- Utah State Route 128
-
For the former highway, see Utah State Route 128 (1931–1933).
State Route 128 Upper Colorado River Scenic Byway
Dinosaur Diamond Prehistoric Highway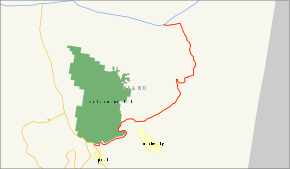
State Route 128 delineated in redRoute information Defined by Utah Code §72-4-118 Maintained by UDOT Length: 44.564 mi[2] (71.72 km) Existed: 1933[1] – present Major junctions West end:  US-191 near Moab
US-191 near MoabEast end: 

 I-70 / US-6 / US-50 near Cisco
I-70 / US-6 / US-50 near CiscoHighway system State highways in Utah
Interstate • US • State (Parks) • Scenic←  SR-127
SR-127SR-130  →
→State Route 128 (SR-128) is a state highway in the U.S. state of Utah. The entire length of the highway has been designated the Upper Colorado River Scenic Byway, as part of the Utah Scenic Byways program. This road also forms part of the Dinosaur Diamond Prehistoric Highway, a National Scenic Byway. Residents of Moab frequently refer to SR-128 as "the river road",[3] after the Colorado River, which the highway follows.
The highway was originally constructed to connect rural cities in eastern Utah with Grand Junction, Colorado, the largest city in the region. Part of the highway was merged into the Utah state highway system in 1931; the rest was taken over by the state and assigned route number 128 in 1933. Today, the highway is used as a scenic drive for visitors to the area.[4]
The highway crosses the Colorado River at the site of the Dewey Bridge, listed on the National Register of Historic Places. This bridge was the longest suspension bridge in Utah until April 2008 when it was destroyed by a fire started by a child playing with matches.[5] The future of the bridge is uncertain, with Grand County conducting a study to determine the feasibility of reconstructing it.
Contents
Route description
State Route 128 begins just north of Moab, where it is commonly known as "the river road". The highway follows the southern bank of the Colorado River through a narrow, steep gorge, described as spectacular by National Geographic.[4] The sheer sandstone walls of the gorge along Route 128 are recommended for their beauty on vacation guides from as far away as France and Germany.[6][7]
As parts of the road are very narrow, with blind corners and no shoulders, the Utah Department of Transportation has prohibited trucks and vehicles over 55,000 pounds (24,948 kg) from the entire highway. In addition, a restriction at the junction with U.S. Route 191 requires vehicles over 15 feet (4.6 m) wide to have two police escorts.[8]
Between Moab and Castle Valley, the Colorado River, and indirectly, Route 128, form the southern boundary of Arches National Park. Arches National Park is so named because of over 2000 natural arches inside park boundaries.[9] While the highway does offer views of several features in the park, there is no park access along the highway.[10] Popular attractions along this portion include Negro Bill Canyon, with hiking trails to Morning Glory Arch, campgrounds and boat docks at a curve in the river called Big Bend.[11]
The gorge widens where the highway passes by Castle Valley and Professor Valley, which have been the shooting locations for many western films (including Wagon Master and Rio Grande) and television commercials.[12] Near the east end of the valley the highway crosses Onion Creek, a steam sourced by springs that contain naturally occurring minerals that produce a strong odor in the water.[13] At the east end of the valley the highway has a view of the Fisher Towers, a set of dark red spires. After leaving the valley, the road winds farther up the river gorge until arriving at the Dewey Bridge, named for Dewey, a nearby ghost town.[14]
After the bridge, the road follows the northern bank of the river for a few miles then exits the Colorado River gorge. At this point the highway proceeds across desert towards the Book Cliffs to terminate at Interstate 70 near Cisco.[10] Cisco is a ghost town along the main line of the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad, founded as a water re-filling station for steam locomotives.[14] The last 3 miles (4.8 km) of the road parallel the railroad and is an old routing of U.S. Route 6/U.S. Route 50, in use before the construction of I-70.[1]
History
Access between Moab and Castle Valley was originally via a pack trail called the Heavenly Stairway. This trail, named for a dramatic descent of over 1,000 feet (300 m), was described as beautiful, but difficult to navigate.[14] Isolated from Utah's population centers, this area depended on Grand Junction and other cities in Colorado for both everyday supplies and a market for agricultural products.[15] Moab residents pushed for a road to be built along the riverbank. By 1902, the trail was replaced with a toll road, called King's Toll Road, after Samuel King. King was an early settler who also operated the toll ferry used prior to the construction of the Dewey Bridge. Rocks inscribed with "Kings Toll Road" can still be found along the roadway. While the road did improve travel, it was not built high enough above the river level and was often flooded.[14]
Dewey Bridge
