- Delay encoding
-
In telecommunications, delay encoding is the encoding of binary data to form a two-level signal such that (a) a "0" causes no change of signal level unless it is followed by another "0" in which case a transition to the other level takes place at the end of the first bit period; and (b) a "1" causes a transition from one level to the other in the middle of the bit period.
Delay encoding is used primarily for encoding radio signals because the frequency spectrum of the encoded signal contains less low-frequency energy than a conventional non-return-to-zero (NRZ) signal and less high-frequency energy than a biphase signal.
Delay encoding is an encoding using only half the bandwidth as biphase encoding but has all the advantages of biphase encoding: To be rewritten: It is guaranteed to have transitions every other bit, meaning that decoding systems can adjust their clock/DC threshold continuously. One drawback is human readability (e.g. on an oscilloscope).
Delay encoding is also known as Miller encoding (apparently named after John Milton Miller).
Some RFID cards, in particular EPC UHF Gen 2 RF cards, use a variant called "Miller sub-carrier coding".[1] Such cards include the CharlieCard. In this system, 2, 4 or 8 cycles of a subcarrier square wave are transmitted for each bit time. The Miller encoding transitions are indicated by 180° phase shifts in the subcarrier, i.e. the subcarrier pauses for 1/2 of a cycle at each transition. (The resultant binary subcarrier is itself either ASK or PSK modulated on another carrier.)
References
- ^ UHF Gen 2 System Overview, p. 19. (March, 2005)
 This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document "Federal Standard 1037C".
This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document "Federal Standard 1037C".Line coding (digital baseband transmission) Main articles 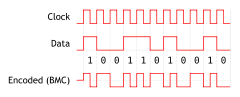
Basic line codes Return to zero (RZ) · Non-return-to-zero, level (NRZ/NRZ-L) · Non-return-to-zero, inverted (NRZ-I) · Non-Return-to-Zero, space (NRZ-S) · Manchester · Differential Manchester/Biphase (Bi-φ)Extended line codes Conditioned Diphase · 4B3T · 4B5B · 2B1Q · Alternate Mark Inversion · Modified AMI code · Coded mark inversion · MLT-3 encoding · Hybrid ternary code · 6b/8b encoding · 8b/10b encoding · 64b/66b encoding · Eight-to-fourteen modulation · Delay/Miller encoding · TC-PAMOptical line codes Carrier-Suppressed Return-to-Zero · Alternate-Phase Return-to-ZeroSee also: Baseband · Baud · Bit rate · Digital signal · Digital transmission · Ethernet physical layer · Pulse modulation methods · Pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM) · Pulse code modulation (PCM) · Serial communication · Category:Line codes Categories:- Encodings
- Line codes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
