- Nucleolin
-
Nucleolin 
PDB rendering based on 2fc8.Available structures PDB 2FC8, 2FC9, 2KRR Identifiers Symbols NCL; C23; FLJ45706; FLJ59041 External IDs OMIM: 164035 HomoloGene: 21821 GeneCards: NCL Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • nucleotide binding
• DNA binding
• RNA binding
• protein binding
• protein C-terminus binding
• telomeric DNA bindingCellular component • nucleus
• nucleoplasm
• nucleolus
• cytoplasm
• cell cortex
• ribonucleoprotein complexBiological process • angiogenesis Sources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 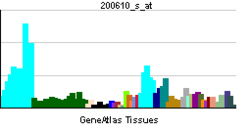
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 4691 n/a Ensembl ENSG00000115053 n/a UniProt P19338 n/a RefSeq (mRNA) NM_005381 n/a RefSeq (protein) NP_005372 n/a Location (UCSC) Chr 2:
232.32 – 232.35 Mbn/a PubMed search [1] n/a Nucleolin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCL gene.[1][2]
Contents
Gene
The human NCL gene is located on chromosome 2 and consists of 14 exons with 13 introns and spans approximately 11kb. The intron 11 of the NCL gene encodes a small nucleolar RNA, termed U20.[3]
Function
Nucleolin (NCL), a eukaryotic nucleolar phosphoprotein, is involved in the synthesis and maturation of ribosomes.[3] The protein is located mainly in dense fibrillar regions of the nucleolus.
Clinical significance
Midkine and pleiotrophin bind to cell-surface nucleolin as a low affinity receptor. This binding can inhibit HIV infection.[4][5]
Interactions
Nucleolin has been shown to interact with PPP1CB,[6] Centaurin, alpha 1,[7] CSNK2A2,[8] Sjogren syndrome antigen B,[9] TOP1,[10][11] P53,[12] S100A11,[13] NPM1[14], Telomerase reverse transcriptase[15], and HuR[16].
References
- ^ Srivastava M, McBride OW, Fleming PJ, Pollard HB, Burns AL (October 1990). "Genomic organization and chromosomal localization of the human nucleolin gene". J Biol Chem 265 (25): 14922–31. PMID 2394707.
- ^ Erard MS, Belenguer P, Caizergues-Ferrer M, Pantaloni A, Amalric F (October 1988). "A major nucleolar protein, nucleolin, induces chromatin decondensation by binding to histone H1". Eur J Biochem 175 (3): 525–30. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14224.x. PMID 3409881.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: NCL nucleolin". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=4691.
- ^ Said EA, Krust B, Nisole S, Svab J, Briand JP, Hovanessian AG (October 2002). "The anti-HIV cytokine midkine binds the cell surface-expressed nucleolin as a low affinity receptor". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (40): 37492–502. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201194200. PMID 12147681.
- ^ Said EA, Courty J, Svab J, Delbé J, Krust B, Hovanessian AG (September 2005). "Pleiotrophin inhibits HIV infection by binding the cell surface-expressed nucleolin". FEBS J. 272 (18): 4646–59. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04870.x. PMID 16156786.
- ^ Morimoto, Hiroyuki; Okamura Hirohiko, Haneji Tatsuji (September 2002). "Interaction of protein phosphatase 1 delta with nucleolin in human osteoblastic cells". J. Histochem. Cytochem. (United States) 50 (9): 1187–93. doi:10.1177/002215540205000905. ISSN 0022-1554. PMID 12185196.
- ^ Dubois, Thierry; Zemlickova Eva, Howell Steven, Aitken Alastair (February 2003). "Centaurin-alpha 1 associates in vitro and in vivo with nucleolin". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. (United States) 301 (2): 502–8. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)03010-3. ISSN 0006-291X. PMID 12565890.
- ^ Li, D; Dobrowolska G, Krebs E G (June 1996). "The physical association of casein kinase 2 with nucleolin". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 271 (26): 15662–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.26.15662. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 8663258.
- ^ Fouraux, Michael A; Bouvet Philippe, Verkaart Sjoerd, van Venrooij Walther J, Pruijn Ger J M (July 2002). "Nucleolin associates with a subset of the human Ro ribonucleoprotein complexes". J. Mol. Biol. (England) 320 (3): 475–88. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00518-1. ISSN 0022-2836. PMID 12096904.
- ^ Haluska, P; Saleem A, Edwards T K, Rubin E H (April 1998). "Interaction between the N-terminus of human topoisomerase I and SV40 large T antigen". Nucleic Acids Res. (ENGLAND) 26 (7): 1841–7. doi:10.1093/nar/26.7.1841. ISSN 0305-1048. PMC 147454. PMID 9512561. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=147454.
- ^ Bharti, A K; Olson M O, Kufe D W, Rubin E H (January 1996). "Identification of a nucleolin binding site in human topoisomerase I". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 271 (4): 1993–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.4.1993. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 8567649.
- ^ Daniely, Yaron; Dimitrova Diana D, Borowiec James A (August 2002). "Stress-Dependent Nucleolin Mobilization Mediated by p53-Nucleolin Complex Formation". Mol. Cell. Biol. (United States) 22 (16): 6014–22. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.16.6014-6022.2002. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 133981. PMID 12138209. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=133981.
