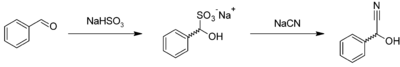- Mandelonitrile
-
Mandelonitrile[1]  2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrileOther namesα-hydroxybenzeneacetonitrile
2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrileOther namesα-hydroxybenzeneacetonitrileIdentifiers CAS number 532-28-5 PubChem 10758 ChemSpider 10304 
KEGG C00561 
ChEBI CHEBI:16910 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - N#CC(O)c1ccccc1
Properties Molecular formula C8H7NO Molar mass 133.15 g mol−1 Density 1.117 g/mL at 25 °C Melting point 28-30 °C
Boiling point 170 °C
Hazards R-phrases R23/24/25 R36/37/38 R41 S-phrases S22 S26 S36/37/39 S45 Main hazards toxic Flash point 113 °C Related compounds Related compounds mandelic acid, phenylacetonitrile  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Mandelonitrile is a chemical compound of the cyanohydrin class. Small amounts of mandelonitrile occur in the pits of some fruits.
Occurrence
The naturally-occurring (R)-(+) enantiomer finds use as an intermediate in the preparation of optically active α-hydroxy carboxylic acids, α-hydroxy aldehydes, α-hydroxy ketones, and 2-amino alcohols[2].
Mandelonitrile is broken down into cyanide and benzaldehyde by the enzyme mandelonitrile lyase.
Preparation
Racemic mandelonitrile may be prepared similar to many other cyanohydrins. In a one pot reaction, benzaldehyde is reacted with sodium bisulfite to give the corresponding adduct, which further reacts with aqueous sodium cyanide to give the racemic product:[3]
References
- ^ Sigma-Aldrich product page
- ^ Kruse, C.G. In Collins, A.N. Sheldrake, G.N. Crosby, J., Eds. Chirality in Industry Chichester, UK , (1992), 279
- ^ Corson, B. B.; Dodge, R. A.; Harris, S. A.; Yeaw, J. S. (1941), "Mandelic Acid", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv1p0336; Coll. Vol. 1: 336
Categories:- Cyanohydrins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.