- Submarine-launched ballistic missile
-
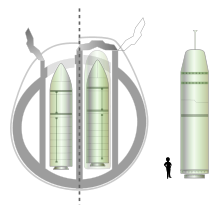
 A Trident II D5 nuclear missile. It is capable of carrying multiple nuclear warheads up to 8,000 km. They are carried by 14 US Navy Ohio class submarines and 4 Royal Navy Vanguard class submarines
A Trident II D5 nuclear missile. It is capable of carrying multiple nuclear warheads up to 8,000 km. They are carried by 14 US Navy Ohio class submarines and 4 Royal Navy Vanguard class submarines
A submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) is a ballistic missile capable of delivering a nuclear warhead that can be launched from submarines. Modern variants usually deliver multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs) each of which carries a warhead and allows a single launched missile to strike several targets. Submarine-launched ballistic missiles should not be confused with submarine-launched cruise missiles, which operate in a different way.
Contents
History
The first practical design of a submarine-based launch platform was developed by the Germans near the end of World War II involving a launch tube which contained a ballistic missile and was towed behind a submarine. The war ended before it could be tested, but the engineers who had worked on it went on to work for the USA and USSR on their SLBM programs. These and other early SLBM systems required vessels to be surfaced when they fired missiles, launch systems eventually were adapted to allow underwater launching in the 1950-1960s. The United States made the first successful underwater launch of a Polaris A1 on 20 July 1960.[1] Forty days later, the Soviet Union made its first successful underwater launch of a submarine ballistic missile in the White Sea on 10 September 1960 from the same converted Project 611 (Zulu Class) submarine that first launched the R-11FM (SS-N-1 Scud-A, naval modification of SS-1 Scud) on 16 September 1955.[2][3] However, the Soviet Union was able to beat the U.S. in launching and testing the first armed SLBM, an R-13 that detonated in the Novaya Zemlya Test Range in the Arctic Ocean, doing so on October 20, 1961.[4]
Ballistic missile submarines have been of great strategic importance for the USA and Russia and other nuclear powers since the start of the Cold War, as they can hide from reconnaissance satellites and fire their nuclear weapons with virtual impunity. This makes them immune to a first strike directed against nuclear forces, allowing each side to maintain the capability to launch a devastating retaliatory strike, even if all land-based missiles have been destroyed. This relieves each side of the necessity to adopt a launch on warning posture, with its grave attendant risk of accidental nuclear war. Additionally, the deployment of highly accurate missiles on ultra-quiet submarines allows an attacker to sneak up close to the enemy coast and launch a missile on a depressed trajectory - a very close range attack which will hit its target in a matter of minutes, thus opening the possibility of a decapitation strike.[citation needed]
Types of SLBMs
Specific types of SLBMs (current, past and under development) include:
 United States
United States
- UGM-27 Polaris and Chevaline (with UK) - decommissioned
- UGM-73 Poseidon - decommissioned
- UGM-96 Trident I (C4) - decommissioned
- UGM-133 Trident II (D5) - active

 Soviet Union / Russia
Soviet Union / Russia
- R-13 NATO name SS-N-4 - decommissioned
- R-21 NATO name SS-N-5 - decommissioned
- RSM-25 [5] R-27 NATO name SS-N-6 - decommissioned
- RSM-40 [5] R-29 "Vysota", NATO name SS-N-8 "Sawfly" - decommissioned
- RSM-45 R-31 NATO name SS-N-17 "Snipe" [5] - decommissioned
- RSM-50 [5] R-29R "Vysota", NATO name SS-N-18 "Stingray" - active
- RSM-52 [5] R-39 "Rif", NATO name SS-N-20 "Sturgeon" - decommissioned
- RSM-54 R-29RM "Shtil", NATO name SS-N-23 "Skiff" - decommissioned (last ship is now under rebuild to R-29RMU "Sineva") [6]
- RSM-54 R-29RMU "Sineva", NATO name SS-N-23 "Skiff" - active
- RSM-56 R-30 "Bulava", NATO name SS-NX-32 - under development
 United Kingdom (U.S. supplied)
