- Mehrangarh Fort
-
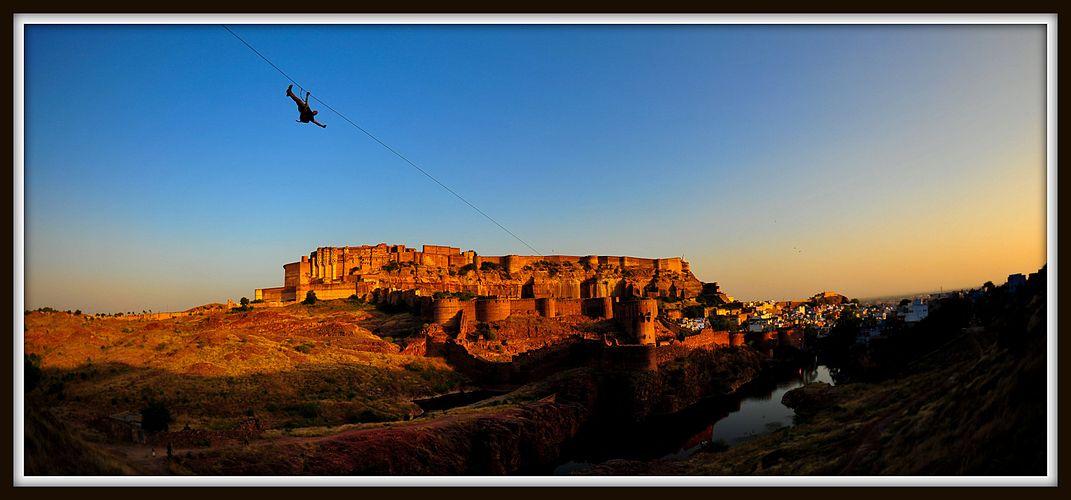
Mehrangarh Fort Jodhpur, India 
View of Mehrangarh FortType Fort Coordinates 26°18′N 73°01′E / 26.30°N 73.02°ECoordinates: 26°18′N 73°01′E / 26.30°N 73.02°E Open to
the publicYes Mehrangarh Fort, located in Jodhpur city in Rajasthan state, is one of the largest forts in India.
The fort is situated 400 feet (122 m) above the city and is enclosed by imposing thick walls. Inside its boundaries there are several palaces known for their intricate carvings and expansive courtyards. A winding road leads to and from the city below. The imprints of cannonball hits by attacking armies of Jaipur can still be seen on the second gate. To the left of the fort is the chhatri of Kirat Singh Soda, a soldier who fell on the spot defending the Mehrangarh fort.
There are seven gates, which include Jayapol (meaning 'victory'), built by Maharaja Man Singh to commemorate his victories over Jaipur and Bikaner armies. Fattehpol (also meaning 'victory') gate was built by Maharaja Ajit Singh to mark the defeat of the Mughals. The palm imprints upon these still attract much attention even today.
The museum in the Mehrangarh fort is one of the most well-stocked museums in Rajasthan. In one section of the fort museum there is a selection of old royal palanquins, including the elaborate domed gilt Mahadol palanquin which was won in a battle from the Governor of Gujarat in 1730. The museum exhibits the heritage of the Rathores in arms, costumes, paintings and decorated period rooms.
Contents
History of Mehrangarh
Rao Jodha (1438–1488), one of Ranmal's 24 sons became the fifteenth Rathore ruler. One year after his accession to the throne, Jodha decided to move his capital to the safer location of Jodhpur as the one thousand years old Mandore fort was no longer considered to provide sufficient security.
The foundation of the fort was laid on May 12, 1459[1] by Jodha on a rocky hill 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) to the south of Mandore. This hill was known as Bhaurcheeria, the mountain of birds. According to legend to build the fort he had to displace the hill's sole human occupant, a hermit called Cheeria Nathji, the lord of birds. Upset at being forced to move Cheeria Nathji cursed Rao Jodha with "Jodha! May your citadel ever suffer a scarcity of water!". Rao Jodha managed to appease the hermit by building a house and a temple in the fort very near the cave the hermit had used for meditation, though only to the extent that even today the area is plagued by a drought every 3 to 4 years. Jodha then took an extreme measure to ensure that the new site proved propitious; he buried a man called Rajiya Bhambi (a Meghwal) alive in the foundations. Rajiya was promised that in return his family would be looked after by the Rathores. To this day his descendants still live in Raj Bagh, Rajiya's Garden, an estate bequeathed them by Jodha.
