- Orotic aciduria
-
Orotic aciduria Classification and external resources 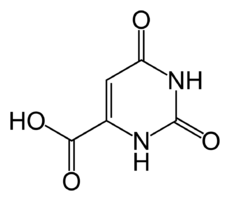
orotic acidICD-9 281.4 OMIM 258900 258920 DiseasesDB 29294 Orotic aciduria refers to an excessive excretion of orotic acid in urine.
Contents
Signs and symptoms
In addition to the characteristic excessive orotic acid in the urine, patients typically have megaloblastic anemia which cannot be cured by administration of vitamin B12 or folic acid.[1]
It also can cause inhibition of RNA and DNA synthesis and failure to thrive. This can lead to mental and physical retardation.
Cause and Genetics
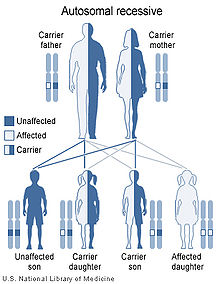
Its hereditary form, an autosomal recessive disorder,[2] can be caused by a deficiency in the enzyme UMPS,[3] a bifunctional protein that includes the enzyme activities of orotate phosphoribosyltransferase and orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase.
It can also arise secondary to blockage of the urea cycle, particularly in ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (or OTC deficiency). You can distinguish this increase in orotic acid secondary to OTC deficiency from hereditary orotic aciduria (seen above) by looking at blood ammonia levels and the BUN. In OTC deficiency, because the urea cycle backs up, you will see hyperammonemia and a decreased BUN.
Treatment
Administration of cytidine monophosphate and uridine monophosphate reduces urinary orotic acid and the anemia.
Administration of uridine, which is converted to UMP, will bypass the metabolic block and provide the body with a source of pyrimidine.
See also
- Pyrimidine biosynthesis
References
- ^ Huguley CM, Bain JA, Rivers SL, Scoggins RB (Jun 1959). "Refractory megaloblastic anemia associated with excretion of orotic acid" (Free full text). Blood 14 (6): 615–634. PMID 13651334. http://www.bloodjournal.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=13651334.
- ^ Winkler JK, Suttle DP (Jul 1988). "Analysis of UMP synthase gene and mRNA structure in hereditary orotic aciduria fibroblasts". Am J Hum Genet. 43 (1): 86–94. PMC 1715274. PMID 2837086. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1715274.
- ^ Suchi M, Mizuno H, Kawai Y, Tsuboi T, Sumi S, Okajima K, Hodgson ME, Ogawa H, Wada Y (Mar 1997). "Molecular cloning of the human UMP synthase gene and characterization of point mutations in two hereditary orotic aciduria families." (Free full text). American journal of human genetics 60 (3): 525–539. ISSN 0002-9297. PMC 1712531. PMID 9042911. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1712531.
External links
- Orotic aciduria hereditary at NIH's Office of Rare Diseases
- Orotic aciduria purines-pyrimidines at NIH's Office of Rare Diseases
Inborn error of purine-pyrimidine metabolism (E79, 277.2) Purine metabolism AnabolismCatabolismPyrimidine metabolism AnabolismOrotic aciduria · Miller syndromeCatabolismCategories:- Autosomal recessive disorders
- Inborn errors of purine-pyrimidine metabolism
- Genetic disorder stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.