The Dewey Bridge, built in 1916, originally carried SR-128 across the Colorado River.[16] The bridge featured an all wood deck measuring 502 feet (153 m) long, 10.2 feet (3.1 m) wide from support to support and 8 feet (2.4 m) wide from rail to rail. The bridge also consisted of two metal towers, a run of seven cables on each side of the bridge deck, and cable anchors.[14]
In 1912 Grand County unsuccessfully petitioned the state to finance the construction of a bridge. In 1913, the ferry was out of service for a time because ice in the river struck the ferry, causing it to sink. This raised the level of urgency for a more reliable river crossing. Grand County held a municipal bond election, and was able to raise $25,000[16] (1913, approximately equivalent to $550,000 in 2008)[17] to finance the construction of a bridge. The county employed the Midland Bridge Company of Kansas City, Missouri, to build it. Plans originally called for the bridge deck to be 12 feet (3.7 m) wide, but with the bonds not producing the expected yields, the deck width was scaled down to 8 feet (2.4 m). In 1916, the bridge was dedicated with a strength test by having approximately 70 attendees attempt cross the bridge at once. The total was seven wagons, two people on horseback and several on foot.[16] The bridge was designed to support the weight of six horses, three wagons, and 9,000 pounds (4,100 kg) of freight.[15]
On the day of its completion, it was the second-longest suspension bridge west of the Mississippi River. The longest was also built by the Midland Bridge Company, who used the same base plans for both bridges. The longer twin to the Dewey Bridge crossed the Little Colorado River along U.S. Route 89 in Cameron, Arizona. The Dewey Bridge remained the longest suspension bridge in Utah until it was destroyed by fire in 2008.[16]
As part of a tribute, a reporter for The Daily Sentinel interviewed locals and visitors about their first experience crossing the bridge. Many recalled how nervous they felt as the bridge would creak and sway under load. One stated, "A lot of people lost a lot of mirrors on that bridge".[5] Drivers with wide vehicles had to fold in their side mirrors to safely cross, as the bridge deck was only 8 feet (2.4 m) wide.[16]
An agreement was reached in 1984 between the Grand County Commission and the Utah Department of Transportation (UDOT) to balance the conflicting public demands to retire and preserve the aging bridge. As part of this agreement, UDOT would commission a new bridge and once finished, transfer ownership of the original bridge back to Grand County. Grand County agreed to petition to have the bridge be included in the National Register of Historic Places, assume maintenance and guarantee the bridge would be preserved.[1] The nomination was approved and the bridge was added to the National Register of Historic Places on July 12, 1984.[18] In 1988, the replacement bridge was completed,[5][19] and the title deed to the Dewey Bridge was handed over to the county in 1989.[1] Grand County completed a restoration project in 2000.[5]
After being replaced for automobile use, the Dewey Bridge was used by the Kokopelli trail, a bicycle trail, and a pedestrian trail. The east approach to the bridge features an abandoned gas station and the ghost town of Dewey. The west approach has been converted to a rest area and park.[10]
On April 6, 2008, a seven-year-old boy accidentally started a fire in a nearby campground while playing with matches. The fire moved up the riverbank and destroyed the bridge's wooden deck and rails.[20] The county funded a study to determine the feasibility and cost of reconstructing the bridge. The engineers determined that the steel cables and towers most likely did not suffer structural damage and could be reused. The study estimated reconstruction costs at $850,000. The engineers determined the original blueprints, preserved in a museum, were of sufficient quality that only minimal engineering work would be required. The county agreed to direct the effort, but will not fund it with taxpayer money.[21] As replicas do not qualify for historical status, historians are debating if using the original towers and cable is enough for the structure to qualify as historical.[22] Grand County has set up an account for interested parties to donate to the reconstruction effort.[23]
Though the Colorado River runs for over 400 miles (640 km) in Utah, there are only three sites with bridges to cross it. One is the Dewey Bridge site where SR-128 traverses the waterway; the other two are an unnamed bridge that carries US-191 (built in 1911, replaced in 1955 and again in 2010) and the Hite Crossing Bridge (built in 1966) used by SR-95.[14]
From trail to highway
With the bridge finished in 1916, by the 1920s the toll road was reconstructed above the ordinary high water mark so it could be used year-round.[14] The road was briefly used for the route of the Midland Trail across eastern Utah. However, by 1923 the trail had been moved to a more direct routing, similar to modern I-70.[24][25] The road from Moab along the river to Castleton was added to the state highway network in 1931, as SR-129.[26] In 1933, the route was redesignated SR-128 and extended to Cisco.[27] The highway was gradually upgraded to a two-lane paved roadway.
