intent is to create a voluntary, non-legally binding framework for international cooperation to facilitate the development, diffusion, deployment, and transfer of existing, emerging and longer term cost- effective, cleaner, more efficient technologies and practices among the Partners through concrete and substantial cooperation so as to achieve practical results; promote and create enabling environments to assist in such efforts; facilitate attainment of the Partners' respective national pollution reduction, energy security and climate change objectives; and provide a forum for exploring the Partners’ respective policy approaches relevant to addressing interlinked development, energy, environment, and climate change issues within the context of clean development goals, and for sharing experiences in developing and implementing respective national development and energy strategies.
The Partnership's inaugural Ministerial meeting established eight government/business taskforces through its Work Plan,[5] posted on the APP website.[6]
- cleaner fossil energy [7]
- renewable energy and distributed generation [8]
- power generation and transmission [9]
- steel [10]
- aluminum [11]
- cement [12]
- coal mining [13]
- buildings and appliances [14]
Ministerial meetings
The inaugural ministerial meeting was held at the Four Seasons Hotel and Government House in Sydney, Australia on January 11 and 12, 2006.[15]
Asia-Pacific Partnership Ministers agreed and released a:
- Charter that provides the framework and structure of the Partnership;[16]
- Communiqué that highlights key outcomes from this meeting;[17] and
- Work Plan that maps out an intensive agenda of work for the taskforces in the near-term.[18]
Partnership Ministers met again in New Delhi, India on October 15, 2007, and released a second communique [19] and admitted Canada as a Partner.[20] The Ministers also met in Shanghai, China on October 26–27, 2009 where they discussed the accomplishments of the Partnership since the New Delhi Ministerial, and received the results of a report analyzing and evaluating the progress of the APP flagship projects.[21]
Support
The Partnership has been publicly supported as an alternative to the Kyoto Protocol by governments and business groups in some countries, particularly in countries where the Kyoto Protocol has not been ratified. Many commentators have particularly welcomed the fact that the Partnership overcomes the impasse between developed and developing countries under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change and the Kyoto Protocol and has led to India and China taking some steps to address their greenhouse gas emissions. Mexico, Russia, and several ASEAN members have expressed interest in joining the Partnership in the future.
Criticism
The Partnership has been criticized by environmentalists who have rebuked the proceedings as ineffectual without mandatory limits on greenhouse-gas emissions. A coalition of national environment groups and networks from all of the APP countries issued a challenge [22] to their governments to make the APP meaningful by agreeing to mandatory targets, creating financial mechanisms with incentives for the dissemination of clean energy technologies, and create an action plan to overcome the key barriers to technology transfer. U.S. Senator John McCain said the Partnership "[amounted] to nothing more than a nice little public relations ploy.",[23] while the Economist described the Partnership as "patent fig-leaf for the refusal of America and Australia to ratify Kyoto".[24]
In the year since the Partnership went into effect, none of the parties have lowered emissions of greenhouse gases.[citation needed] Although it should be noted that under the Kyoto Protocol Australia is able to increase its emissions from 1990 levels to 108%.
Successes
Proponents of the Partnership have lauded the APP’s achievements since it’s inception in 2006. In its over three years, the Partnership has established a record of achievement in promoting collaboration between our governments and private sector in key energy-intensive sectors and activities. The Partnership has worked to develop and implement detailed action plans across key sectors of the energy economy, and to date has endorsed 175 collaborative projects including 22 flagship projects across all the seven Partner countries. These projects have, inter alia, helped power plant managers improve the efficiency of their operations, trained cement plant operators how to save energy at their facilities, assisted in pushing solar photovoltaics toward commercialization, and improved design, equipment and operations of buildings and appliances. The Partnership has been widely noted for its innovative work in public-private sector cooperation, and stands as an example of the benefits of international cooperative efforts in addressing climate change.[25]
See also
- Mitigation of global warming
- FutureGen, a cancelled geosequestration project of the United States
- Asian brown cloud
References
- ^ APP Charter
- ^ Tonda MacCharles, "PM wants to join opponents of mandatory emission goals: Harper heading to APEC meeting in Australia to actively involve Canada in the workings of AP-6", The Star, August 30, 2007
- ^ "U.S. Joins Asia-Pacific Partnership on Clean Energy Technologies: Partnership formed with Australia, China, Japan, India, South Korea", U.S. Department of State, statement from the Office of the Press Secretary, U.S. White House, July 28, 2005
- ^ "US agrees climate deal with Asia", BBC News, July 28, 2005
- ^ APP Work Plan
- ^ APP Website
- ^ Cleaner Fossil Energy Task Force Webpage
- ^ Renewable Energy and Distributed Generation Task Force Webpage
- ^ Power Generation and Transmission Task Force Webpage
- ^ Steel Task Force Webpage
- ^ Aluminum Task Force Webpage
- ^ Cement Task Force Webpage
- ^ Coal Mining Task Force Webpage
- ^ Buildings and Appliances Task Force Webpage
- ^ APP Sydney Ministerial Meeting Webpage
- ^ APP Charter
- ^ APP Sydney Ministerial Communique
- ^ APP Workplan
- ^ APP New Delhi Ministerial Communique
- ^ APP New Delhi Ministerial Meeting Webpage
- ^ APP Fact Sheet
- ^ Climate Action Network Australia
- ^ Amanda Griscom Little, "Pact or Fiction? New Asia-Pacific climate pact is long on PR, short on substance", Grist.org article, August 4, 2005]
- ^ "Better late than never: India talks about tackling climate change", The Economist, July 30, 2007
- ^ Shanghai Communiqué
External links
- Asia-Pacific Partnership Website - Includes information on the work of the Partnership, individual Task Force and other meeting pages, and documents in all Partner languages
- Australian Department of Foreign Affairs Website Partnership Webpage - Includes documents
- China's Asia-Pacific Partnership Website - Includes documents in Chinese
- Japan's Asia-Pacific Partnership Website - Includes information in Japanese
- Korea's Asia-Pacific Partnership Website - Includes information in Korean
- U.S. Government's Asia-Pacific Partnership Website
- Joint Press Release: Asia-Pacific Partnership Sets New Path to Address Climate Change
- & China - The Lure of Cheap Coal
- Wikinews July 28, 2005
- US agrees climate deal with Asia - BBC
- Climate pact: For good or bad? - BBC
- CNN July 27, 2005
- First meeting for 'Kyoto rival' - BBC
- AAP report
- Sydney Morning Herald report
- AusBC report
Categories:- Association of Southeast Asian Nations laws
- Organizations associated with the Association of Southeast Asian Nations
- Climate institutions and programs
- Energy development
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.