- Charles VII of France
-
Charles VII the Victorious 
Portrait of Charles VII, by Jean Fouquet, tempera on wood, Louvre Museum, Paris, c. 1445–1450 King of France Reign 21 October 1422 – 22 July 1461 Coronation 17 July 1429 Predecessor Charles VI Successor Louis XI Spouse Marie of Anjou Issue Louis XI of France
Yolande, Duchess of Savoy
Magdalena, Princess of Viana
Charles, Duke of Berry
Joan, Duchess of Bourbon
Catherine of ValoisHouse House of Valois Father Charles VI of France Mother Isabella of Bavaria-Ingolstadt Born 22 February 1403
Paris, FranceDied 22 July 1461 (aged 58)
Mehun-sur-Yèvre, FranceBurial Saint Denis Basilica Charles VII (22 February 1403 – 22 July 1461), called the Victorious (French: le Victorieux)[1] or the Well-Served (French: le Bien-Servi), was King of France from 1422 to his death,[2] though he was initially opposed by Henry VI of England, whose Regent, the Duke of Bedford, ruled much of France including the capital, Paris. The English and Burgundians also initially controlled Reims, the city in which Valois kings were traditionally crowned.
He was a member of the House of Valois, the son of Charles VI, but his succession to the throne was left questionable by the English occupation of northern France. He was, however, famously crowned in Reims in 1429 through Joan of Arc's effort to free France from the English. His later reign was marked by struggles with his son, the future Louis XI.
Contents
Early life
Born in Paris, Charles was the fifth son of Charles VI of France and Isabella of Bavaria-Ingolstadt. His four elder brothers, Charles (1386), Charles (1392–1401), Louis (1397–1415) and John (1398–1417) had each held the title of Dauphin of France, heir to the French throne, in turn; each had died childless, leaving Charles with a rich inheritance of titles.[3]
See also: Assassination of John the FearlessAlmost immediately after his accession to the title of Dauphin, Charles was forced to face the threat to his inheritance, being constrained to flee Paris in May 1418 after the soldiers of John the Fearless, Duke of Burgundy attempted to capture the city. In the following year, Charles attempted to make a reconciliation between himself and the Duke, meeting him on a bridge at Pouilly, near Melun, in July 1419. This proving insufficient, the two met again on 10 September 1419, on the bridge at Montereau. The Duke, despite previous history, proved over-trusting in his young cousin, assuming the meeting to be entirely peaceful and diplomatic, and bringing with him only a small escort; the Dauphin's men reacted to the Duke's arrival, however, by setting upon him and killing him. Charles's level of involvement remained questionable ever afterward: although he claimed to have been unaware of his men's intentions, it was considered unlikely by those who heard of the murder,[4] and furthered the feud between the family of Charles VI and the Dukes of Burgundy. Charles himself was later required by treaty with Philip the Good, John's son, to pay penance for the murder, but he never did so; nonetheless, it is claimed, the event left him with a lifelong phobia of bridges.[citation needed]
In his adolescent years, Charles was noted for his bravery and style of leadership: at one point after becoming Dauphin, he led an army against the English, dressed in the red, white and blue that represented France; his heraldic device was a mailed fist clutching a naked sword. However, two events in 1421 broke his confidence: he was forced, to his great shame, to withdraw from battle against Henry V of England; and his parents then repudiated him as the legitimate heir to the throne, claiming that he was the product of one of his mother's extramarital affairs (for which she was notorious). Humiliated, and in fear of his life, the Dauphin fled to the protection of Yolande of Aragon, the so-called Queen of the Four Kingdoms, in southern France, where he was protected by the forceful and proud Queen Yolande, and married her daughter, Marie.
On the death of Charles's insane father, Charles VI, the succession was cast into doubt: if the Dauphin was legitimate, then he was the rightful heir to the throne. If not, the heir was the Duke of Orléans, in English captivity. In addition, the Treaty of Troyes, signed by Charles VI in 1420, mandated that the throne pass to Henry VI of England, the son of the recently deceased Henry V and Catherine of Valois, daughter of Charles VI. None of the three candidates had an unquestionable claim to the throne; the English, however, being already in control of northern France, including Paris, were able to enforce their King's claim in those parts of France they occupied. Northern France was thus ruled by an English regent based in Normandy, for Henry VI. (See Dual monarchy of England and France.)
Charles, unsurprisingly, claimed the title King of France for himself; however, by indecision and a sense of hopelessness, he failed to make any attempts to throw the English out. Instead, he remained south of the Loire River, where he was still able to exert some small amount of power, maintaining an itinerant court in the Loire Valley at castles such as Chinon, being customarily known as "Dauphin" still, or derisively as "King of Bourges" (named after the town where he generally lived), periodically considering flight to the Iberian Peninsula, and allowing the English to advance in power.