The state legislature extended SR-128 about 3 miles (5 km) at its east end in 1969, due to the pending construction of Interstate 70. Plans called for the freeway to bypass the Cisco area, including the terminus of SR-128. The legislature transferred a portion of SR-4 (the legislative designation for what was then signed US-6/US-50) near Cisco to the proposed junction with I-70. When that part of I-70 was completed in 1971, signs were changed to SR-128 on its portion of the old road, while the remainder of the bypassed road through Cisco was relinquished to the county.[28]
The highway was recognized by the Utah Scenic Byways program for its scenic value and given the name Upper Colorado River Scenic Byway.[29][30] The highway was recognized as a National Scenic Byway and named as part of the Dinosaur Diamond Scenic Byway in 1998.[31] A petition is currently before the Federal Highway Administration to recognize Route 128 as an All-American Road. To meet this criterion the highway must be deemed by the administration to have enough scenic value to be a "destination unto itself".[31]
Major intersections
The entire route is located within Grand County.
Mile[2] Destinations Notes 0.000  US-191 – Moab, Junction I-70
US-191 – Moab, Junction I-701.088 View area – Camping information and Riverway Regulations 6.348 View area – Drinks Canyon 8.112 View area – Big Bend 15.529 Castle Valley, Manti-La Sal National Forest 20.157 Onion Creek Road 20.994 View area – Fisher Towers 26.634 Rest area – Dewey Bridge 41.530 Cisco road Former US-6/US-50 44.432 

 I-70 / US-6 / US-50 – Thompson Springs, Grand Junction
I-70 / US-6 / US-50 – Thompson Springs, Grand Junction44.564 End State Maintenance 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi See also
- Dewey Bridge Member – a type of Entrada Sandstone named for the Dewey Bridge
- State Route 279 – Lower Colorado River Scenic Byway
References
- ^ a b c d Utah Department of Transportation, Highway Resolutions: Route 128PDF (766 KB), (November 2007), Retrieved on 2008-05-15
- ^ a b "Route 0128P". Utah Department of Transportation. http://www.dot.utah.gov/main/uconowner.gf?n=15511303951685090. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
- ^ "Highway 128 — The River Road Experience". Canyonlands Natural History Association. http://www.cnha.org/product.cfm?id=B3CC3439-3048-C277-115EC894C633CF16. Retrieved 2009-07-28.
- ^ a b "Colorado River Scenic Byway". National Geographic Guide to Scenic Highways and Byways (Second ed.). National Geographic Society. 1995. p. 201. ISBN 0792274687.
- ^ a b c d Harmon, Gary (2008-04-07). "Historic Dewey Bridge lost to fire". Grand Junction, Colorado: The Daily Sentinel. Archived from the original on 2008-06-26. http://web.archive.org/web/20080626085420/http://www.gjsentinel.com/services/content/services/archives.html. Retrieved 2008-06-27.
- ^ "The USA - Fisher Towers & Route UT 128" (in French). The USA. 2008-03-02. http://theusa.free.fr/fisher_towers.htm. Retrieved 2008-08-24.
- ^ Steimle, Von Lothar (2002-06-17). "In Utah am berühmtesten Felsbogen der Welt" (in German). Rhine Main.Net. http://www.rhein-main.net/sixcms/detail.php/5rmn01.c.502402.de. Retrieved 2008-08-24.
- ^ "State of Utah, Secondary Highways with Additional Restrictions" (PDF). Utah Motor Carrier Division / Utah Department of Transportation. http://www.utahmc.com/trucking_guide/pdf/secondary_restrictions.pdf. Retrieved 2007-11-17.
- ^ "Arches National Park". U.S. Department of the Interior–National Park Service. http://www.nps.gov/arch/index.htm. Retrieved 2008-08-23.
- ^ a b c Benchmark Maps (2002). Utah Road and Recreation Atlas (Map). 1:250000. p. 71. ISBN 0-929591-74-7. http://www.benchmark.com.
- ^ "Colorado Riverway Recreation Area". Moab Area Travel Council. Archived from the original on August 7, 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070807182838/http://discovermoab.com/blm_riverway.htm. Retrieved 2008-07-19.
- ^ "Movies filmed in the Moab area". Moab Area Travel Council. http://www.discovermoab.com/movie.htm. Retrieved 2008-07-29.
- ^ "Onion Creek TMDL Grand County, Utah" (PDF). Utah Department of Environmental Quality/Division of Water Quality. http://www.waterquality.utah.gov/TMDL/Onion_Creek_TMDL.pdf. Retrieved 2008-03-04.