- ^ Sakaguchi, Masakiyo; Miyazaki Masahiro, Takaishi Mikiro, Sakaguchi Yoshihiko, Makino Eiichi, Kataoka Noriyuki, Yamada Hidenori, Namba Masayoshi, Huh Nam-ho (November 2003). "S100C/A11 is a key mediator of Ca2+-induced growth inhibition of human epidermal keratinocytes". J. Cell Biol. (United States) 163 (4): 825–35. doi:10.1083/jcb.200304017. ISSN 0021-9525. PMC 2173690. PMID 14623863. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2173690.
- ^ Li, Y P; Busch R K, Valdez B C, Busch H (April 1996). "C23 interacts with B23, a putative nucleolar-localization-signal-binding protein". Eur. J. Biochem. (GERMANY) 237 (1): 153–8. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0153n.x. ISSN 0014-2956. PMID 8620867.
- ^ Khurts, Shilagardi; Masutomi Kenkichi, Delgermaa Luvsanjav, Arai Kuniaki, Oishi Naoki, Mizuno Hideki, Hayashi Naoyuki, Hahn William C, Murakami Seishi (December 2004). "Nucleolin interacts with telomerase". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 279 (49): 51508–15. doi:10.1074/jbc.M407643200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 15371412.
- ^ Tominaga, K; Srikantan S, Lee EK, Subaran SS, Martindale JL, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M (August 2011). "Competitive Regulation of Nucleolin Expression by HuR and miR-494". Mol. Cell Biol. (United States) 31 (20): 4219–31. PMID 21859890.
Further reading
- Tuteja R, Tuteja N (1999). "Nucleolin: a multifunctional major nucleolar phosphoprotein". Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 33 (6): 407–36. doi:10.1080/10409239891204260. PMID 9918513.
- Pasternack MS, Bleier KJ, McInerney TN (1991). "Granzyme A binding to target cell proteins. Granzyme A binds to and cleaves nucleolin in vitro". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (22): 14703–8. PMID 1860869.
- Belenguer P, Caizergues-Ferrer M, Labbé JC et al. (1990). "Mitosis-specific phosphorylation of nucleolin by p34cdc2 protein kinase". Mol. Cell. Biol. 10 (7): 3607–18. PMC 360797. PMID 2192260. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=360797.
- Srivastava M, Fleming PJ, Pollard HB, Burns AL (1989). "Cloning and sequencing of the human nucleolin cDNA". FEBS Lett. 250 (1): 99–105. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(89)80692-1. PMID 2737305.
- Tuteja N, Huang NW, Skopac D et al. (1995). "Human DNA helicase IV is nucleolin, an RNA helicase modulated by phosphorylation". Gene 160 (2): 143–8. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(95)00207-M. PMID 7642087.
- Jordan P, Heid H, Kinzel V, Kübler D (1995). "Major cell surface-located protein substrates of an ecto-protein kinase are homologs of known nuclear proteins". Biochemistry 33 (49): 14696–706. doi:10.1021/bi00253a007. PMID 7993898.
- Nicoloso M, Caizergues-Ferrer M, Michot B et al. (1994). "U20, a novel small nucleolar RNA, is encoded in an intron of the nucleolin gene in mammals". Mol. Cell. Biol. 14 (9): 5766–76. PMC 359102. PMID 8065311. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=359102.
- Ishikawa F, Matunis MJ, Dreyfuss G, Cech TR (1993). "Nuclear proteins that bind the pre-mRNA 3' splice site sequence r(UUAG/G) and the human telomeric DNA sequence d(TTAGGG)n". Mol. Cell. Biol. 13 (7): 4301–10. PMC 359985. PMID 8321232. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=359985.
- Eggert M, Möws CC, Tripier D et al. (1996). "A fraction enriched in a novel glucocorticoid receptor-interacting protein stimulates receptor-dependent transcription in vitro". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (51): 30755–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.51.30755. PMID 8530516.
- Bharti AK, Olson MO, Kufe DW, Rubin EH (1996). "Identification of a nucleolin binding site in human topoisomerase I". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (4): 1993–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.4.1993. PMID 8567649.
- Li YP, Busch RK, Valdez BC, Busch H (1996). "C23 interacts with B23, a putative nucleolar-localization-signal-binding protein". Eur. J. Biochem. 237 (1): 153–8. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0153n.x. PMID 8620867.
- Li D, Dobrowolska G, Krebs EG (1996). "The physical association of casein kinase 2 with nucleolin". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (26): 15662–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.26.15662. PMID 8663258.
- Zhou G, Seibenhener ML, Wooten MW (1998). "Nucleolin is a protein kinase C-zeta substrate. Connection between cell surface signaling and nucleus in PC12 cells". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (49): 31130–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.49.31130. PMID 9388266.
- Haluska P, Saleem A, Edwards TK, Rubin EH (1998). "Interaction between the N-terminus of human topoisomerase I and SV40 large T antigen". Nucleic Acids Res. 26 (7): 1841–7. doi:10.1093/nar/26.7.1841. PMC 147454. PMID 9512561. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=147454.
- Borggrefe T, Wabl M, Akhmedov AT, Jessberger R (1998). "A B-cell-specific DNA recombination complex". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (27): 17025–35. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.27.17025. PMID 9642267.
- Larrucea S, González-Rubio C, Cambronero R et al. (1998). "Cellular adhesion mediated by factor J, a complement inhibitor. Evidence for nucleolin involvement". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (48): 31718–25. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.48.31718. PMID 9822633.
- Parada CA, Roeder RG (1999). "A novel RNA polymerase II-containing complex potentiates Tat-enhanced HIV-1 transcription". EMBO J. 18 (13): 3688–701. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.13.3688. PMC 1171446. PMID 10393184. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1171446.
PDB gallery Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 2 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.