- Double boiler
-
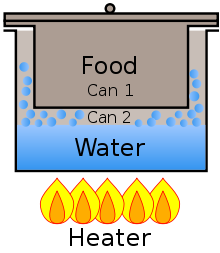
A double boiler, also known as a bain Marie, is a stove top apparatus used to cook delicate sauces such as beurre blanc, to melt chocolate without burning or seizing, or cook any other thick liquid or porridge that would normally burn if not stirred constantly. It consists of an upper vessel containing the substance to be cooked that is situated above a lower pot of water. When brought to a boil, the steam produced in the lower pot transfers heat to the upper pot.
This apparatus utilizes the properties of water to establish a constant temperature. The phase change of water from liquid to vapor occurs at 100°C (212°F). Therefore, as long as the lower pot does not become pressurized or boiled dry, the maximum temperature contacted by the upper vessel will be the boiling point of water, and scalding or uneven heat is avoided. The steam will either condense on the upper vessel or escape, but the temperature of the vapor phase will remain constant. In order to maximize the efficiency of the heat transfer process, the base of the upper vessel is constructed of a thinner, lower-gauge metal than the lower pot.
The lid on the upper vessel must fit tightly, or else steam may enter the upper vessel and affect the cooking substance. Manufacturers usually design the upper vessel and the lower pot as a set, a single lid fitting both.
See also
Cooking techniques Dry ConductionConvectionRadiationWet High heatLow heatIndirect heatFat-based High heatBlackening · Browning · Frying (Deep frying · Pan frying · Shallow frying · Stir frying (bao)) · SautéingLow heatMixed medium Device-based Non-heat See also Categories:- Cookware and bakeware
- Boilers
- Kitchenware stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.