- Pulse-amplitude modulation
-
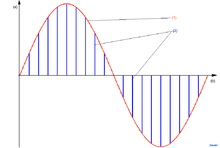
Pulse-amplitude modulation, acronym PAM, is a form of signal modulation where the message information is encoded in the amplitude of a series of signal pulses.
Example: A two-bit modulator (PAM-4) will take two bits at a time and will map the signal amplitude to one of four possible levels, for example −3 volts, −1 volt, 1 volt, and 3 volts.
Demodulation is performed by detecting the amplitude level of the carrier at every symbol period.
Contents
Generation of PAM
In this the signal is sampled at regular intervals and each sample is made proportional to the magnitude of the signal at the instant of sampling.These sampled pulses may then be sent either directly by a channel to the receiving end or may be made to modulated using a carrier wave before transmission.
Types
There are two types of pulse amplitude modulation: 1.Single polarity PAM: In this a suitable fixed dc level is added to the signal to ensure that all the pulses are positive going. 2.Double polarity PAM: In this the pulses are both positive and negative going.
Pulse-amplitude modulation is widely used in baseband transmission of digital data, with non-baseband applications having been largely replaced by pulse-code modulation, and, more recently, by pulse-position modulation.
In particular, all telephone modems faster than 300 bit/s use quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM). (QAM uses a two-dimensional constellation).
Use in Ethernet
Some versions of the Ethernet communication standard are an example of PAM usage. In particular, the Fast Ethernet 100BASE-T2 medium (now defunct), running at 100 Mbit/s, uses five-level PAM modulation (PAM-5) running at 25 megapulses/sec over two wire pairs. A special technique is used to reduce inter-symbol interference between the unshielded pairs.[citation needed] Current common 100 Mbit networking technology is 100BASE-TX which delivers 100 Mbit in each direction over a single twisted pair – one for each direction. Later, the gigabit Ethernet 1000BASE-T medium raised the bar to use four pairs of wire running each at 125 megapulses/sec to achieve 1000 Mbit/s data rates, still utilizing PAM-5 for each pair.
The IEEE 802.3an standard defines the wire-level modulation for 10GBASE-T as a Tomlinson-Harashima Precoded (THP) version of pulse-amplitude modulation with 16 discrete levels (PAM-16), encoded in a two-dimensional checkerboard pattern known as DSQ128. Several proposals were considered for wire-level modulation, including PAM with 12 discrete levels (PAM-12), ten levels (PAM-10), or eight levels (PAM-8), both with and without Tomlinson-Harashima Precoding (THP).
Use in photobiology
The concept is also used for the study of photosynthesis using a PAM fluorometer. This specialized instrument involves a spectrofluorometric measurement of the kinetics of fluorescence rise and decay in the light-harvesting antenna of thylakoid membranes, thus querying various aspects of the state of the photosystems under different environmental conditions.
Use in electronic drivers for LED lighting
Pulse-amplitude modulation has also been developed for the control of light-emitting diodes (LEDs), especially for lighting applications. LED drivers based on the PAM technique offer improved energy efficiency over systems based upon other common driver modulation techniques such as pulse-width modulation (PWM) as the forward current passing through an LED is relative to the intensity of the light output and the LED efficiency increases as the forward current is reduced.
Pulse-amplitude modulation LED drivers are able to synchronize pulses across multiple LED channels to enable perfect colour matching. Due to the inherent nature of PAM in conjunction with the rapid switching speed of LEDs it is possible to use LED lighting as a means of wireless data transmission at high speed.
See also
- Amplitude-shift keying
- Carrier Sense Multiple Access
- Pulse-code modulation
- Pulse-position modulation
- Pulse-width modulation
- Pulse-density modulation
- Pulse forming network
- Quadrature amplitude modulation
- 8VSB
Line coding (digital baseband transmission) Main articles 
Basic line codes Return to zero (RZ) · Non-return-to-zero, level (NRZ/NRZ-L) · Non-return-to-zero, inverted (NRZ-I) · Non-Return-to-Zero, space (NRZ-S) · Manchester · Differential Manchester/Biphase (Bi-φ)Extended line codes Optical line codes Carrier-Suppressed Return-to-Zero · Alternate-Phase Return-to-ZeroSee also: Baseband · Baud · Bit rate · Digital signal · Digital transmission · Ethernet physical layer · Pulse modulation methods · Pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM) · Pulse code modulation (PCM) · Serial communication · Category:Line codesCategories:- Quantized radio modulation modes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.