Mehrangarh (etymology: 'Mihir' (Sanskrit) -sun or Sun-deity; 'garh' (Sanskrit)-fort; i.e.'Sun-fort'); according to Rajasthani language pronunciation conventions,'Mihirgarh' has changed to 'Mehrangarh'; the Sun-deity has been the chief deity of the Rathore dynasty.[2] Though the fortress was originally started in 1459 by Rao Jodha, founder of Jodhpur, most of the fort which stands today dates from the period of Jaswant Singh (1638–78). The fort is located at the centre of the city spreading over 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) atop a high hill. Its walls, which are up to 36 metres (118 ft) high and 21 metres (69 ft) wide, protect some of the most beautiful and historic palaces in Rajasthan.
Entry to the fort is gained though a series of seven gates. The most famous of the gates are:
- Jai Pol ("Gate of Victory"), built by Maharaja Man Singh in 1806 to celebrate his victory in a war with Jaipur and Bikaner.
- Fateh Pol, built to celebrate a victory over the Mughals in 1707;
- Dedh Kamgra Pol, which still bears the scars of bombardment by cannonballs;
- Loha Pol, which is the final gate into the main part of the fort complex. Immediately to the left are the handprints (sati marks) of the ranis who in 1843 immolated themselves on the funeral pyre of their husband, Maharaja Man Singh.
Within the fort, several brilliantly crafted and decorated palaces are found. Of these, Moti Mahal (Pearl Palace), Phool Mahal (Flower Palace), Sheesha Mahal (Mirror Palace), Sileh Khana, and Daulat Khana are notable. One also finds the fort museum comprising several palaces. This museum houses an exquisite collection of palanquins, howdahs, royal cradles, miniatures, musical instruments, costumes and furniture. The ramparts of the fort are home to not only several excellently preserved old cannon (including the famous Kilkila) but also offer a breath-taking view of the city.
Period rooms
- Moti Mahal - The Pearl Palace
Built by Raja Sur Singh (1595–1619), the Moti Mahal is the largest of the Mehrangarh Museum's period rooms. Sur Singh's Moti Mahal has five alcoves leading onto hidden balconies; it is believed they were built for his five queens to listen in on court proceeding.
- Sheesha Mahal - The Hall Of Mirrors
It is a fine example of a typical Rajput Sheesh Mahal. The mirror-work includes large, regular pieces, rather than an intricate mosaic of tiny fragments; another thing is the superimposition over the mirror-work of brightly painted religious figures made in plaster.
- Phool Mahal - The Palace Of Flowers
The Phool Mahal was created by Maharaja Abhaya Singh (1724–1749). The grandest of Mehrangarh's period rooms the Phool Mahal was in all likelihood a private and exclusive chamber of pleasure; dancing girls once swooned in exhaustion here under a ceiling rich in gold filigree.
- Takhat Vilas - Maharaja Takhat Singh's Chamber
Built and lived in by Maharaja Takhat Singh (1843–1873), Jodhpur's last ruler to reside in the Mehrangarh Fort, Takhat Vilas is an interesting blend of styles, most traditional, but some, like the glass balls on the ceiling, testifying to the modern age which arrived with the British.
Galleries in Mehrangarh Museum
Elephant's howdahs
The howdahs were a kind of two-compartment wooden seat (mostly covered with gold and silver embossed sheets), which were fastened on to the elephant's back. The front compartment, with more leg space and a raised protective metal sheet, was meant for kings or royalty, and the rear smaller one for a reliable bodyguard disguised as a fly-whisk attendant.
Palanquins
Palanquins were a popular means of travel and circumambulation for the ladies of the nobility up to the second quarter of the 20th century. They were also used by male nobility and royals on special occasions.
Daulat Khana - Treasures of Mehrangarh Museum
This gallery displays one of the most important and best preserved collections of fine and applied arts of the Mughal period of Indian history, during which the Rathore rulers of Jodhpur maintained close links with the Mughal emperors. It also has the remains of Emperor Akbar.
Armoury
This gallery displays a rare collection of armour from every period in Jodhpur. On display are sword hilts in jade, silver, rhino horn, ivory, shields studded with rubies, emeralds and pearls and guns with gold and silver work on the barrels. The gallery also has on display the personal swords of many emperors, among them outstanding historical piece like the Khanda of Rao Jodha, weighing over 7 pounds, the sword of Akbar the Great and the sword of Timur the Lame.
