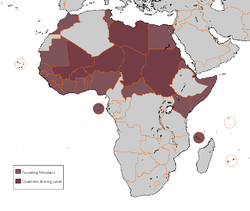
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States
-
Community of Sahel-Saharan States
تجمع دول الساحل والصحراء
Communauté des Etats Sahélo-SahariensHeadquarters Tripoli, Libya Official language English, French, Arabic and Portuguese Type Trade bloc Membership 28 member states Leaders - Secretary General Mohamed Al-Madani Al-Azhari Establishment - Signed 4 February 1998 Website
http://www.cen-sad.org/African Union 
This article is part of the series:
InstitutionsExecutiveLegislatureJudiciaryAdvisory bodiesFinancial bodiesDecentralised bodies
CEN-SAD or the Community of Sahel-Saharan States (French: Communauté des Etats Sahélo-Sahariens Arabic: تجمع دول الساحل والصحراء) aims to create a free trade area. There are questions with regard to whether its level of economic integration qualifies it under the Enabling clause.
Contents
Establishment
CEN-SAD was established in February 1998 by six countries, but since then its membership has grown to 28. One of its main goals is to achieve economic unity through the implementation of the free movement of people and goods in order to make the area occupied by member states a free trade area. At the international level, CEN-SAD gained observer status at the UN General Assembly in 2001 and concluded association and cooperation accords with the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (ECA) as well as with UN specialized agencies and institutions such as UNDP, WHO, UNESCO, FAO, and the Permanent Interstate Committee for drought control in the Sahel.
All CEN-SAD member countries are also participating in other African economic unions, that have the aim to create a common African Economic Community. The envisioned Free Trade Area of CEN-SAD would be hard to practically implement, because it is overlapping with the envisioned Customs Unions of ECOWAS, ECCAS and COMESA and other trade blocs more advanced in their integration.
2007 Summit
The African leaders sought to reconcile differences between neighbours Chad and Sudan over the Darfur conflict and boost Somalia's embattled Transitional Federal Government at a regional summit in Libya on June 3, 2007.[1]
CEN-SAD Games
Beginning in 2009, CEN-SAD member states will take part in planned periodic international sporting and cultural festivals, known as the Community of Sahel-Saharan States Games (Jeux de la Communauté des Etats Sahélo-Sahariens).[1] The first CEN-SAD Games were held in Niamey, Niger from 4–14 February 2009. Thirteen nations competed in Under-20 sports (athletics, basketball, judo, football, handball, table tennis and traditional wrestling) and six fields of cultural competition (song, traditional creation and inspiration dancing, painting, sculpture and photography). The second CEN-SAD Games are scheduled to take place in the Chadian capitol of N’Djamena in February 2011.[2]
List of members
Founding members:
Countries that joined later:
 Central African Republic (1999)
Central African Republic (1999) Eritrea (1999)
Eritrea (1999) Djibouti (2000)
Djibouti (2000) Gambia (2000)
Gambia (2000) Senegal (2000)
Senegal (2000) Egypt (2001)
Egypt (2001) Morocco (2001)
Morocco (2001) Nigeria (2001)
Nigeria (2001) Somalia (2001)
Somalia (2001) Tunisia (2001)
Tunisia (2001) Benin (2002)
Benin (2002) Togo (2002)
Togo (2002) Côte d'Ivoire (2004)
Côte d'Ivoire (2004) Guinea-Bissau (2004)
Guinea-Bissau (2004) Liberia (2004)
Liberia (2004) Ghana (2005)
Ghana (2005) Sierra Leone (2005)
Sierra Leone (2005) Comoros (2007)
Comoros (2007) Guinea (2007)
Guinea (2007) Kenya (2008)
Kenya (2008) Mauritania (2008)
Mauritania (2008) São Tomé and Príncipe (2008)
São Tomé and Príncipe (2008)
References
- ^ La première édition des Jeux de la CEN-SAD en février 2009 au Niger, APANEWS, 17 June 2008.
- ^ Maiden CEN-SAD Games ends in glory in Niamey . APA News. 2009-02-15.
External links
- CEN-SAD Community of Sahel-Saharan States Website
- African Union page on CEN-SAD
This article about or relating to the African Union is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.