- Toluene diisocyanate
-
Toluene-2,4-diisocyanate 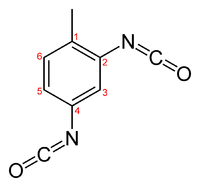
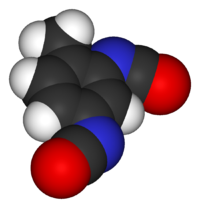 2,4-diisocyanato-1-methyl-benzeneOther namesTolylene diisocyanate
2,4-diisocyanato-1-methyl-benzeneOther namesTolylene diisocyanate
Methyl phenylene diisocyanateIdentifiers CAS number 584-84-9 
ChemSpider 13835351 
ChEBI CHEBI:53556 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1086446 
RTECS number CZ6300000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - Cc1ccc(cc1\N=C=O)\N=C=O
Properties Molecular formula C9H6N2O2 Molar mass 174.2 g/mol Appearance Colorless to pale yellow, liquid Density 1.214 g/cm3, liquid Melting point 21.8 °C (295.0 K)
Boiling point 251 °C (524 K)
Solubility in water Reacts Hazards MSDS External MSDS EU classification Very toxic (T+)
Carc. Cat. 3R-phrases R26, R36/37/38, R40,
R42/43, R52/53S-phrases (S1/2), S23, S36/37, S45, S61 NFPA 704 Flash point 127 °C Related compounds Related isocyanates Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate
Naphthalene diisocyanateRelated compounds Polyurethane Supplementary data page Structure and
propertiesn, εr, etc. Thermodynamic
dataPhase behaviour
Solid, liquid, gasSpectral data UV, IR, NMR, MS  diisocyanate (verify) (what is:
diisocyanate (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Toluene diisocyanate (TDI) is an aromatic diisocyanate. It is produced for reaction with polyols to form polyurethanes. It exists in two isomers, 2,4-TDI (CAS: 584-84-9) and 2,6-TDI (CAS: 91-08-7). 2,4-TDI is produced in the pure state, but TDI is often marketed as 80/20 and 65/35 mixtures of the 2,4 and 2,6 isomers respectively. It is a highly produced diisocyanate, accounting for 34.1% of the global isocyanate market in 2000, second only to MDI.[1] All major producers of TDI are members of the International Isocyanate Institute, whose aim is the promotion of the safe handling of TDI in the workplace, community and environment.
Contents
Synthesis
There are six steps to the synthesis of pure 2,4-TDI:[1]
- Nitration: Reaction of toluene with nitric acid and a catalyst to form dinitrotoluene
- Hydrogenation: Reaction of the dinitrotoluene with hydrogen and a catalyst to form a mixture of isomers of toluene diamine (TDA)
- Purification: Distillation of the TDA mixture to produce meta-TDA
- Phosgenation: Reaction of the meta-TDA with phosgene to form a crude TDI mixture
- Purification: Distillation of the crude TDI mixture to produce an 80:20 mixture of 2,4-TDI and 2,6-TDI, known as TDI (80/20)
- Differentiation: Separation of the TDI (80/20) to produce pure 2,4-TDI and a 65:35 mixture of 2,4-TDI and 2,6-TDI, known as TDI (65/35)
Chemistry
Each of the isocyanate functional groups in TDI can react with a hydroxyl group to form a urethane linkage.
2,4-TDI is an asymmetrical molecule and thus has two isocyanate groups of different reactivity. The 4-position is approximately four times more reactive than the 2-position. 2,6-TDI is a symmetrical molecule and thus has two isocyanate groups of similar reactivity, similar to the 2-position on 2,4-TDI. However, since both isocyanate groups are attached to the same aromatic ring, reaction of one isocyanate group will cause a change in the reactivity of the second isocyanate group.[1]
Hazards
Exposure to TDI and its vapors should be avoided. It is a well-documented causative agent of asthma.
Information on handling, personal protective equipment, exposure monitoring, transport, storage, sampling and analysis of TDI, dealing with accidents, and health and environmental information have been published [2]
TDI is one of eleven statutorily listed "Extremely Hazardous Substances" under the New Jersey Toxic Catastrophe Prevention Act whose release "would produce a significant likelihood that persons exposed will suffer acute health effects resulting in death or permanent disability." N.J.S.A. 13:1K-21(e)
See also
References
2. Allport DC, Gilbert, DS and Outterside SM (eds) (2003). MDI and TDI: safety, health & the environment: a source book and practical guide. Chichester, Wiley. http://eu.wiley.com/WileyCDA/WileyTitle/productCd-0471958123.html
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 0339
- IARC Monograph: "Toluene Diisocyanates"
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
- Hazards of TDI, MDI, and HDI
- NIOSH Safety and Health Topic: Isocyanates, from the website of the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
- International Isocyanate Institute http://www.diisocyanates.org
Categories:- Isocyanates
- Monomers
- IARC Group 2B carcinogens
- Aromatic compounds
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

