- Ohio gubernatorial election, 2006
-
Ohio gubernatorial election, 2006 
2002 ← November 7, 2006 → 2010 

Nominee Ted Strickland Ken Blackwell Party Democratic Republican Popular vote 2,435,384 1,474,285 Percentage 60.54% 36.65%
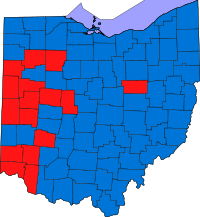
County Results
Governor before election
Elected Governor
Elections in Ohio 
 Federal offices
Federal officesPresidential Elections 2004 · 2008
Presidential primaries Senate elections 1974 · 1980 · 1986 · 1988 · 1992 · 1994 · 1998 · 2000 · 2004 · 2006 · 2010 · 2012
House of Representatives elections Special elections  State offices
State officesGubernatorial elections 1998 · 2002 · 2006 · 2010 · Complete List
Lieutenant Governor elections Secretary of State elections Attorney General elections State Auditor elections State Treasurer elections State Supreme Court elections  Columbus, Ohio
Columbus, OhioList of mayors of Columbus, Ohio  City of Cincinnati
City of CincinnatiMayoral elections 2009
City Council elections  City of Cleveland
City of ClevelandMayoral elections 1978 (recall) · 2009
City of Dayton Dayton elections Dayton City Commission
Montgomery County The Ohio gubernatorial election of 2006 was held on November 7, 2006, and was a race for the Governor and Lieutenant Governor of Ohio. Incumbent Governor Bob Taft could not run for re-election, as Ohio governors are limited to two consecutive terms in office.
The general election for governor pitted Ohio Secretary of State Ken Blackwell, the Republican nominee, against U.S. Representative Ted Strickland of Ohio's 6th congressional district (representing Steubenville, Marietta and Portsmouth), the Democratic nominee.
Their running mates for lieutenant governor was former Ohio Attorney General Lee Fisher for Strickland and state Representative Tom Raga for Blackwell. (Candidates for governor and lieutenant governor in Ohio run on a single ballot line).
Strickland captured about 60 percent of the vote; Blackwell conceded to Strickland at about 8:45 p.m. EST on November 7, 2006.[1] Strickland served from 2007 to 2011.
Contents
Historical background
National attention
As the election approached, there was increasing national attention on the Ohio gubernatorial election, focused largely on the ability of the Republican party to maintain control in Ohio. Results in Ohio in 2006 were regarded as a possible bellwether for the 2008 presidential election;[2] Ohio was considered a crucial swing state, with 20 electoral votes. Since the Republican Party's inception in 1854, no Republican presidential candidate has ever been elected to office without the electoral votes of Ohio. In contrast, a Democratic candidate has won the national election without the support of Ohio seven times (1836, 1844, 1856, 1884, 1892, 1944, 1960). Overall, Ohio's electoral votes have gone to the winner of the election 78% of the time.
Comedian and talk-show host Jon Stewart taped The Daily Show from October 30 to November 2, 2006, at the Roy Bowen Theater on the campus of Ohio State University. The series of episodes was entitled "Battlefield Ohio: The Daily Show’s Midwest Midterm Midtacular" and was intended to bring further national attention to the election in Ohio.[3] This was only the second time that the show had been filmed in a location other than New York City.
Ohio, Blackwell, and the 2004 election
Main article: 2004 United States election voting controversiesOhio played a decisive role in the 2004 presidential election, as Ohio's electoral votes would have been sufficient to swing the election from George W. Bush to John Kerry had Kerry won in Ohio. Given the importance of the state, Blackwell's role in the conduct of the election was closely scrutinized. As Ohio Secretary of State, Blackwell was the state's chief elections officer. He was also an honorary co-chair for the Bush re-election campaign in Ohio and the most prominent backer of a ballot measure to ban same-sex marriage on the same ballot.
Leading up to the election Blackwell made a number of decisions about the election process, most of which placed additional restrictions on voting. Opponents argued that Blackwell's decisions would have the effect of suppressing turnout among vulnerable populations, most of whom would be expected to vote for Kerry in the presidential contest—and that Blackwell had a conflict of interest as a co-chair of Bush's re-election campaign. Supporters argued that the Secretary of State had always been a partisan political office and that there was nothing wrong with Blackwell having a preference in the presidential elections; they denied that Blackwell's decisions were designed to benefit Bush.
Reaction to Blackwell's conduct was so strong that a coalition of left-leaning organizations attempted to amend the Ohio Constitution to abolish the Secretary of State's oversight of elections, as part of a package of election reforms. The proposal was rejected by voters in November 2005.[citation needed] Dissatisfaction with Blackwell's involvement in the 2004 election apparently hurt him with Ohio's African-American community; according to exit polls, Blackwell received only 20% of the vote in 2006,[4] compared to much higher showings in his previous races.[citation needed] Exit polls showed that confidence in the election process among Ohio voters was even lower than voters in Florida, the state which produced an unprecedented five-week post-election fight in 2000.[5] But among voters "very confident" that votes would be counted accurately, Blackwell actually led Strickland.
