- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa
-
Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa
Marché commun de l'Afrique orientale et australe
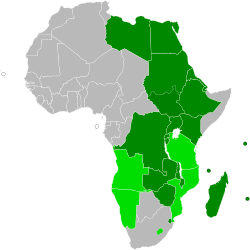
Mercado Comum da África Oriental e AustralAnthem: People of Africa[1] Map of membership in the COMESACurrent membersFormer membersSeat of Secretariat Lusaka, Zambia Official languages English, French and Portuguese Type Trade bloc Membership 20 member states Leaders - Secretary General Sindiso Ngwenya Establishment - Signed 5 November 1993 - Ratified 8 December 1994 Website
http://www.comesa.int/The Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa, is a free trade area with nineteen member states stretching from Libya to Zimbabwe. COMESA formed in December 1994, replacing a Preferential Trade Area which had existed since 1981. Nine of the member states formed a free trade area in 2000 (Djibouti, Egypt, Kenya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Sudan, Zambia and Zimbabwe), with Rwanda and Burundi joining the FTA in 2004 and the Comoros and Libya in 2006.
COMESA is one of the pillars of the African Economic Community.
In 2008, COMESA agreed to an expanded free-trade zone including members of two other African trade blocs, the East African Community (EAC) and the Southern Africa Development Community (SADC).
Contents
Membership
Current members:
 Burundi (21 Dec 1981)
Burundi (21 Dec 1981) Comoros (21 Dec 1981)
Comoros (21 Dec 1981) Democratic Republic of the Congo (21 Dec 1981)
Democratic Republic of the Congo (21 Dec 1981) Djibouti (21 Dec 1981)
Djibouti (21 Dec 1981) Egypt (6 Jan 1999)
Egypt (6 Jan 1999) Eritrea (1994)
Eritrea (1994) Ethiopia (21 Dec 1981)
Ethiopia (21 Dec 1981) Kenya (21 Dec 1981)
Kenya (21 Dec 1981) Libya (3 June 2005) (at the 10th Summit of COMESA)
Libya (3 June 2005) (at the 10th Summit of COMESA) Madagascar (21 Dec 1981)
Madagascar (21 Dec 1981) Malawi (21 Dec 1981)
Malawi (21 Dec 1981) Mauritius (21 Dec 1981)
Mauritius (21 Dec 1981) Rwanda (21 Dec 1981)
Rwanda (21 Dec 1981) Seychelles (2001)
Seychelles (2001) South Sudan (2011) [2]
South Sudan (2011) [2] Sudan (21 Dec 1981)
Sudan (21 Dec 1981) Swaziland (21 Dec 1981)
Swaziland (21 Dec 1981) Uganda (21 Dec 1981)
Uganda (21 Dec 1981) Zambia (21 Dec 1981)
Zambia (21 Dec 1981) Zimbabwe (21 Dec 1981)
Zimbabwe (21 Dec 1981)
Former members:
 Lesotho (quit in 1997)
Lesotho (quit in 1997) Mozambique (quit in 1997)
Mozambique (quit in 1997) Tanzania (quit on September 2, 2000)
Tanzania (quit on September 2, 2000) Namibia (quit on May 2, 2004)
Namibia (quit on May 2, 2004) Angola (Suspended itself in 2007) [3][4]
Angola (Suspended itself in 2007) [3][4]
Organs of the Common Market
The following organs have decision-making power according to the treaties
- The COMESA Authority, composes of Heads of States or Government.
- The COMESA Council of Ministers
- The COMESA Court of Justice
- The Committee of Governors of Central Banks
The following lower policy organs make recommendations to the above:
- The Inter-governmental Committee
- The Twelve Technical Committees
- The Consultative Committee of the Business Community and other Interest Groups
- The COMESA Secretariat.
Other institutions created to promote development are:
- The PTA Bank (Eastern and Southern African Trade and Development Bank) in Nairobi, Kenya
- The COMESA Clearing House in Harare, Zimbabwe
- The COMESA Association of Commercial Banks in Harare, Zimbabwe
- The COMESA Leather Institute in Ethiopia
- The COMESA Re-Insurance Company (ZEP-RE)in Nairobi, Kenya
- The Regional Investment Agency in Cairo, Egypt
Comparison with other regional blocs
African Economic Community Pillars
regional
blocs (REC)1Area (km²) Population GDP (PPP) ($US) Member
statesin millions per capita AEC 29,910,442 853,520,010 2,053,706 2,406 54 ECOWAS 5,112,903 251,646,263 342,519 1,361 15 ECCAS 6,667,421 121,245,958 175,928 1,451 11 SADC 9,882,959 233,944,179 737,335 3,152 15 EAC 1,817,945 124,858,568 104,239 1,065 5 COMESA 12,873,957 406,102,471 735,599 1,811 20 IGAD 5,233,604 187,969,775 225,049 1,197 7 Other
African
blocsArea (km²) Population GDP (PPP) ($US) Member
statesin millions per capita CEMAC 2 3,020,142 34,970,529 85,136 2,435 6 SACU 2 2,693,418 51,055,878 541,433 10,605 5 UEMOA 2 3,505,375 80,865,222 101,640 1,257 8 UMA 3 5,782,140 84,185,073 491,276 5,836 5 GAFTA 4 5,876,960 166,259,603 635,450 3,822 5 1 The Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR) is a signatory to the AEC, but not participating in any bloc yet
2 Economic bloc inside a pillar REC
3 Proposed for pillar REC, but objecting participation
4 Non-African members of GAFTA are excluded from figuressmallest value among the blocs comparedlargest value among the blocs comparedDuring 2004. Source: CIA World Factbook 2005, IMF WEO Database