United Kingdom (U.S. supplied)
- UGM-27 Polaris and Chevaline - decommissioned
- UGM-133 Trident II (D5) - active
 France
France
- M1 - decommissioned
- People's Republic of China Navy
Types of ballistic-missile submarines
Specific types ballistic-missile submarine, which have included diesel-electric (SSBs) as well as nuclear-powered (SSBNs) units, include:
 United States
United States
- George Washington class SSBN - former
- Ethan Allen class SSBN - former
- Lafayette class SSBN - former
- James Madison class SSBN - former
- Benjamin Franklin class SSBN - former
- Ohio class SSBN - active
 Russia
Russia
- Zulu IV Class SSB - former
- Golf I Class SSB - former
- Golf II Class SSB - former
- Hotel I class SSBN - former
- Hotel II class SSBN - former
- Hotel III class SSBN - former
- Yankee I class SSBN - former
- Yankee II class SSBN - former
- Delta I class SSBN - former
- Delta II class SSBN - former
- Delta III class SSBN - active
- Typhoon class SSBN - active
- Delta IV class SSBN - active
- Borei class SSBN - To be operational by 2012
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
- Resolution class SSBN - former
- Vanguard class SSBN - active
 France
France
- Redoutable class SSBN - former
- Triomphant class SSBN - active
 People's Republic of China
People's Republic of China
- Golf Class SSB - test platform
- Type 092 (Xia class) submarine SSBN - inactive
- Type 094 (Jin class) submarine SSBN - active
- Type 096 (Tang class) submarine - in development
 India
India
- Arihant class submarine SSBN - Projected to become operational in 2011.[10]
See also
- ICBM
- Nuclear navy
- Nuclear strategy
- Nuclear warfare
- Submarine-based launch vehicles
- Submarine-launched missile
- Vertical launching system
- List of NATO reporting names for ballistic missile submarines
References
- ^ "Missiles 1963", Flight International: 752, 7 November 1963, http://www.flightglobal.com/pdfarchive/view/1963/1963%20-%201949.html
- ^ Wade, Mark. "R-11". Encyclopedia Astronautica. http://www.astronautix.com/lvs/r11.htm. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- ^ Dygalo, V.A.. "Start razreshaju (in Russian)". Nauka i Zhizn'. http://www.nkj.ru/archive/articles/10079/. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- ^ Polmar, Norman (2010). Project Azorian: The CIA and the Raising of the K-129. Naval Institute Press. p. 21. ISBN 9781591146902.
- ^ a b c d e Korabli VMF SSSR, Vol. 1, Part 1, Yu. Apalkov, Sankt Peterburg, 2003, ISBN 5-8172-0069-4
- ^ "SSBN K-51 Verkhoturye arrived to Zvezdochka for repairs today". Rusnavy.com. 2010-08-23. http://rusnavy.com/news/navy/index.php?ELEMENT_ID=10095. Retrieved 2010-10-08.
- ^ [1]
- ^ http://www.drdo.gov.in/drdo/English/dpi/Frontline02Jan09.pdf
- ^ 'INS Arihant' to sail on deterrent patrol after commissioning
- ^ "India joins elite club with nuclear submarine launch - Latest Current-affairs News". In.com. http://www.in.com/news/readnews-current-affairs-india-joins-elite-club-with-nuclear-submarine-launch-10138511-93408-hp.html. Retrieved 2010-08-14.
External links
- Video showing the launch of a Trident SLBM.
- Estimated Strategic Nuclear Weapons Inventories (September 2004)
- R-11 SLBM
- Trident Submarines Are Killing Machines Unparalleled In Human History.
Types of missile By platform Air-to-air missile (AAM) · Air-to-surface missile (ASM) · Surface-to-air missile (SAM) · Surface-to-surface missile (SSM) · Ballistic missile · Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) · Submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) · Anti-ballistic missile (ABM) · Intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) · Cruise missile · Anti-ship missile (AShM) · Anti-submarine missile · Anti-tank missile (ATGM) · Anti-satellite weapon (ASAT) · Air-launched ballistic missile · Anti-ship ballistic missile (ASBM)By guidance Anti-radiation · Wire guidance · Infrared guidance · Beam riding · Laser guidance · Active radar guidance · Semi-active radar guidance · Unguided rocketsLists
Categories:- Missile types
- Submarine-launched ballistic missiles
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.