Republican control
Entering the 2006 campaign, Ohio had been dominated for a decade by Republicans. Republicans had held the governorship for sixteen years, occupied all statewide constitutional offices, and controlled both houses of the state legislature.
Important scandals
Bob Taft
Main article: Bob TaftAt a low point in his popularity in November 2005, Taft garnered only a 6.5% approval rating.[6] According to polling organization Survey USA, this was a lower proportion than any governor in the United States.[7] A poll taken in May 2006 indicated that only 2% of Ohio residents "strongly approved" of Taft's performance. The low approval ratings led pollster John Zogby to comment, "I'm not aware of anyone who's ever sunk lower."[6][8]
Taft's low approval ratings follow several years of scandals. In 2005, Taft pled no contest to four ethics violations involving illegal gifts totaling $5,800.[9] He was convicted of four misdemeanors and was ordered to pay a $4,000 fine and apologize to the people of Ohio. Taft is the only Ohio governor to be convicted of a crime while in office.
Thomas Noe and Coingate
Main article: Coingate scandalIn 1996 the Republican controlled Ohio General Assembly removed a restriction requiring that state investments only be in safer, though lower-yielding, bonds. After the restriction was eliminated, hundreds of millions of dollars in state funds were invested by a number of investment firms with close ties to the Republican party. Among those investments was $50 million of the Ohio Bureau of Worker's Compensation fund which was given to Thomas Noe, an investor in rare and unusual coins and major donor to the Republican Party including then-governor Bob Taft.[10]
In 2005 it was revealed that Noe could only account for $13 million of the original investment. Among the missing funds were two coins worth over $300,000 alone. Throughout 2005, there was a protracted legal battle over the release of records which Noe claimed were privileged and prosecutors claimed were in the public domain. The Ohio Supreme Court ruled 5-2 in favor of the prosecutors. On February 13, 2006, Noe was indicted on 53 counts, including: engaging in a pattern of corrupt activity (which carries a mandatory 10 year sentence), 11 counts of theft, 11 counts of money laundering, 8 counts of tampering with records, and 22 counts of forgery. The charges also accuse Noe of personally stealing $2 million. On November 20, 2006, Noe was found guilty of theft, money laundering, forgery and corrupt activity, and was sentenced to serve 18 years in prison, fined $213,000, ordered to pay the $2 million dollar cost of his prosecution and make restitution to the Ohio Bureau of Worker's Compensation.
Also in 2006, Noe pled guilty to three charges of using over a dozen people in 2004 as illegal "conduits" to make donations to George W. Bush's re-election campaign of over $45,000 in order to skirt laws limiting donations in federal campaigns to $2,000. Noe was convicted and sentenced to 27 months in federal prison and ordered to pay a $136,000 fine.[11]
Primaries
Republican
On May 2, 2006, Blackwell won the Republican nomination with 56% of the vote, defeating Attorney General Jim Petro.[12] State auditor Betty Montgomery had also been a candidate, but withdrew from the contest and instead ran for state attorney general, an office she lost to Democrat Marc Dann.[13] Despite commercials preaching his conservative values, Petro was never able to shake his previous pro-choice stance.[14] As the election approached, the barbs grew worse between Petro and Blackwell, only serving to bring more negative attention to the Ohio GOP.
Democratic
Strickland won the Democratic nomination with 79% of the vote against state representative Bryan Flannery.[15] Strickland was originally also in a tough fight for the nomination, as Columbus Mayor Michael Coleman was also campaigning and raising money. Before attacks were traded between the nominees, Coleman bowed out, citing a need to spend more time with his family.[16]
General election
Campaign finance
The race for the 2006 election was, in 2006, the most expensive in Ohio's history. Reflective of both the national significance of the race, as well as the powerful fund-raising capabilities of both parties, Blackwell and Strickland passed the previous fund raising record set in 1998. That record, set when current Governor Bob Taft was running against Lee Fisher (Strickland's running mate), totaled a combined $18 million by the end of the election. As of September 9, 2006, Blackwell and Strickland had already raised a combined $21.2 million dollars. Strickland led Blackwell, $11.2 million to $10 million.[17] Most of the money raised in Ohio by both major party candidates came from a single zip code in downtown Columbus, which is home to their respective parties, labor and political groups, lobbyists and lawyers.[18]
A significant amount of money was spent by private groups on behalf of the candidates as well, the estimated combined total at the time of the May 2 primary was $50 million.[19]
Polling
Since the first polls on the general election matchup were taken in November 2005, Strickland led Blackwell, though the margin substantially increased in March 2006.