- ^ a b c d e f g Daughters of Utah Pioneers (1972). Grand Memories. pp. 127, 144. OCLC 4790603.
- ^ a b "Utah History Resource Center – Markers and Monuments – Dewey Bridge". State of Utah. 2006-10. http://history.utah.gov/apps/markers/detailed_results.php?markerid=2944. Retrieved 2007-10-13.
- ^ a b c d e "Historic American Engineering Record – UT0411". U.S. Library of Congress. http://hdl.loc.gov/loc.pnp/hhh.ut0411. Retrieved 2008-02-24.
- ^ "Consumer Price Index Inflation Calculator". U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics–U.S. Department of Labor. http://data.bls.gov/cgi-bin/cpicalc.pl. Retrieved 2008-08-29.
- ^ "National Register Information system". National Park Service. http://www.nps.gov/history/nr/research/index.htm. Retrieved 2004-12-02.
- ^ Federal Highway Administration–National Bridge Inventory. "National Bridge Inventory–structure:Utah - 0C+734". http://www.fhwa.dot.gov/bridge/nbi/ascii.cfm. Retrieved 2008-02-16.
- ^ The Daily Sentinel staff (2008-04-07). "Fire destroys Dewey Bridge". Grand Junction, Colorado: The Daily Sentinel. http://www.gjsentinel.com/blogs/content/shared-gen/blogs/communities/breaking/entries/2008/04/07/fire_destroys_dewey_bridge.html. Retrieved 2008-04-07.
- ^ Bigler, Craig (2009-01-08). "Study finds Dewey Bridge could be reconstructed for about $850,000". The Times-Independent. http://www.moabtimes.com/pages/full_story?page_label=results_content&id=1295386-Study-finds-Dewey-Bridge-could-be-reconstructed-for-about-&article-Study-finds-Dewey-Bridge-could-be-reconstructed-for-about-%20=&widget=push&open=&. Retrieved 2008-01-10.
- ^ Schenck, Travis (2008-05-30). "Preservation committee launches Dewey Bridge feasibility study". Moab, Utah: The Times-Independent. http://www.moabtimes.com/pages/full_story?page_label=results_content&id=77546-Preservation-committee-launches-Dewey-Bridge-feasibility-study&article-Preservation-committee-launches-Dewey-Bridge-feasibility-study%20=&widget=push&open=&troys_dewey_bridge.html. Retrieved 2008-06-13.
- ^ Georg, Ron (2008-05). "Group seeks donations to rebuild Dewey Bridge". Moab, Utah: The Times Independent. http://www.moabtimes.com/pages/full_story?article-Group-seeks-donations-to-rebuild-Dewey-Bridge%20=&page_label=results_content&id=71159-Group-seeks-donations-to-rebuild-Dewey-Bridge&widget=push&open=&. Retrieved 2008-06-13.
- ^ "Midland Trail Will Come down River by Way of Moab, Legislature Decides". Moab, Utah: Grand Valley Times. 1919-04-19. http://udn.lib.utah.edu/u?/gvt,112797. Retrieved 2008-07-07.
- ^ "Paving Must Come in 1923; Work on Details is Pushed,". Price, Utah: The News-Advocate. 1923-02-01. http://udn.lib.utah.edu/u?/newsadvocate,36574. Retrieved 2008-07-07.
- ^ "Designation of State Roads", Chapter 55, Session Laws of Utah, 1931: "(129) From Moab along south bank of Colorado river to Castleton."
- ^ "Designation of Secondary State Roads", Chapter 30, Session Laws of Utah, 1933: "(128) From Moab along south bank of Colorado river to Cisco."
- ^ "Route 4" (PDF). Utah Department of Transportation. September 2007. http://www.udot.utah.gov/main/uconowner.gf?n=200609121732583. Retrieved 2008-05-15.
- ^ "Upper Colorado River Scenic Byway 128". Utah Office of Tourism. http://www.utah.com/byways/upper_colorado.htm. Retrieved 2007-11-17.
- ^ "Utah Administrative Code". State of Utah. http://www.rules.utah.gov/publicat/code/r926/r926-007.htm. Retrieved 2007-12-03.
- ^ a b "Dinosaur Diamond Prehistoric Highway". Dinosaur Diamond Partnership. http://www.dinosaurdiamond.org/. Retrieved 2007-11-17.
External links
- SR-128 (photo guide) by Lalas Reisen (German)
- Photo Gallery – Dewey Bridge by Dave Beeden
- Pictures of the Dewey Bridge burning by Skez
Categories:- Colorado River
- Transportation in Grand County, Utah
- State highways in Utah
- Utah Scenic Byways
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.