The Maid of Orléans
French Monarchy
Capetian Dynasty
(House of Valois)Philip VI Children John II John II Children Charles V Louis I of Anjou John, Duke of Berry Philip the Bold Charles V Children Charles VI Louis, Duke of Orléans Charles VI Children Isabella of Valois Michelle of Valois Catherine of Valois Charles VII Charles VII Children Louis XI Charles, Duke of Berry Louis XI Children Charles VIII Charles VIII In 1429, however, came a change. Orléans had been under siege since October 1428. The English regent, the Duke of Bedford (the uncle of Henry VI) was advancing into the Duchy of Bar, ruled by Charles's brother-in-law, René. The French lords and soldiers loyal to Charles were becoming increasingly desperate.
Meanwhile, in the little village of Domrémy, on the border between Lorraine and Champagne, a teenage girl named Jeanne d'Arc (in English: Joan of Arc), believing she had been given a divine mission after apparently hearing the voices of angels, demanded of the Duke of Lorraine the soldiers and resources necessary to bring her to Chinon, and the Dauphin. Granted an escort of five veteran soldiers and a letter of referral to Charles by the governor of Vaucouleurs, Robert Baudricourt, Jeanne rode to Chinon, where Charles was in residence, arriving there on 10 March 1429.
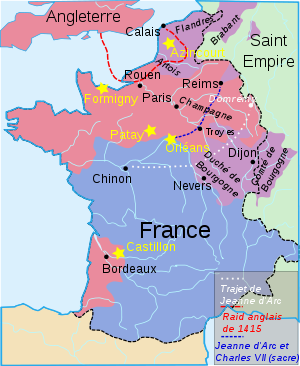 1429
1429 Territories controlled by CharlesMain battlesEnglish raid of 1415 Path of Jeanne d'Arc to Reims in 1429
Territories controlled by CharlesMain battlesEnglish raid of 1415 Path of Jeanne d'Arc to Reims in 1429What followed would later pass into legend. When Jeanne arrived at Chinon, Charles—testing Jeanne's claim to recognise him despite having never seen him—disguised himself as one of his courtiers, and stood in their midst when Jeanne (who was herself dressed in men's clothing) entered the chamber. Jeanne, immediately identifying him, bowed low to him and embraced his knees, declaring "God give you a happy life, sweet King!" Despite attempts to claim that another man was in fact the King, Charles was eventually forced to admit that he was indeed such. Thereafter Jeanne referred to him as "Dauphin" or "Gentle Dauphin" until he was crowned in Reims four months later. After a private conversation between the two (during which, Charles later stated Jeanne knew secrets about him that he had voiced only in silent prayer to God) Charles became inspired, and filled with confidence. Thereafter, he became secure in his intention to claim his inheritance by travelling to Reims.[citation needed]
One of the important factors that aided in the ultimate success of Charles VII was the support from the powerful and wealthy family of his wife Marie d'Anjou (1404–1463), particularly his mother-in-law the Queen Yolande of Aragon. Despite whatever affection he had for his wife, the great love of Charles VII's life was his mistress, Agnès Sorel.
Jeanne d'Arc then set about leading the French forces at Orléans, forcing the English to lift the siege and thus turning the tide of the war. After the French won the Battle of Patay, Charles was crowned King Charles VII of France on 17 July 1429, in Reims Cathedral as the de jure king.
Jeanne was later captured by the Burgundians who handed her over to the English. Tried for heresy she was burned at the stake on 30 May 1431. Charles VII did nothing to save the one to whom he owed his throne, though he probably could have engineered her release.
Charles and Philip the Good, Duke of Burgundy, then signed the Treaty of Arras, thus allowing the Burgundians to return to the side of the French just as things were going badly for their English allies. With this event, Charles attained the goal that was essential, that no prince of the blood recognised Henry VI as King of France.[5]
Over the following two decades, the French recaptured Paris from the English and eventually recovered all of France with the exception of the northern port of Calais and the Channel Islands.
Close of reign
Charles's later years were marked by increasing hostility between himself and his heir, Louis. Louis demanded real power to accompany his position as the Dauphin; Charles refused. Accordingly, Louis stirred dissent and made plots in attempts to destabilise his father. He quarrelled with his father's mistress, Agnès Sorel, on one occasion driving her with a bared sword into Charles's bed, according to one source. Eventually, in 1446, after Charles's last son, also named Charles, was born, the King banished the Dauphin to the Dauphiny. The two never met again; Louis thereafter refused the King's demands that he return to court, eventually fleeing to the protection of Philip the Good, Duke of Burgundy, in 1456.
