- Proportionality (mathematics)
-
This article is about proportionality, the mathematical relation. For other uses of the term, see Proportionality (disambiguation).
In mathematics, two variable quantities are proportional if one of them is always the product of the other and a constant quantity, called the coefficient of proportionality or proportionality constant. In other words, x and y are proportional if the ratio
 is constant. We also say that one of the quantities is proportional to the other. For example, if the speed of an object is constant, it travels a distance that is proportional to the travel time.
is constant. We also say that one of the quantities is proportional to the other. For example, if the speed of an object is constant, it travels a distance that is proportional to the travel time.If a linear function transforms 0, a and b into 0, c and d, and if the product a b c d is not zero, we say a and b are proportional to c and d. An equality of two ratios such as
 where no term is zero, is called a proportion.
where no term is zero, is called a proportion.Contents
Geometric illustration
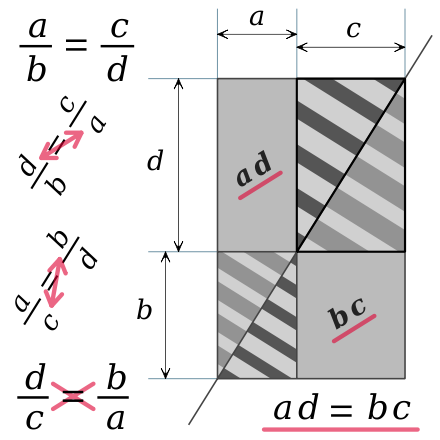
When the duplication of a given rectangle preserves its shape, the ratio of the large dimension to the small dimension is a constant number in all the copies, and in the original rectangle. The largest rectangle of the drawing is similar to one or the other rectangle with stripes. From their width to their height, the coefficient is
 A ratio of their dimensions horizontally written within the image, at the top or the bottom, determines the common shape of the three similar rectangles.
A ratio of their dimensions horizontally written within the image, at the top or the bottom, determines the common shape of the three similar rectangles.The common diagonal of the similar rectangles divides each rectangle into two superposable triangles, with two different kinds of stripes. The four striped triangles and the two striped rectangles have a common vertex: the center of an homothetic transformation with a negative ratio – k or
 , that transforms one triangle and its stripes into another triangle with the same stripes, enlarged or reduced. The duplication scale of a striped triangle is the proportionality constant between the corresponding sides lengths of the triangles, equal to a positive ratio obliquely written within the image:
, that transforms one triangle and its stripes into another triangle with the same stripes, enlarged or reduced. The duplication scale of a striped triangle is the proportionality constant between the corresponding sides lengths of the triangles, equal to a positive ratio obliquely written within the image:
 or
or 
In the proportion
 , the terms a and d are called the extremes, while b and c are the means, because a and d are the extreme terms of the list (a, b, c, d), while b and c are in the middle of the list. From any proportion, we get another proportion by inverting the extremes or the means. And the product of the extremes equals the product of the means. Within the image, a double arrow indicates two inverted terms of the first proportion.
, the terms a and d are called the extremes, while b and c are the means, because a and d are the extreme terms of the list (a, b, c, d), while b and c are in the middle of the list. From any proportion, we get another proportion by inverting the extremes or the means. And the product of the extremes equals the product of the means. Within the image, a double arrow indicates two inverted terms of the first proportion.Consider dividing the largest rectangle in two triangles, cutting along the diagonal. If we remove two triangles from either half rectangle, we get one of the plain gray rectangles. Above and below this diagonal, the areas of the two biggest triangles of the drawing are equal, because these triangles are superposable. Above and below the subtracted areas are equal for the same reason. Therefore, the two plain gray rectangles have the same area: a d = b c.
Symbol
The mathematical symbol '∝' is used to indicate that two values are proportional. For example, A ∝ B.
In Unicode this is symbol U+221D.
Direct proportionality
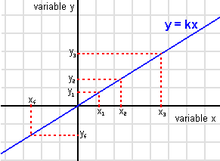
Given two variables x and y, y is (directly) proportional to x (x and y vary directly, or x and y are in direct variation) if there is a non-zero constant k such that
The relation is often denoted
and the constant ratio
is called the proportionality constant or constant of proportionality.
Examples
- If an object travels at a constant speed, then the distance traveled is proportional to the time spent traveling, with the speed being the constant of proportionality.
- The circumference of a circle is proportional to its diameter, with the constant of proportionality equal to π.
- On a map drawn to scale, the distance between any two points on the map is proportional to the distance between the two locations that the points represent, with the constant of proportionality being the scale of the map.
- The force acting on a certain object due to gravity is proportional to the object's mass; the constant of proportionality between the mass and the force is known as gravitational acceleration.
Properties
Since
is equivalent to
it follows that if y is proportional to x, with (nonzero) proportionality constant k, then x is also proportional to y with proportionality constant 1/k.
If y is proportional to x, then the graph of y as a function of x will be a straight line passing through the origin with the slope of the line equal to the constant of proportionality: it corresponds to linear growth.
Inverse proportionality
The concept of inverse proportionality can be contrasted against direct proportionality. Consider two variables said to be "inversely proportional" to each other. If all other variables are held constant, the magnitude or absolute value of one inversely proportional variable will decrease if the other variable increases, while their product (the constant of proportionality k) is always the same.
Formally, two variables are inversely proportional (or varying inversely, or in inverse variation, or in inverse proportion or in reciprocal proportion) if one of the variables is directly proportional with the multiplicative inverse (reciprocal) of the other, or equivalently if their product is a constant. It follows that the variable y is inversely proportional to the variable x if there exists a non-zero constant k such that
The constant can be found by multiplying the original x variable and the original y variable.
As an example, the time taken for a journey is inversely proportional to the speed of travel; the time needed to dig a hole is (approximately) inversely proportional to the number of people digging.
The graph of two variables varying inversely on the Cartesian coordinate plane is a hyperbola. The product of the X and Y values of each point on the curve will equal the constant of proportionality (k). Since neither x nor y can equal zero (if k is non-zero), the graph will never cross either axis.
Hyperbolic coordinates
Main article: Hyperbolic coordinatesThe concepts of direct and inverse proportion lead to the location of points in the Cartesian plane by hyperbolic coordinates; the two coordinates correspond to the constant of direct proportionality that locates a point on a ray and the constant of inverse proportionality that locates a point on a hyperbola.
Exponential and logarithmic proportionality
A variable y is exponentially proportional to a variable x, if y is directly proportional to the exponential function of x, that is if there exist non-zero constants k and a
Likewise, a variable y is logarithmically proportional to a variable x, if y is directly proportional to the logarithm of x, that is if there exist non-zero constants k and a
Experimental determination
To determine experimentally whether two physical quantities are directly proportional, one performs several measurements and plots the resulting data points in a Cartesian coordinate system. If the points lie on or close to a straight line that passes through the origin (0, 0), then the two variables are probably proportional, with the proportionality constant given by the line's slope.
See also
- Correlation
- Eudoxus of Cnidus
- Golden ratio
- Proportional font
- Rule of three (mathematics)
- Sample size
- Similarity
Growth
- Linear growth
- Hyperbolic growth
Categories:- Mathematical terminology
- Ratios
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.