Paintings
 Folio from the Shiva Purana at Mehrangarh Museum, c. 1828.
Folio from the Shiva Purana at Mehrangarh Museum, c. 1828.
This Gallery displays colours of Marwar-Jodhpur, the finest example of Marwar paintings.
The Turban Gallery
The Turban Gallery in the Mehrangarh Museum seeks to preserve, document and display the many different types of turbans once prevalent in Rajasthan; every community, region and, indeed, festival having had its own head-gear.
The Folk Music Instruments Gallery
There are a number of different types and kinds of folk musical instruments, some particular to a group or community, and some to a region.
Tourist attractions in Mehrangarh
National Geological Monument
The Jodhpur Group - Malani Igneous Suite Contact on which the Mehrangarh Fort has been built has been declared a National Geological Monument by the Geological Survey of India to encourage Geotourism in the country. This unique geological feature is part of the Malani Igenus Suite seen in the Thar desert region, spread over an area of 43,500 km2. This unique geological feature represents the last phase of igneous activity of Precambrian age in the Indian Subcontinent.[3][4]
The Chamunda Mataji Temple
The Chamunda Mataji was Rao Jodha's favorite goddess, he brought her idol from the old capital of Mandore in 1460 and installed her in Mehrangarh (Maa Chamunda was the kul devi of Parihar rulers of Mandore). She remains the Maharaja's and the Royal Family's Isht Devi or adopted goddess and is worshipped by most of Jodhpur's citizens as well. Crowds throng Mehrangarh during the Dussehra celebrations.
2008 Stampede
A human stampede occurred on September 30, 2008, at the Chamunda Devi temple inside of the Mehrangarh Fort, in which 249 people were killed and more than 400 injured.
See article: 2008 Jodhpur stampede
See also
Tourist attractions in Jodhpur
- Jodhpur Group - Malani Igneous Suite Contact
- Jaswant Thada
- Mandore
Rulers of Jodhpur
- Hanwant Singh, 1947–1953
- Gaj Singh II, 1953–Present
Notes
- ^ Mehrangarh Fort-Jodhpur
- ^ Mr Yashwant Singh, an official guide to the Fort.
- ^ "Monuments of Stratigraphic Significance, Malani volcanics overlain by Jodhpur sandstone". Geological Survey of India. 2001. http://www.portal.gsi.gov.in/portal/page?_pageid=127,529424&_dad=portal&_schema=PORTAL. Retrieved 2009-03-23.
- ^ "Regional Geological and Tectonic Setting" (PDF). pp. 68–73. http://prr.hec.gov.pk/Chapters/338-3.pdf. Retrieved 2009-03-25.
Further reading
- Crump, Vivien; Toh, Irene (1996) (hardback). Rajasthan. London: Everyman Guides. p. 400. ISBN 1-85715-887-3.
- Beny, Rolof; Matheson, Sylvia (1984). Rajasthan - Land of Kings. New York: The Vendome Press. p. 200 pages. ISBN 0-86565-046-2.
- Tillotson, G.H.R (1987) (Hardback). The Rajput Palaces - The Development of an Architectural Style (First ed.). New Haven and London: Yale University Press. p. 224 pages. ISBN 03000 37384.
- SuryanagariJodhpur by Prem Bhandari
- Maharaja Umaid Singhji by Prem Bhandari
- Paintings from the royal collection of the Mehrangarh Museum Trust, Jodhpur British Museum
External links
- Mehrangarh Museum Trust
- Website for Mehrangarh Fort in Jodhpur - Mehrangarh Fort Information
- Mehrangarh Fort, Rajasthan Tourism
Forts in Rajasthan Achalgarh · Amber Fort · Bhainsrorgarh · Bijai Garh · Chittorgarh Fort · Jaigarh Fort · Jaisalmer Fort · Jalore Fort · Junagarh Fort · Kankwadi · Khandar Fort · Kuchaman City · Kumbhalgarh · Lohagarh Fort · Mehrangarh Fort · Nahargarh Fort · Neemrana · Ranthambore Fort · Siwana · Taragarh Fort · Timan Garh
Categories:- Forts in Rajasthan
- Jodhpur
- Visitor attractions in Jodhpur
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.