The greatest margin recorded in an individual poll was found in the October 26, 2006, SurveyUSA poll which showed Strickland leading by 30 points. The smallest recorded margin was the February 6, 2006, Zogby poll showing Strickland leading by a mere 3 points. When the results are averaged across the different polls, the greatest margin was in October 2006 with a difference of 22.6 points in favor of Strickland. The smallest average margin was during January 2006 with Strickland leading Blackwell by 4 points.
Source Date Strickland (D) Blackwell (R) Peirce (L) Fitrakis (G) Survey USA November 6, 2006 55% 38% 2% 1% University of Cincinnati November 6, 2006 59% 37% 4% (Independents combined) CNN October 31, 2006 59% 36% Survey USA October 26, 2006 62% 32% 1% 1% Quinnipiac October 18, 2006 59% 32% NY Times/CBS News October 18, 2006 53% 29% 2% (Independents combined) University of Cincinnati October 14, 2006 52% 38% 3% 1% Survey USA October 12, 2006 60% 32% 2% 1% Rasmussen October 6, 2006 52% 40% Zogby September 28, 2006 48.3% 39.7% Survey USA September 28, 2006 56% 35% 2% 2% Rasmussen September 20, 2006 54% 35% Quinnipiac September 19, 2006 56% 34% University of Cincinnati September 17, 2006 50% 38% 3% 2% Zogby September 11, 2006 47.5% 41.8% Zogby August 28, 2006 49.7% 41.4% Rasmussen August 27, 2006 57% 32% Survey USA August 7, 2006 57% 35% 2% 1% Rasmussen August 1, 2006 50% 39% Zogby July 24, 2006 48.4% 43.8% Columbus Dispatch July 23, 2006 47% 27% Rasmussen June 27, 2006 50% 37% Zogby June 21, 2006 49.1% 44.3% Survey USA June 13, 2006 53% 37% 2% 1% University of Cincinnati May 25, 2006 50% 44% 2% (Independents combined) Rasmussen May 18, 2006 52% 36% Rasmussen April 25, 2006 52% 35% Rasmussen March 31, 2006 50% 40% Rasmussen February 19, 2006 47% 35% Zogby February 6, 2006 38% 35% Rasmussen January 7, 2006 44% 40% Rasmussen November 15, 2005 42% 36% Results
2006 gubernatorial election, Ohio Party Candidate Votes % ±% Democratic Ted Strickland 2,307,420 60.4 +22.1 Republican Ken Blackwell 1,406,792 36.8 -19.0 Libertarian Bill Peirce 67,596 1.8 n/a Green Bob Fitrakis 38,987 1.0 n/a Majority 900,628 21.6 Turnout 3,820,795 Democratic gain from Republican Swing Strickland won the overwhelming majority of Ohio's counties, although Blackwell did respectably in some traditionally Republican areas, mostly in western Ohio.[20]
Note that while Bill Pierce and Bob Fitrakis were endorsed by the Libertarian and Green parties, respectively, they appeared as independents on the ballot.
References
- ^ [1]
- ^ Urbina, Ian (April 21, 2006). "In the Race for Ohio Governor, All Sides Agree on a Need for Change". The New York Times. http://select.nytimes.com/gst/abstract.html?res=FB0E10F73F5B0C728EDDAD0894DE404482. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
- ^ [2]
- ^ "CNN.com - Elections 2006". CNN. http://www.cnn.com/ELECTION/2006//pages/results/states/OH/G/00/epolls.0.html. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
- ^ "CNN.com - Elections 2006". CNN. http://www.cnn.com/ELECTION/2006/pages/results/states/FL/G/00/epolls.0.html. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
- ^ a b [3]
- ^ [4]
- ^ [5]
- ^ [6]
- ^ [7]
- ^ [8]
- ^ [9]
- ^ [10]
- ^ [11]
- ^ [12]
- ^ "Coleman drops out of Ohio governor's race". November 29, 2005. http://www.bizjournals.com/columbus/stories/2005/11/28/daily12.html.
- ^ [13]
- ^ [14]
- ^ Smyth, Julie Carr (2006-05-04). "Ohio again center of political stage". The Cincinnati Post (Associated Press) (E. W. Scripps Company): p. A2. Archived from the original on 2006-08-21. http://web.archive.org/web/20060821161314/http://news.cincypost.com/apps/pbcs.dll/article?AID=/20060504/NEWS01/605040371. "Spending estimates already have reached $50 million."
- ^ "CNN.com - Elections 2006". CNN. http://www.cnn.com/ELECTION/2006//pages/results/states/OH/G/00/map.html. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
See also
Categories:- Ohio gubernatorial elections
- Ohio elections, 2006
- United States gubernatorial elections, 2006
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.