In 1458, Charles became ill: a sore on his leg (an early symptom, perhaps, of diabetes or another condition) refused to heal, and the infection in it caused a serious fever. The King summoned Louis to him from his exile in Burgundy; but the Dauphin refused, and employed astrologers to foretell the exact hour of his father's death. The King lingered on for the next two and a half years: increasingly ill, but unwilling to die. During this time he also had to deal with the case of his rebellious vassal John V of Armagnac.
Finally, however, there came a point in July 1461 when the King's physicians concluded that Charles would not live past August. Ill and weary, the King became delirious, convinced that he was surrounded by traitors loyal only to his son. Under the pressure of sickness and fever, the King went mad. By now another infection in his jaw had caused a tumor or abscess in his mouth; the swelling of this became so large that, for the last week of his life, Charles could swallow no food or water. Although he asked the Dauphin to come to his deathbed, Louis refused, instead waiting for his father to die at Avesnes, in Burgundy. Thus, at Mehun-sur-Yèvre, attended by his younger son, Charles, and aware of his elder son's final betrayal, the King starved to death. He died on 22 July 1461, and was buried, at his request, beside his parents in Saint-Denis.
Legacy
Although Charles VII's legacy is far overshadowed by the deeds and eventual martyrdom of Joan of Arc, he himself was also responsible for successes unprecedented in the history of the Kingdom of France. When he died, France controlled the territories traditionally governed by England and possessed its first standing army, which in time would yield the powerful gendarme cavalry companies, notable in the wars of the sixteenth century. He also established the University of Poitiers in 1432, and his policies had brought some economic prosperity to his subjects. His rule as a monarch had at times been marked by indecisiveness and inaction, and his final years were marked by hostility between himself and his elder son. Nonetheless, it is to his credit that he left his kingdom in a better condition than he had found it.
Ancestry
Ancestors of Charles VII of FranceChildren
Charles married his second cousin Marie of Anjou on 18 December 1422. They were both great-grandchildren of King John II of France and his first wife Bonne of Bohemia through the male-line. They had fourteen children:
- Louis XI, King of France (1423–1483), married Charlotte of Savoy, by whom he had issue including King Charles VIII of France, Anne of France, and Joan of France, Duchess of Berry.
- John of France (Jean de France) (1424–1425)
- Radegonde of France (Radegonde de France) (1428–1444), betrothed to Sigismund, Archduke of Austria
- Catherine of Valois (Catherine de France) (1428–1446), married Charles the Bold in 1440
- James of France (Jacques de France) (1432–1437)
- Yolande of Valois (Yolande de France) (1434–1478), married the future Amadeus IX, Duke of Savoy in 1452. Upon his death in 1472, she became regent of Savoy. She was the mother of ten children.
- Joan of Valois (Jeanne de France) (1435–82), married the future John II, Duke of Bourbon in 1452. No issue.
- Philip of France (Philippe de France) (4 February 1436 – 11 June 1436)
- Margaret of France (Marguerite de France) (1437–1438)
- Marie of France (Marie de France) (7 September 1438 – 14 February 1439)
- Joan (Jeanne de France) (7 September 1438 – 26 December 1446)[6]
- Marie of France (Marie de France) (1441 – died in childhood)
- Magdalena of Valois (Madeleine de France) (1443–1495), married Gaston of Foix, Prince of Viana, in 1462, by whom she had issue.
- Charles, Duke of Berry (Charles de France) (1446–1472), died without legitimate issue.
Mistresses
- Odette de Champdivers{1390–1424} – formerly mistress to Charles VII's uncle Louis of Valois, Duke of Orléans and his father Charles VI of France
- Agnès Sorel, by whom he had three illegitimate daughters.
- Antoinette de Maignelais, cousin of Agnès Sorel.
Charles VII in the arts
- Appears as Charles, The Dauphin in Jean Anouilh's play The Lark
- Appears as Charles the Dauphin in George Bernard Shaw's play Saint Joan
- Appears as the Dauphin in Maxwell Anderson's Joan of Lorraine
- Appears as a significant character in Thomas Keneally's novel "Blood Red, Sister Rose".
- Appears as 'The Dauphin' in William Shakespeare's Henry VI Part 1, and as 'King Charles' in Henry VI Part III.
- Two Russian operas from the late 19th century portray Charles VII (and Agnès Sorel) among the dramatis personæ. These are Pyotr Tchaikovsky's The Maid of Orléans and César Cui's The Saracen.
- Charles VII's relationship with Joan of Arc is imagined fancifully in the 1975 Broadway musical Goodtime Charley.
- Charles VII has been represented in the movies by Raymond Hatton (1917), Jean Debucourt (1929), Gustaf Gründgens (1935), Emlyn Williams (1935), Max Adrian (1944), José Ferrer (1948), Paul Colline (1955), Richard Widmark (1957), Daniel Gélin (1978), Keith Drinkel (1979), Oleg Kulko (1993), John Malkovich (1999), Neil Patrick Harris (1999)
Sources
- Hanawalt, Barbara, The Middle Ages: An Illustrated History
- Taylor, Aline, Isabel of Burgundy
See also
References and notes
- ^ Wagner, John A., Encyclopedia of the Hundred Years War, (Greenwood Press:Westport, 2006), 89.
- ^ Charles Cawley, Medieval Lands, France, Capetian Kings[page needed]
- ^ Wagner, 89.
- ^ Wagner, 90.
- ^ Brady, Thomas A., Handbook of European History 1400–1600, Vol.2, (E.J.Brill:Leiden, 1994), 373.
- ^ France Capetian Kings
Charles VII of FranceBorn: 22 February 1403 Died: 22 July 1461Regnal titles Preceded by
Charles the MadKing of France
disputed with Henry VI of England
21 October 1422 – 22 July 1423Succeeded by
Louis the PrudentPreceded by
John of ValoisDauphin of Viennois
5 April 1417 – 3 July 1423Duke of Touraine
Count of Poitou
1417 – 21 October 1422Vacant Merged in the crownDuke of Berry
1417 – 21 October 1422Vacant Merged in the crownTitle next held byCharles IICount of Ponthieu
1417 – 21 October 1422Vacant Merged in the crownTitle next held byCharles IIList of French monarchs Detailed Family Tree • Simplified Family Tree Merovingians
(481–751)Clovis Ist (481–511) • Chlothar I (511–561) • Charibert I (561–567) • Guntram (561–593) • Chilperic I (561–584) • Sigebert I (561–575) • Chlothar II (584–629) • Dagobert I (629–639) • Sigebert II (639–656) • Clovis II (639–657) • Chlothar III (657–673) • Theuderic III (673–691) • Clovis III (691–695) • Childebert III (695–711) • Dagobert III (711–715) • Chilperic II (715–721) • Chlothar IV (717–719) • Thierry IV (721–737) • Childeric III (737–751)Carolingians
(843–888, 898–922, 936–987)Pepin III (751–768) • Carloman I (768–771) • Charlemagne (768–814) • Louis I (814–840) • Charles I (843–877) • Louis II (877–879) • Louis III (879–882) • Carloman II (879–884) • Charles II (885–888) • Charles III (898–922) • Louis IV (936–954) • Lothair IV (954–986) • Louis V (986–987)Robertians
(888–898, 922–923)Eudes of Paris (888–898) • Robert I (922–923)Bosonids
(923–936)House of Capet
(987–1328)Hugh (987–996) • Robert II (996–1031) • Henry I (1031–1060) • Philip I (1060–1108) • Louis VI (1108–1137) • Louis VII (1137–1180) • Philip II (1180–1223) • Louis VIII (1223–1226) • Louis IX (1226–1270) • Philip III (1270–1285) • Philip IV (1285–1314) • Louis X (1314–1316) • John I (1316) • Philip V (1316–1322) • Charles IV (1322–1328)House of Valois
(1328–1498)Philip VI (1328–1350) • John II (1350–1364) • Charles V (1364–1380) • Charles VI (1380–1422) • Charles VII (1422–1461) • Louis XI (1461–1483) • Charles VIII (1483–1498)House of Valois-Orléans
(1498–1515)House of Valois-Angoulême
(1515–1589)Francis I (1515–1547) • Henry II (1547–1559) • Francis II (1559–1560) • Charles IX (1560–1574) • Henry III (1574–1589)House of Bourbon
(1589–1792)Henry IV (1589–1610) • Louis XIII (1610–1643) • Louis XIV (1643–1715) • Louis XV (1715–1774) • Louis XVI (1774–1792) • Louis XVII (claimant, 1792–1795)House of Bonaparte
First Empire (1804–1814, 1815)Napoleon I (1804–1814, 1815) • Napoleon II (1815)House of Bourbon
Bourbon Restoration
(1814, 1815–1830)House of Orléans
July Monarchy (1830–1848)Louis Philippe I (1830–1848)House of Bonaparte
Second Empire (1852–1870)Guerin · Hatton · Renaud · Bernard I · Emenon · Ranulph I · Ranulph II · Gauzbert · Robert I · Ebalus · Aymar · Ebalus · William I · William II · William III · William IV · Eudes · William V · William VI · William VII · William VIII · Eleanor · Louis* · Henry* · William IX · Otto · Richard · Alphonse · Philip · John I · John II · John III · Charles · François
- Count through marriage
Categories:- Kings of France
- French monarchs
- Roman Catholic monarchs
- House of Valois
- Dauphins of Viennois
- Armagnac faction
- Dauphins of France
- Dukes of Berry
- People of the Hundred Years' War
- Joan of Arc
- People from Paris
- 1403 births
- 1461 deaths
- Recipients of the Golden Rose
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.







